* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download CHAPTER 11
Major depressive disorder wikipedia , lookup
Separation anxiety disorder wikipedia , lookup
Rumination syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Excoriation disorder wikipedia , lookup
Dementia praecox wikipedia , lookup
Bipolar II disorder wikipedia , lookup
Emergency psychiatry wikipedia , lookup
Panic disorder wikipedia , lookup
Bipolar disorder wikipedia , lookup
Autism spectrum wikipedia , lookup
Mental disorder wikipedia , lookup
Antisocial personality disorder wikipedia , lookup
Antipsychotic wikipedia , lookup
History of psychiatry wikipedia , lookup
Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders wikipedia , lookup
Depersonalization disorder wikipedia , lookup
Causes of mental disorders wikipedia , lookup
Abnormal psychology wikipedia , lookup
Classification of mental disorders wikipedia , lookup
Conduct disorder wikipedia , lookup
Generalized anxiety disorder wikipedia , lookup
History of mental disorders wikipedia , lookup
Narcissistic personality disorder wikipedia , lookup
Controversy surrounding psychiatry wikipedia , lookup
Child psychopathology wikipedia , lookup
Dissociative identity disorder wikipedia , lookup
Spectrum disorder wikipedia , lookup
Asperger syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Conversion disorder wikipedia , lookup
Schizoaffective disorder wikipedia , lookup
Sluggish schizophrenia wikipedia , lookup
Schizophrenia wikipedia , lookup
Social construction of schizophrenia wikipedia , lookup
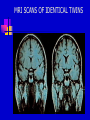
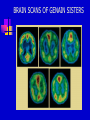
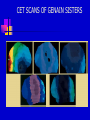
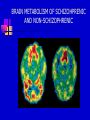
CHAPTER 11 SCHIZOPHRENIA AND OTHER PSYCHOTIC DISORDERS PSYCHOTIC DISORDERS Symptoms Alternations in perceptions, thoughts, or consciousness (delusions and hallucination) DSM-IV categories Schizophrenia Schizophreniform disorder Schizoaffective disorder Delusional disorder Brief psychotic disorder Shared psychotic disorder Psychotic disorder due to general medical condition Substance-induced psychotic disorder SCHIZOPHRENIA Symptoms Disturbance lasts at least 6 months, including One month of active phase that includes 2 positive or one positive and one negative symptom, and Decline in social or occupational functioning. DSM-IV subtypes Paranoid Catatonic Disorganized Undifferentiated Residual POSITIVE AND NEGATIVE SYMPTOMS Positive Delusions – Faulty interpretations of reality Hallucinations – Faulty sensory perceptions Disordered speech Disorganized and bizarre behavior Negative Flat affect Poverty of speech Lack of motivation or directedness Loss of energy Loss of feelings of pleasure EXAMPLES OF NEGATIVE SYMPTOMS Flat affect Avoid eye contact Immobile, expressionless face Lack of emotion when discussing emotional material Apathetic and uninterested Monotonous voice, low and difficult to hear Poverty of speech Long lapses before responding to questions or failure to answer Restriction on quantity of speech Slow speech Loss of directedness Slow movements Reduction of voluntary movements Inability to initiate activities Little interest in social participation CAUSES OF SCHIZOPHRENIA No known cause, but research has focused on Genetic factors Schizophrenic spectrum disorders Neurodevelopmental model Family studies Twin studies Adoption studies Diathesis-stress theory and family and community vulnerability High-risk studies focusing on family and birth history and markers of attention and cognition deficits MRI SCANS OF IDENTICAL TWINS AUDITORY HALLUCINATIONS BRAIN SCANS OF GENAIN SISTERS CET SCANS OF GENAIN SISTERS PRENATAL EXPOSURE TO INFLUENZA AND ADULT SCHIZOPHRENIA THE FAMILY FACTOR IN SCHIZOPHRENIA TREATMENT OF SCHIZOPHRENIA Antipsychotic drugs – Some have adverse side effect (tardive dyskinesia) Skills training Family programs Community support Combined treatment approaches Long-term outcome studies- Prognosis poor though deteriorative effects plateau after 5 to 10 years SKILLS TRAINING Social skills Self-awareness Affect regulation Social cue recognition Cognitive skills Training in elementary cognitive functions Strategies for dealing with cognitive deficits Cognitive restructuring about source of hallucinations Self-care and symptom-identification Improved grooming and self-care Self-monitoring for symptoms of relapse Skills for dealing with stress Identify indicators of stress Apply cognitive and behavioral techniques FAMILY PROGRAMS Education about probable causes, symptoms. and course Information about treatment Instruction in problem-solving and crisis management skills Decease negative expressed emotion (EE) Relapse recognition BRAIN METABOLISM OF SCHIZOHPRENIC AND NON-SCHIZOPHRENIC OTHER PSYCHOTIC DISORDERS Schizoaffective disorder – Delusions or hallucinations combined with symptoms of depression or manic mood Delusional disorder – Less bizarre than schizophrenia delusions; usually related to a particular topic and have some foundation in real life. Shared psychotic disorder – Two or more people who share shame delusional belief; one originates, the other follows. Occurrence is rare. DELUSIONAL CONTENT IN PSYCHOSES Schizophrenia Variety of bizarre content Being controlled or persecuted by others Finding reference to oneself in other’s behavior or in printed materials Depression Unjustified guilty Perceived bodily changes Mania Great self-importance Grandiosity Delusional disorder Loved by celebrity/high-status person Suspect spouse or lover of being unfaithful Possession of special and unrecognized talent