* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Early Embryonic Development
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Hematopoietic stem cell wikipedia , lookup
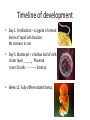
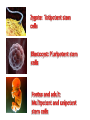
Early Embryonic Development Stem Cells Stem Cells – Part 1 The Information What are they? Where do we get them from? Are they all the same? Why are we interested in them? How cells become specialised • Correct stimulus is given to unspecialised cells e.g. a chemical stimulus • Some genes are switched on and become active; other genes are switched off • m-RNA is made from the active genes • m-RNA moves to the ribosomes; the ribosomes read the m-RNA and the appropriate protein is made • The protein can permanently alter the structure and function of cells Stem Cells – What are they? . A type of source or master cell that can ........ . Undifferentiated cells Which keep dividing And can give rise to other cell types Potency • • • • How much stem cells differentiate is called potency Stem cells vary in their potency: Totipotent: can give rise to any cell and so can produce a whole organism Pluripotent: potential to develop into many cell types but not all of them. Multipotent: cells retain the capacity to make a few types of cell Unipotent: make one type of cell e.g. Skin cells What are they and where are they found? Timeline of development • Day 1: Fertilisation – a zygote is formed Series of rapid cell divisions No increase in size • Day 5: Blastocyst – a hollow ball of cells Outer layer Placenta Inner 50 cells Embryo • Week 12: Fully differentiated foetus. Stem cells and their use in medicine Sources of stem cells: •Multipotent cells from adults •Spare embryos from IVF (pluripotent) •Umbilical cord stem cells •Therapeutic cloning or admixed embryos http://www.wellcome.ac.uk/Aboutus/Policy/Spotlight-issues/Human-Fertilisationand-EmbryologyAct/Humanadmixedembryos/index.htm Different view points Just a last point.... Ethical considerations • Where do you stand on the issue of using embryonic stem cells? • What are the advantages and disadvantages of using them in research?