* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Amino Acids, Peptides and Proteins
Survey
Document related concepts
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
Protein domain wikipedia , lookup
Homology modeling wikipedia , lookup
Protein folding wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Circular dichroism wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Intrinsically disordered proteins wikipedia , lookup
Protein mass spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Alpha helix wikipedia , lookup
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
Ribosomally synthesized and post-translationally modified peptides wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
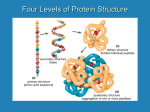
Amino Acids, Peptides and Proteins 1. α-Amino Acids R H COOH O H2N H2N H R OH (S) or L amino acids a) dipolar nature (isoelectric points) b) synthesis (racemic) i) from α-bromoacids ii) Strecker synthesis from aldehydes iii) reductive amination of α-ketoacids iv) amidomalonate synthesis 2. Peptides (up to 50 amino acids) R H N-terminal H O N OH N H2N O R" H H R’ H C-terminal O a) amino acid analysis b) sequencing i) Edman degradation (N-terminal) ii) carboxypeptidase (C-terminal) c) peptide synthesis (step-by-step and solid-phase) 3. Proteins (large peptides, occasionally with something else attached) a) structure (primary, secondary, tertiary and quaternary) b) classifications 64 α-Amino Acids O H 2N R = side chain ~ 500 known in nature OH 20 in humans H R Examples: 10 of them essential O O H2N H2N OH H H OH H valine neutral, bulky, hydrophobic proline 2o cyclic, bending in the peptide chain O O O H OH H glycine smallest, not chiral H2N O H N H2N OH H NH2 lysine basic, nucleophilic, used in catalysis OH CO2H aspartic acid acidic, carboxylate available, used in catalysis H 2N OH H cysteine crosslinking, catalysis O H2 N histidine basic, catalytic side chain OH H HN N 65 SH Peptide Structure Determination 1. Amino acid analysis: a) hydrolysis with HCl/H2O b) column chromatography c) detection with ninhydrin O H2N O OH O OH O RCOH H R N OH + NaOH/H2O CO2 O O O (purple) 66 Peptide Structure Determination 2. The Edman degradation: a) treatment with phenyl isothiocyanate (Ph-N=C=S) b) mild acid hydrolysis c) the resulting phenylthiohydantoin is identified by chromatography C H2N N NH SH N O HN Peptide H R Ph Ph Ph O S N Ph O NH H Peptide Next cycle N O HN H S R 67 OH HN NH H Ph S N R H+ Peptide H R S HN NH R Peptide Peptide Structure Determination 3. C-terminal residue determination a) enzyme (carboxypeptidase) used to hydrolyze one amino acid at the C-terminus b) identifaction of the amino acid c) further hydrolysis 4. Putting together peptide (protein) structure from fragments Asp-Arg-Val Arg-Val-Tyr Val-Tyr-Ile Ile-His-Pro Pro-Phe Asp-Arg-Val-Tyr-Ile-His-Pro-Phe 68 (angiotensin II) (Di)Peptide Synthesis a) protect the amino group of amino acid 1 O O O H2N O O O H R1 O BOC N HN OH H O OH OH H R1 H R1 b) protect the carboxyl group of amino acid 2 H2N O O O PhCH2OH/HCl OH H2N H2N OCH 2Ph H R2 H R2 H R2 OR c) couple the two amino acids using DCC H O O BOC N + OH H2N H DCC OCH2Ph H R2 BOC N H R2 H R1 O OCH 2Ph N H R1 H O d) remove the protective groups H O BOC N H R1 O H R2 OCH 2Ph CF COOH H2N 3 N H OCH2Ph N H R1 O H R2 H O H2/Pd or NaOH O H2N H R1 H R2 N OH O H Note: side-groups of same amino acids require extra protectiondeprotection! 69 Peptide Synthesis Solid-Phase Technique 1. BOC-protected amino acid is linked to the polystyrene beads (SN2 ester bond formation) 2. The beads are washed (to remove excess reagents) and treated with CF3COOH to remove BOC group 3. A second BOC-protected amino acid is coupled to the first one using DCC. The beads are washed. 4. The cycle of deprotection, coupling and washing is repeated asmany times as desired to add amino acid units to the growing chain. 5. After the desired peptide has been made, the treatment with anhydrous HF removes the final BOC group and cleaves the ester bond to the polymer 6. The peptide is purified The yields of the reactions are critical! For a dodecapeptide (20 aa) it requires 40 chemical steps (not counting special treatment for some side groups). If the yield is 90% per step the overall yield is only (0.940) 1.5% If the yield is 99% per step the overall yield is only (0.9940) 67% If the yield is 99.9% per step the overall yield is only (0.99940) 96% 70 Protein Structure and Function 1. Primary structure sequence of amino acids 2. Secondary structure three-dimensional structure of segments α-helical, β-pleated sheets) (α 3. Tertiary structure three-dimensional arrangements of segments 4. Quaternary structure three-dimensional shape of several proteins in a protein complex -------------------------------------------------------------------------Protein denaturation --------------------------------------------------------------------------Fibrous proteins (insoluble) Globular proteins (soluble) Simple proteins Conjugated proteins (carbohydrates, nucleic acids) Enzymes: holoenzymes = apoenzyme + cofactor (vitamin) 71