* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lecture 5: Earthquakes I. What are earthquakes? II. The elastic
Reflection seismology wikipedia , lookup
Seismic retrofit wikipedia , lookup
1880 Luzon earthquakes wikipedia , lookup
2009–18 Oklahoma earthquake swarms wikipedia , lookup
Earthquake prediction wikipedia , lookup
Surface wave inversion wikipedia , lookup
1906 San Francisco earthquake wikipedia , lookup
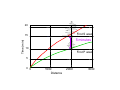
1 Lecture 5: Earthquakes I. What are earthquakes? II. The elastic rebound theory III. Seismology: The Study of Earthquakes A. Seismographs B. How do seismographs work? IV. Seismic waves A. Definition B. Modes of vibration 1. Surface waves 2. Body waves 3. Types of body waves a. Primary or P waves ` b. Secondary or S waves C. Records of Seismic Waves V. Locating the Source of an Earthquake A. Focus B. Epicenter C. Determining the distance to earthquake 1. Difference in Velocities of S & P waves: 2. Travel time graphs 3. Using travel time graphs 20 First S wave Time (min) 15 5 minutes 10 First P wave 5 0 0 1000 Distance 2000 3000 2 D. Finding the location of the earthquake: Triangulation VI Earthquake belts VII. Earthquake intensity and magnitude A. Intensity: Mercalli Scale B. Magnitude: The Richter Scale C. Moment magnitude VII Prediction and Minimizing Risks 1. Clear coincidence of earthquakes with plate boundaries 2. Depth of earthquake related to type of boundary 3. Forecasts based on history and movement along faults 4. Importance of local geology