* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download ionic and covalent bonds
Halogen bond wikipedia , lookup
Electrochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Oxidation state wikipedia , lookup
Nanofluidic circuitry wikipedia , lookup
Metastable inner-shell molecular state wikipedia , lookup
Rutherford backscattering spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Photoelectric effect wikipedia , lookup
Atomic nucleus wikipedia , lookup
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Electrical resistivity and conductivity wikipedia , lookup
Low-energy electron diffraction wikipedia , lookup
Hydrogen bond wikipedia , lookup
Electron scattering wikipedia , lookup
Auger electron spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Atomic orbital wikipedia , lookup
Electron transport chain wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
Bent's rule wikipedia , lookup
Molecular orbital diagram wikipedia , lookup
Electronegativity wikipedia , lookup
Resonance (chemistry) wikipedia , lookup
History of molecular theory wikipedia , lookup
Electron configuration wikipedia , lookup
Metallic bonding wikipedia , lookup
Atomic theory wikipedia , lookup
Bond valence method wikipedia , lookup
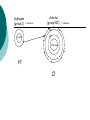
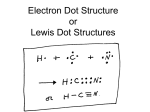
Pg. 56 of IAN IONIC AND COVALENT BONDS OBJECTIVE: To learn the different types of chemical bonds. RESEARCH Octet Rule: atoms want 8 electrons in the valence (outer) energy level Ionic Bond: bond in which one or more electrons from one atom are removed and attached to another atom. This creates positive and negative ions which attract each other. (Acids, bases, salts do this): H+ Cl- or Na+Clusually a metal and a non-metal (Group I & Group VII) hydrogen (group I) 1 valence e- chlorine (group VII) 8e- 1 proton 2e17 protons H+ Cl- 7 valence e- Covalent Bond: forms between atoms when they share one or more electrons. usually 2 nonmetals. Carbon has 6 electrons (4 in the valence level). Carbon forms covalent bonds by sharing electrons. Pg. 55 of IAN OUTPUT- Electron Dot Diagrams Examples: cut and paste CH4 and O2 electron dot diagrams: Label your diagrams: CH4 = methane 02 = oxygen Homework: Create an electron dot model of: C2H4 (acetylene) Answer the following question: What is the difference between an ionic and a covalent bond?