* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download DNA - SD308.org
DNA repair protein XRCC4 wikipedia , lookup
Homologous recombination wikipedia , lookup
Zinc finger nuclease wikipedia , lookup
DNA sequencing wikipedia , lookup
DNA profiling wikipedia , lookup
DNA polymerase wikipedia , lookup
DNA replication wikipedia , lookup
Microsatellite wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom National DNA Database wikipedia , lookup
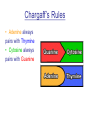
DNA DeoxyriboNucleic Acid What can DNA do? • Carries information from one generation to the next • Determines the heritable characteristics of organisms • Genes must be easily copied DNA Structure • DNA is a long molecule made up of units called – Nucleotides • 3 basic components – 5-carbon sugar » Deoxyribose – Phosphate group – Nitrogenous base Nitrogenous Bases • There are four Nitrogenous Bases – Purines: Two rings in their structures • Adenine • Guanine – Pyrimidines: One ring in their structure • Cytosine • Thymine Backbone of DNA • Formed by sugar and phosphate groups of each nucleotide • The nitrogenous bases stick out sideways from the chain • Nucleotides can be joined together in any order – Any sequence is possible!! Chargaff’s Rules • Adenine always pairs with Thymine • Cytosine always pairs with Guanine Double Helix • Rosalind Franklin – Used X-ray diffraction – Had the evidence that the double helix existed but didn’t put it all together • Watson and Crick – Tried to put together a model of DNA – Wasn’t until they saw Franklin’s X-rays that they discovered the double helix pattern Double Helix cont. • Looks like a twisted ladder • Hydrogen bonds between certain nitrogenous bases provide the force to keep the structure together • Hydrogen bonds can only form between certain base pairs – Adenine and thymine – Guanine and cytosine – Proves Chargaff’s rules