* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download What is Evolution?
The Selfish Gene wikipedia , lookup
Microbial cooperation wikipedia , lookup
Sociobiology wikipedia , lookup
Theistic evolution wikipedia , lookup
The Descent of Man, and Selection in Relation to Sex wikipedia , lookup
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
Sexual selection wikipedia , lookup
Saltation (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Genetics and the Origin of Species wikipedia , lookup
Inclusive fitness wikipedia , lookup
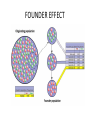
Objective: I can determine why natural selection is a key part of Evolution. Agenda: 1. Natural Selection and Darwin’s ideas 2. Evolution Activity 3. Start Pre-lab How would you define POPULATION? • _________________________ _________________________ _________________________ What is Evolution? • Change in the genetic makeup of a population over time. • Fitness – _____________________________________ ____________________. – Populations can evolve, not individuals. • Diverse gene pool good for long-term survival of a species. ________________are important! • How do genetic variations occur? Where does Variation come from? • Mutation – random changes to DNA • ____________________ • environmental damage • Sexual reproduction – _________________ • genetic recombination – new arrangements of alleles in every offspring • __________________________________ “The Origin of Species” • Documented the occurrence of ____________. • Suggested that the mechanism for evolution was ______________. Observations: Observation 1 – _______________________________ _______________________________. . Observation 2 • Traits are inherited from _________________. Observation 3 All species are capable of producing more _______________ their environment can support. Observation 4 • Owing to lack of food or other resources, __________________________________. Inference 1 • Individuals _______________________ higher probability of surviving and reproducing in a given environment tend to leave more offspring than other individuals. Inference 2 • This unequal ability of individuals to survive and reproduce will lead to the accumulation of favorable traits in the population over generations. Nature • Determines which characteristics are favorable. • _______________________. • Result - “Natural Selection” Artificial Selection • When man determines the characteristics that survive and reproduce. • Result - the various breeds of animals and plants we’ve developed. Evolution Success Measured By • ______________ • ______________ • Whoever lives long enough and has kids is the “winner” in evolution. Requirements • In order for Natural Selection to work, you must have: – _____________________. – Long periods of time (according to Darwin). Natural Selection 1. Populations are the units of Evolution. 2. __________________________________. Comment • Acquired characteristics may allow a species to evolve "outside" of Natural Selection. • _______________ Essence of Darwin’s ideas • Natural selection – heritable variation exists in populations – ______________________ • more offspring than the environment can support – _____________ • for food, mates, nesting sites, escape predators – differential survival • successful traits = _____________ – differential reproduction • adaptations become more common in population Lamarckian vs. Darwinian view • LaMarck – in reaching higher vegetation giraffes stretch their necks & transmits the acquired longer neck to offspring • Darwin – giraffes born with longer necks survive better & leave more offspring who inherit their long necks Effects of Selection DIRECTIONAL SELECTION STABILIZING SELECTION DISRUPTIVE SELECTION • Changes in the average trait of a population giraffe neck horse size human birth weight rock pocket mice In addition to natural selection, evolutionary change is also driven by random processes… II. GENETIC DRIFT • The smaller the population, the less genetic variety it has. • In a very small population, alleles can be lost from one generation to the next, simply by random chance. • When a population evolves only because of this type of random sampling error, _____________is taking place. Genetic Drift • Chance events changing frequency of traits in a population – not adaptation to environmental conditions • not selection – ____________ • small group splinters off & starts a new colony • it’s random who joins the group – ___________ • a disaster reduces population to small number & then population recovers & expands again but from a limited gene pool • who survives disaster may be random FOUNDER EFFECT BOTTLENECK EFFECT Ex: Cheetahs All cheetahs share a small number of alleles less than 1% diversity 2 bottlenecks 10,000 years ago Ice Age last 100 years poaching & loss of habitat Conservation issues Peregrine Falcon • Bottlenecking is an important concept in conservation biology of endangered species – loss of alleles from gene pool – __________________ – __________________ Breeding programs must consciously outcross Golden Lion Tamarin Human Impact on variation • How do we affect variation in other populations? – Artificial selection/Inbreeding • Animal breeds – ___________________ • Insecticide usage – ___________________ • resistant bacterial strains