* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Evolution
Sexual selection wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Evidence of common descent wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary mismatch wikipedia , lookup
Theistic evolution wikipedia , lookup
Organisms at high altitude wikipedia , lookup
Sociobiology wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Natural selection wikipedia , lookup
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
Punctuated equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
Inclusive fitness wikipedia , lookup
The eclipse of Darwinism wikipedia , lookup
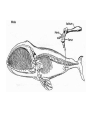
Evolution Review Who’s the man? Charles Darwin What did Darwin observe on his Journey on the HMS Beagle? • Many different species of plant and animal life • Fossils of extinct animals How did Darwin explain the differences in the Galapagos finches? He proposed that the 13 different finches had come from a… • Common ancestor What is a population? • A group of one species of organism in a specific geographical area that can interbreed. Evolution is a.. • Well-accepted theory of how organisms have changed over time by natural selection. • Darwin based his ideas on: • 1. observations of nature • 2. Malthus’s theory about exponential population growth • 3. his experience breeding animals Tenets of Evolution • • • • • Populations have the potential to grow… exponentially They don’t because.. resources are limited There are differences in individuals (genetic variation) • These differences can help some individuals survive better than others • Those that survive longer pass more of their genes on to the next generation. What is Natural Selection? • The idea that individuals with traits that make them well-suited to the environment will survive and reproduce, passing on their genes, at a higher rate than less suited individuals. • This will cause a change in frequency of alleles in the population Process of becoming better suited to the environment is called.. • Adaptation • What does natural selection act on? • On populations over many generations. What is needed for natural selection to occur? • Genetic variation (differences) in the individuals must exist • Otherwise all members of the population would have the same advantage for survival What are 4 sources of genetic variation? • 1. Mutations- errors in base pairs caused by mutagens, energy exposure, or errors in replication • 2. Meiosis- two events occur: • Random alignment • Crossing over 3. Immigration- new genes come into population 4. Sexual Reproduction- combining the alleles of mother and father What 4 processes change allelic frequency? • 1. Natural Selection- environment determines which traits will survive and be passed on • 2. Artificial Selection (breeding)- humans decide which traits will be bred for • 3. Gene Flow • 4. Genetic Drift Gene Flow • Genes moving in and out of a population • Give two examples: • 1. immigration– new individuals move in • 2. emigration- individuals move out Genetic Drift • This is a ___________change in allelic frequency that is due to chance.. Not environmental pressure. • Answer= RANDOM Gradualism vs Punctuated Equilibrium • Hypothesis that evolution occurs in short bursts of rapid change, then periods of no change is… • Punctuated equilibrium • Hypothesis that evolution occurs gradually at a slow, constant rate is.. • Gradualism What has to happen for a new species to become established? • First, Reproductive Isolation from the original group • Example: a flock of birds gets separated and blown toward an island by a storm • They are now isolated from their original group on another island. • Over time, in 2 different environments, they become more and more different When does speciation occur? • When they can no longer interbreed with the original group of birds • A speciation event= • A new species When a group of organisms starts a new colony, it is called.. • The Founder Effect What is a genetic bottleneck? • This happens when a natural disaster (earthquake, volcano, etc) kills off a group of the original population, and the allelic frequencies change (genes are lost). Now the group has different amounts of the alleles for certain traits. When 2 species become … • More different, it’s called… • Divergence (diverse=different) • More alike, it’s called… • Convergence (converge=coming together) What are Vestigial structures? • Those anatomical features that no longer have a purpose • Examples: in whales… • They have small back limbs, inherited from an ancestor that moved on land. See next slide. What are Homologous structures? • Similar structures in different species that suggest that they have a common ancestor • Example: the forearm of many vertebrates (humans, bats, alligators, etc) have similar bones. See next slide. Contrast: Scientific theory, law, and hypothesis • Theory= an explanation of how a natural phenomenon occurs • Law= describes a phenomenon (mathematically) • Hypothesis= a prediction based on research and prior knowledge