* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Beyond Element 83 are very unstable (radioactive)
Nuclear fission product wikipedia , lookup
Fallout shelter wikipedia , lookup
Radioactive waste wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear binding energy wikipedia , lookup
Radioactive decay wikipedia , lookup
Isotope analysis wikipedia , lookup
Isotopic labeling wikipedia , lookup
Valley of stability wikipedia , lookup
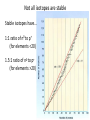
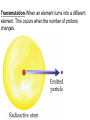
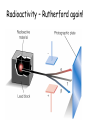
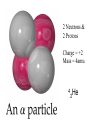
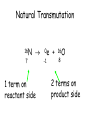
TOPIC: Radioactivity & Natural Transmuations Do Now: Where on your reference table can you find radioactive particles? Not all isotopes are stable Stable isotopes have… 1:1 ratio of n0 to p+ (for elements <20) 1.5:1 ratio of n0 to p+ (for elements >20) Beyond Element 83 are very unstable (radioactive) • No amount neutrons can hold nucleus together once it has 83+ protons • All Elements 83 and above on PT are radioactive • Other elements may have radioactive isotopes applet Radioisotopes- unstable nucleus – they are radioactive the nucleus of element emits subatomic particles and/or electromagnetic waves… by emitting these particles, nucleus changes into different element (it’s trying to become more stable) Radioactive Decay Series • Sometimes 1 transmutation isn’t enough to achieve stability • Some radioisotopes go through several changes before they achieve stability (and are no longer radioactive) U-238 PB-206 Transmutation-When an element turns into a different element. This occurs when the number of protons changes. These subatomic particles that are emitted were discovered around 1900 • Alpha rays • Beta rays • Gamma rays Radioactivity – Rutherford again! Penetration & Shielding 2 Neutrons & 2 Protons Charge = +2 Mass = 4amu 4 He 2 Beta Particle – fast moving electron Transmutation • 2 types –Natural –Artificial Natural Transmutation Happens all by itself (spontaneous) Not affected by anything in environment • 1 term on reactant side • Original isotope • 2 terms on product side • Emitted Particle • New Isotope Natural Transmutation 16N 7 1 term on reactant side 0e -1 + 16O 8 2 terms on product side Balancing Nuclear Equations 16N 7 0e -1 + 16O 8 Conservation of mass number: 16 = 0 + 16 Conservation of atomic number: 7 = -1 + 8 so Y = 228 232 = 4 + Y 232Th 90 4He 2 + Y X Z Conservation of Mass Number: sum of mass numbers on left side must = sum of mass numbers on right side 232Th 90 42He + 228 X Z 90 = 2 + Z so Z = 88 Conservation of Atomic Number: sum of atomic numbers on left side must = sum of atomic numbers on right side