* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Platelet
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
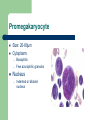
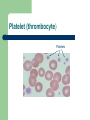
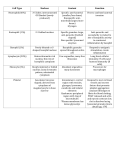
MLAB1415- Hematology Keri Brophy-Martinez Platelets Platelets Production – Bone marrow Differentiation – Comes from the CFU-GEMM Platelets Regulation – TPO= thrombopoietin Influences all stages of megakaryocyte production Made in liver, kidney and spleen Binds receptors in peripheral blood – Bound TPO does not stimulate bone marrow progenitor cells – For example: Increased platelet count, more TPO is bound, stimulation of bone marrow is decreased Function of platelets Normally circulate in a discoid shape Help to maintain hemostasis and capillary integrity (this will be discussed in detail in Coagulation) Platelet to platelet interactions Platelet to coagulation protein interactions Aid in healing injured tissue Overview of Hemostasis When vascular injury occurs, platelets do the following: – Adhere to the injured vessel – Aggregate and transform into reactive spiny spheres that interact with one another and form into a platelet plug – Consolidate with fibrin into a clot – Stabilize with the aid of a coagulation factor Platelets: maturation sequence Megakaryoblast Size: 20-45µm Cytoplasm – – Nucleus – – – – – Blue, scanty, pseudopodia No granules Single, round/oval, may be indented Central or eccentric Red purple with fine and distinct chromatin 1-2 nucleoli Nucleus divides by endoreplication meaning the nuclear material reduplicates, but the nucleus does not divide resulting in a multilobed nucleus and abundant cytoplasm. N:C ratio = 4:1 Megakaryoblast Promegakaryocyte Size: 20-80µm Cytoplasm: – – Basophilic Few azurophilic granules Nucleus – Indented or bilobed nucleus Megakaryocyte – – Size: 30-100µm Cytoplasm – Nucleus – – Pinkish blue/abundant Irregular border with occasional pseudopods Abundant granules Lobulated Purple with granular chromatin No nucleoli N:C ratio = 1:1 to 1:2 Membrane ruptures after maturation is complete, cytoplasm fragments resulting in 1000 to 2000 platelets. The nucleus is phagocytized. Megakaryocyte Platelet (thrombocyte) Size: 1-4µm Cytoplasm – Light blue (actually fragments of megakaryoctye cytoplasm) – Fine scattered granules Nucleus not present Reference range: 150,000 - 450,000/µl Lifespan is 8-10 days Platelet (thrombocyte) Platelets References Harmening, D. M. (2009). Clinical Hematology and Fundamentals of Hemostasis. Philadelphia: F.A Davis. McKenzie, S. B., & Williams, J. L. (2010). Clinical Laboratory Hematology . Upper Saddle River: Pearson Education, Inc.