* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Social Control
In-group favoritism wikipedia , lookup
Belongingness wikipedia , lookup
Expectation states theory wikipedia , lookup
False consensus effect wikipedia , lookup
Self-categorization theory wikipedia , lookup
Social loafing wikipedia , lookup
Role conflict wikipedia , lookup
Social dilemma wikipedia , lookup
Social tuning wikipedia , lookup
System justification wikipedia , lookup
Social perception wikipedia , lookup
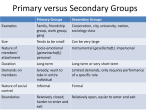
Social Control Social Structure Macrosociology • Focuses on broad features of society • Conflict theory, functionalist viewpoints part of the macrosociological perspective • The goal is to examine the large scale influences of society Microsociology • Examines social interaction • Focus on face to face interaction • This approach is favored by symbolic interactionists *Major Components of Social Structure • People’s particular roles and statuses affect how they relate to one another. • Social Structure – Network of interrelated statuses and roles that guides human interactions. • *Status – Socially defined positions in a group in a society. • *Role – Behavior – the rights and obligations – expected of someone occupying a particular status. Status and Roles: • Ascribed Status – Status assigned according to standards that are beyond a person’s control. Age, sex, family history and race are examples. • Achieved Status – Status acquired by an individual on the basis of some special skill, knowledge, or ability. • Master Status – Status that plays the greatest role in shaping a person’s life and determining his or her social identity. • Role Conflict- Situation that occurs when fulfilling the expectation of one role makes it difficult to fulfill the expectations of another role. People can fall short of expectations because some of their roles contradict each other • Ex. Parents are expected to keep their kids safe and provide for them while maintaining a career and friendships. Often parents have to adjust their work role to fulfill their needs as a parent. • Role Strain – Situation that occurs when a person has difficulty meeting the expectations of a single role EX- Keeping Students engaged and motivated for 86 minutes in 90degrees in May Groups and Leadership • Social Institution – statuses and roles are organized to satisfy one or more basic needs of society (Groups) Basic needs of a society is providing physical and emotional support for members, transmitting knowledge, producing goods and services, and maintaining social control • • • Primary Groups: Interact over a long period of time on a direct and personal basis Secondary Groups: Interaction is impersonal and temporary in nature Selected leaders—people that influence the attitudes and opinions of others and who: Define boundaries—members can tell who belongs and who does not Set goals, assign tasks, and make decisions Control members’ behavior—if members violate group norms, the group cannot survive long • Conformity- social influence involving a change in belief or behavior in order to fit in with a group. This change is in response to real (involving the physical presence of others) or imagined (involving the pressure of social norms / expectations) group pressure. Roles and Leadership • Social Exchange – interacting in an effort to receive a reward or a return for one’s actions • Competition – two or more people or groups in opposition to achieve a goal that only one can attain • Conflict – the deliberate attempt to control a person by force, to oppose someone else,to harm another person, or to resist the will of another • Cooperation – two or more people or groups working together to achieve a goal that will benefit more than one of them • Coercion- Control trough force and fear or the threat of force