* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download measure earthquakes
Reflection seismology wikipedia , lookup
Surface wave inversion wikipedia , lookup
1880 Luzon earthquakes wikipedia , lookup
2009–18 Oklahoma earthquake swarms wikipedia , lookup
Seismic retrofit wikipedia , lookup
Earthquake prediction wikipedia , lookup
Earthquake engineering wikipedia , lookup
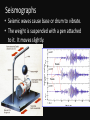
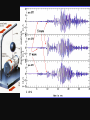
Do Now -Clear your desk of all but your ISN and textbook. -Title p. 107 of your ISN, Monitoring Earthquakes and then add it to your TOC -On p. 106 of your ISN, answer this question: How do you think we measure earthquakes? AGENDA • Do now • PowerPoint and notes • Video • Wrap up • Journey to the Center of the Earth How big was that earthquake? • There are 3 commonly used scales that exist to measure earthquakes 1. Mercalli Scale – Rates earthquakes according to their damage at a given place. – Same earthquake can have different ratings depending on the location. See p. 55 of your textbook. 2. The Richter Scale • Determines the magnitude by measuring seismic waves and fault movement. • Measured by seismograph. • Accurate measurements for small nearby earthquakes, inaccurate for large and distant earthquakes. While watching this video… • Be ready to answer this question: –Explain how scientists measure an earthquake’s seismic waves. Seismographs • Seismic waves cause base or drum to vibrate. • The weight is suspended with a pen attached to it. It moves slightly. 3. The Moment Magnitude Scale • Estimates the total energy released by an earthquake. • Can be used near or far away • Studies data from seismographs to show strength of seismic waves. *The earthquake in Haiti (2010) had a moment magnitude of 7. *Typically, a moment magnitude of 8 is needed to create a large tsunami. Instruments That Monitor Faults (look at textbook p. 63 for great visuals) • Tiltmeter- measures the tilting or raising of land • Creep Meter- measures horizontal movement of ground • Laser-Ranging Devices- detects horizontal fault movement with a laser • GPS Satellites- measures elevation and horizontal movement of faults Wrap Up! Which device could a scientist NOT use to measure the movement of the the San Andreas Fault? Exit Ticket A seismograph records the strength of an earthquake’s seismic waves. Think about what we learned earlier this week. What does this seismogram reinforce about S, P and surface waves? Stations 1.Work on your station packets. 2.Continue working on your Journey to the Center of the Earth.