* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cells of the innate immune system
Monoclonal antibody wikipedia , lookup
Lymphopoiesis wikipedia , lookup
Immune system wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Innate immune system wikipedia , lookup
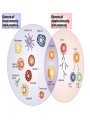
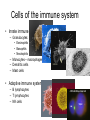
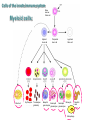
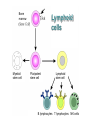
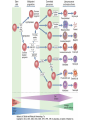
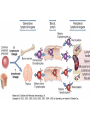
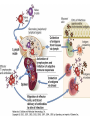
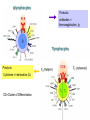
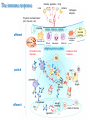
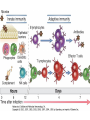
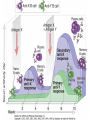
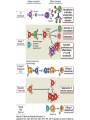
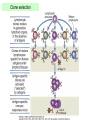
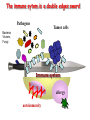
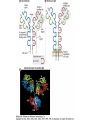
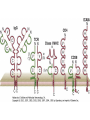
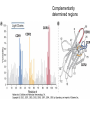
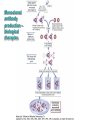
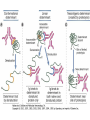
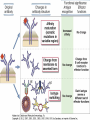
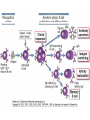
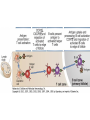
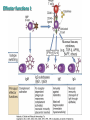
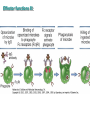
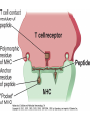
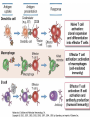
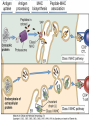
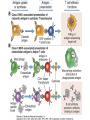
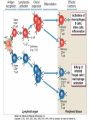
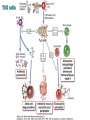
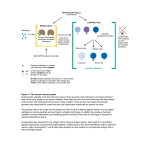
Therapies targeting the Immune System: Stimulation Suppression Modulation immunhomeostasis Innate immunity Immediate response Uptake, processing, presentation of Cannot be transfered antigen/pathogen to an other individual Regulatory Recognition of mechanisms molecular patterns Effector mechanisms No memory Adaptive immunity Requires same days to be activated Can be transfered to an other individual with antibodies or cells High degree of specificity Immunological memory Elements of innate immunity (rapid response) Elements of adaptive immunity (slow response) Cells of the immune system • Innate immune system: – Granulocytes: • Eosinophils • Basophils • Neutrophils – Monocytes – macrophages – Dendritic cells – Mast cells • Adaptive immune system: – B lymphocytes – T lymphocytes – NK cells Cells of the innate immune system Myeloid cells: Bone marrow Stem cell Myeloid stem cell Mast cell Erythrocytes Trombocytes (platelets) Pluripotent stem cell Lymphoid Stem cell Monocyte Basophil Eosinophil Neutrophil granulocytes granulocytes granulocytes makrofág Macrophage Dendritic cells Bone marrow Myeloid stem cell Lymphoid cells Pluripotent stem cell Lymphoid stem cell B lymphocytes T lymphocytes NK cells B lymphocytes Products: antibodies = Immunoglobulins, Ig T lymphocytes Products: Cytokines = Interleukins (IL) CD=Cluster of Differentiation Lymphocyte populations in human blood The immune response bacteria parasites fungi proteins virus Pathogens, antigens Physical, chemical barrier (skin, mucose, etc) Antimicrobial peptides Innate immune system afferent Dendritic cell Complement activation NK cell Granulocyte Mast cell Adaptive immune system Humoral immune response Cellular immune response central efferent Death of microbe Innate immunity Adaptive immunity RNS DNS Recognized structures Pathogen associated molecular patterns (PAMP) Receptors Sequences of proteins Pattern recognition receptors (PRR) mIg (BCR) MANNÓZ TLR1 – TLR10 Genes csíravonalban kódolt, öröklődő szekvenciák - limitált specificitás Somatic recombination Fine specificity, huge repertoire Y Expression of receptors Non-clonal – the same structures for the given cell type a,b g, d (TCR) Y Y Y Clonal – only T- and B cells appr. 1010 variations Clone selection The immune sytem is a double edges sward Pathogens Tumor cells Bacteria Viruses, Fungi Immune system allergy autoimmunity autoimmunitás Immunoglobulins • Membrane bound: B cell’s antigen receptor (mIgG, mIgM) • Signalling to B cells (via Igα, Igβ) • Secreted antibodies by plasma cells, 109 different specificities! • 5 classes (isotypes: IgM, IgD, IgG, IgA, IgE) • Effector functions eliminate antigen Complementarity determined regions Monoclonal antibody production – biological therapies Effector functions I: Effector functions II: Effector functions III: Antigen recognition by the T cell receptors • Recognize MHC-bound peptides • Mediate activation signal for T cells as part of TCR complex) • Stimulate T cell proliferation and cytokine secretion Structure of MHCI and MHCII CD8 CD4 Main Histocompatibiliy Complex, highly polymorphic, more than 250 allels for some of the genes! Bind peptides, display them to T cells (CD8+ or CD4+). Class I: bind 8-11 amino acid peptide, class II binds up to 30 amino acid peptides, structurally related (anchor amino acids) Helper T cells TH1 cells TH2 cells T cell cytotoxicity