* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Presentation
Casualties of the 2010 Haiti earthquake wikipedia , lookup
Kashiwazaki-Kariwa Nuclear Power Plant wikipedia , lookup
Seismic retrofit wikipedia , lookup
1908 Messina earthquake wikipedia , lookup
2011 Christchurch earthquake wikipedia , lookup
Earthquake engineering wikipedia , lookup
2010 Canterbury earthquake wikipedia , lookup
2008 Sichuan earthquake wikipedia , lookup
1880 Luzon earthquakes wikipedia , lookup
1992 Cape Mendocino earthquakes wikipedia , lookup
April 2015 Nepal earthquake wikipedia , lookup
1570 Ferrara earthquake wikipedia , lookup
2009–18 Oklahoma earthquake swarms wikipedia , lookup
Earthquake prediction wikipedia , lookup
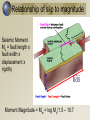
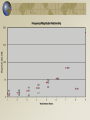
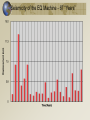
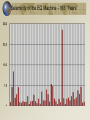
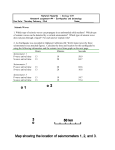
Earthquake Machine, part 2 Mechanical Modeling to Increase Student Understanding of Complex Earth Systems Developed by Michael Hubenthal - IRIS Consortium Objectives Describe global trends for Earthquake occurrence and magnitude Interpret a Gutenberg Richter plot (Frequency vs. Magnitude) Critically analyze an argument Describe the importance of sharing science results with peers in the science process Studying Earthquake Recurrence 3 Developing arguments…. How many beads are in the box???? Relationship of slip to magnitude Seismic Moment Mo = fault length x fault width x displacement x rigidity Moment Magnitude = Mw = log Mo/1.5 – 10.7 Visualizing magnitude with the model B Seismic Moment Mo = fault length x fault width x displacement x rigidity Moment Magnitude = Mw = log Mo/1.5 – 10.7 In earthquake machine, this means magnitude is directly related to fault displacement 6 #1 #2 Extra credit “There are long periods of quiet between earthquakes” “Most earthquakes are huge, deadly and destructive events” “There hasn’t been an earthquake in a long time; therefore the next one must be huge.” Develop an argument either for or against one statement based on your experimentation with the earthquake machine. “There are always long periods between earthquakes.” “All earthquakes are huge, deadly, and destructive events” Time Predictable Stress Characteristic Time Slip Predictable Calaveras Fault Data (Bufe et al., 1977) Seismicity of the EQ Machine - 67 “Years” Seismicity of the EQ Machine - 163 “Years” Summary • There are many more small earthquakes than large earthquakes • There are more short time periods between earthquakes than long time periods • In the earthquake machine, the longer since the last earthquake, the larger the earthquake is likely to be • This isn’t usually true in the Earth 17