* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Hardy-weinberg equilibrium
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Fetal origins hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
The Selfish Gene wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Group selection wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
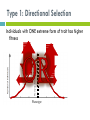
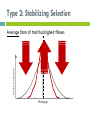
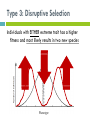
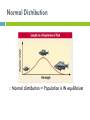
Science Starter #4 – 2/27/17 Draw a graph that shows a normal distributed population being disruptively selected for. What might happen to this population? TURN IN YOUR: 1) Histogram Lab 2) Evidence Packet TAKE OUT A SHEET OF PAPER FOR NOTES 9.3 A quick recap of types of selection Three types of selection: 1. 2. 3. Directional Stabilizing Disruptive Type 1: Directional Selection average population average New population New Individuals with ONE extreme form of trait has higher fitness Phenotype Type 2: Stabilizing Selection New population average Average form of trait has highest fitness Phenotype Type 3: Disruptive Selection Individuals with EITHER extreme trait has a higher fitness and most likely results in two new species Phenotype NOTES 9.3: HARDY-WEINBERG EQUILIBRIUM Ch. 16-1 pp. 317-320 The Gene Pool Gene Pool- total genetic information stored in a population Ex. Alleles for green and brown skin in a frog population Gene Frequency: Each allele exists at a certain percentage 6 frogs = total of 12 alleles (skin color gene = two alleles) 7 G (green) alleles and 5 g (brown) alleles Normal Distribution Normal distribution = Population is IN equilibrium Hardy-Weinberg Genetic Equilibrium G. H. Hardy and Wilhelm Weinberg Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium describes populations that are NOT evolving s http://oyster.ignimgs.com/mediawiki/apis.ign .com/pokemon-x-yversion/e/e6/Pxywikiraise6.png Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium (HWE) Genotype frequencies stay the same over time as long as FIVE conditions are met: Conditions for HWE: #1 Large Population Population: group of the same species that live in a specific area Ideally an infinitely large population Conditions for HWE: #2 No Gene Flow Gene flow: process of genes moving from one population to another Ex: Movement of individuals into and exit of the populations (Immigration and emigration) Conditions for HWE: #3 No Mutations Mutation: change in the sequence of DNA Alleles in the population stay the same Conditions for HWE: #4 Random Mating The selection of choosing a mate between individuals is random Conditions for HWE: #5 No Selection Occurs All phenotypes of the population have equal chances of surviving and reproducing Natural selection does not happen