* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download DNA vs RNA
Zinc finger nuclease wikipedia , lookup
DNA sequencing wikipedia , lookup
Homologous recombination wikipedia , lookup
DNA repair protein XRCC4 wikipedia , lookup
DNA profiling wikipedia , lookup
DNA replication wikipedia , lookup
DNA polymerase wikipedia , lookup
Microsatellite wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom National DNA Database wikipedia , lookup
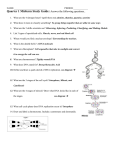
History of DNA A Chargaff, Erwin Discovered a relationship in the nitrogenous bases ADENINE (A) = THYMINE (T) GUANINE (G) = CYTOSINE (C) B Rosalind Franklin (1952) Took an X-ray of the DNA structure so the patterns could be seen. THE X-RAYS SHOW THAT DNA IS TWISTED AROUND EACH OTHER LIKE A HELIX AND HAS 2 STRANDS. X-ray of DNA C Watson and Crick (1953) Studied the structure of the DNA by building a 3-D model of the molecule AFTER using clues from Franklin’s X-ray of DNA. They proposed that DNA is made up of 2 chains of nucleotides held together by nitrogenous bases & that the 2 strands are twisted together in a shape called a double helix Features Name DNA Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA) RNA Ribonucleic Acid (RNA) 1. Phosphate Group – PO4 2. Sugar – Deoxyribose 3. Nitrogen Base – also called nitrogenous bases Chargaff’s Rule * Adenine A (Base pair rule) * Guanine G * Thymine T A=T&C=G * Cytosine C NUCLEOTIDE NUCLEOTIDE Structure 1. Phosphate Group – PO4 2. Sugar - Ribose 3. Nitrogen Base * Adenine A * Guanine G * Uracil U * Cytosine C Shape (Description) Location Looks like a twisted ladder. Actually called a double helix. ½ a ladder – a single stranded Euk cells – DNA is ONLY in the nuclues Prok cells – DNA is a single, circular chr in cytoplasm Found in the nucleus (transcription) and in the cytoplasm (translation) Function Store and transmit genetic information (heredity); blueprints for life; Instructions (CODE) for protein synthesis Helper molecule mRNA – copies & carries code out to ribosomes rRNA – protein factories (ribosomes) tRNA – transports amino acids; helps to construct proteins