* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Our Body`s Defense
Infection control wikipedia , lookup
Hygiene hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Lymphopoiesis wikipedia , lookup
Herd immunity wikipedia , lookup
Germ theory of disease wikipedia , lookup
Immune system wikipedia , lookup
Plant disease resistance wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Transmission (medicine) wikipedia , lookup
African trypanosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Innate immune system wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Sociality and disease transmission wikipedia , lookup
X-linked severe combined immunodeficiency wikipedia , lookup
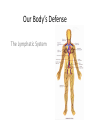
The Lymphatic System • Helps fight infection • Plays an important role in the body’s immunity to disease • Supports the cardiovascular system What does it do? • Maintains the body’s fluid balance – Carries excess fluid away from body tissues – Assists the body in its defense against pathogens Structure of • Lymph • Lymphocytes Our Body’s Defense The Lymphatic System Lymph • Clear yellow fluid that fills the areas around the body cells Lymphocytes • Specialized white blood cells that provide the body with immunity and protects the body against pathogens – B-Cells – T-Cells B-Cells • Lymphocytes that are stimulated to multiply when they come in contact with a pathogen • Produce antibodies that attack the pathogen • Produce memory cells that create immunity T-Cells • Lymphocytes that are stimulated to enlarge and multiply when they encounter a pathogen • Killer cells-stop the spread of disease • Helper cells-aide in the activation of B-cells and Killer T-cells and control the body’s immune system Other important terms: • Pathogen – An organism that causes disease • Lymphatic Vessels – Carry lymph to lymph ducts in the neck and chest Terms: • Lymph Nodes – Masses of tissue which serve to filter lymph before it returns to the blood • Spleen – Organ that keeps the body free of foreign substances and stores B-Cells Terms • Tonsils – Mass of lymphatic tissue that filters out pathogens that enter the mouth and nose • Thymus Gland – Produces lymphocytes in infants and children