* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download ROME
Centuriate Assembly wikipedia , lookup
Roman army of the late Republic wikipedia , lookup
Roman Republic wikipedia , lookup
Constitution of the Roman Empire wikipedia , lookup
Roman Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Senatus consultum ultimum wikipedia , lookup
Roman Senate wikipedia , lookup
Legislative assemblies of the Roman Republic wikipedia , lookup
Promagistrate wikipedia , lookup
Early Roman army wikipedia , lookup
Conflict of the Orders wikipedia , lookup
Roman consul wikipedia , lookup
Constitutional reforms of Sulla wikipedia , lookup
Constitutional reforms of Augustus wikipedia , lookup
History of the Constitution of the Roman Republic wikipedia , lookup
History of the Roman Constitution wikipedia , lookup
Executive magistrates of the Roman Republic wikipedia , lookup
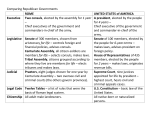
ROME Greece retold or something new? Geography's impact Italy is shaped like a boot with protective mountains (Alps in the north) and the Sea (Mediterranean and Adriatic) surrounding it The Tiber River ran down the middle At this point in history why would this be a positive and negative? The Founders 700-600’s BC People from the north formed cities in the central western section of Italy called Latium Etruscans from the northern kingdoms established a monarchy and tried to rule all of Italy Greeks sailed west and settled southern Italy and the Island of Sicily Romulus and Remus create Rome A REPUBLIC IS BORN 509 BC the monarchies are overrun by wealthy landowners who establish a Republic A Republic is a government run by elected officials (in this case elected by only men) The Republic is run by 3 different government groups The Senate The Magistrates The Popular Assemblies The Senate Senators could control public funds They managed foreign affairs Acted as a court to determine guilt At times when necessary they could propose a dictator to the magistrates to rule for a period of 6 months Magistrates Consuls: Two men were elected to each serve one year terms as chief executives. They ran the government, governed the military, and could appoint dictators. They also could veto each other and the senate Praetors: Helped the Consuls run military when at war and the judiciary when at peace Censors: Registered citizens to determine social standing and oversaw morals in society Assemblies 10 Tribunes were elected to oversee the government They could override the work of the Senate Could Could act as secondary courts deny the Consul the right to make war or peace if the people did not approve. They were supposed to be the voice of the people Society Patricians: Wealthy landowners that controlled most of the government Plebeians: Poor farmers or other day laborers. Initially not allowed to hold public office but could vote In 450 BC forced the government to write down the laws (Twelve Tables) so they could understand the law Gained the right to hold public office Forced the government to allow one consul to always come from Plebeian class Began to use the law to enforce genuine equality Military All males needed to serve in the army The army was divided into legions with about 5000 legionnaires Sometimes there were groups of non-citizens forced into units called auxilia Conquered people could not vote, paid taxes, provided men as soldiers, and gave land to Roman farmers to link civilizations