* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Shielding vs. Deshielding
Freshwater environmental quality parameters wikipedia , lookup
History of molecular theory wikipedia , lookup
Multiferroics wikipedia , lookup
Biological aspects of fluorine wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Bent's rule wikipedia , lookup
Institute of Chemistry Ceylon wikipedia , lookup
Safety data sheet wikipedia , lookup
Drug discovery wikipedia , lookup
History of chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Cation–pi interaction wikipedia , lookup
Condensed matter physics wikipedia , lookup
Al-Shifa pharmaceutical factory wikipedia , lookup
Chemical bond wikipedia , lookup
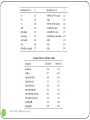
Chemical potential wikipedia , lookup
Chemical industry wikipedia , lookup
Chemical weapon proliferation wikipedia , lookup
Chemical plant wikipedia , lookup
Chemical weapon wikipedia , lookup
Chemical Corps wikipedia , lookup
Asymmetric induction wikipedia , lookup
Host–guest chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Aromatization wikipedia , lookup
Electron paramagnetic resonance wikipedia , lookup
Resonance (chemistry) wikipedia , lookup
Rotational spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
2-Norbornyl cation wikipedia , lookup
Chemical thermodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Spin crossover wikipedia , lookup
Chemical imaging wikipedia , lookup
Aromaticity wikipedia , lookup
Ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Isotopic labeling wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Analytical chemistry wikipedia , lookup
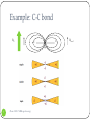
Shielding vs. Deshielding If a nuclei sees a smaller total magnetic field, it is said to be shielded. When a nuclei is shielded, its NMR frequency is shifted upfield lower chemical shift Shielded lower Deshielded higher 1 Chem 3500 - NMR spectroscopy Mesomeric effect: definition The mesomeric effect or resonance effect in chemistry is a property of the substituents or functional groups in a chemical compound. The effect is used in a qualitative way and describes the electron withdrawing or releasing properties of the substituents based on relevant resonance structures and is symbolized by the letter M. The mesomeric effect is negative (-M) when the substituent is an electron-withdrawing group and the effect is positive (+M) when based on resonance the substituent is an electron releasing group. 2 Chem 3500 - NMR spectroscopy Mesomeric effect: Examples 5.29 ppm -M: electron-withdrawing effect 6.52 deshielded 3 Chem 3500 - NMR spectroscopy +M: electron-releasing effect 3.74 shielded Mesomeric effect: releasing group 4 Chem 3500 - NMR spectroscopy Mesomeric effect: withdrawing groups 5 Chem 3500 - NMR spectroscopy Magnetic anisotropy of bonds Chemical bonds are anisotropic in space: they have different properties along different axis When a chemical bond is placed in a external magnetic field, it will generate a local field around itself that will also be anisotropic. 6 Chem 3500 - NMR spectroscopy Example: C-C bond B0 7 Chem 3500 - NMR spectroscopy C C Blocal Example: benzene ring 8 Chem 3500 - NMR spectroscopy More examples 9 Chem 3500 - NMR spectroscopy Predicting 1H chemical shifts: Shoolery’s rule Several factors can influence the 1H chemical shift: carbon substitution, electronegativity, mesomeric effect,… Those effects are additive If methane is used as the base compound, the contribution of each of substituent can be added up following the empirical Shoolery’s rule: 0.23 10 Chem 3500 - NMR spectroscopy 11 Chem 3500 - NMR spectroscopy Alkenes The presence of a double bond affects the protons on the allylic carbon atoms by shifting their chemical shift up (deshielding) CH2 H 1.5 12 Chem 3500 - NMR spectroscopy H 2.1 Tobey-Simon Rule The Tobey-Simon rule is an empirical system to predict the chemical shifts of protons attached to double bonds δ 5.28 gem cis Htrans H Hcis gem R 13 Chem 3500 - NMR spectroscopy trans 14 Chem 3500 - NMR spectroscopy Aromatic compounds Substituent has a similar effect on the chemical shifts of the aromatic ring than on alkenes. Results from the inductive and resonance effects. Prediction possible: δ 7.27 Si But it does NOT work when 2 substituents are ortho to each other… 15 Chem 3500 - NMR spectroscopy Substituent Parameters for Aromatic Proton 16 Chem 3500 - NMR spectroscopy Protons on Heteroatoms (N,S,O) Chemical shifts are very sensitive to pH, temperature, solvent and concentration Typical ranges are: 17 Acids RCOOH 10.5-12 ppm Phenols ArOH 4.0-7.0 ppm Alcohols ROH 0.5-5.0 ppm Amines RNH2 0.5-5.0 ppm Amides RCONH2 5.0-8.0 ppm Enols CH=CH-OH >15 ppm Chem 3500 - NMR spectroscopy