* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit 5: Ancient Rome 700 BC to 500 AD
Cursus honorum wikipedia , lookup
Promagistrate wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Roman architecture wikipedia , lookup
Constitutional reforms of Sulla wikipedia , lookup
Military of ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Travel in Classical antiquity wikipedia , lookup
Slovakia in the Roman era wikipedia , lookup
Roman army of the late Republic wikipedia , lookup
Constitutional reforms of Augustus wikipedia , lookup
Demography of the Roman Empire wikipedia , lookup
Romanization of Hispania wikipedia , lookup
Education in ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Food and dining in the Roman Empire wikipedia , lookup
Roman Republican governors of Gaul wikipedia , lookup
Roman funerary practices wikipedia , lookup
Switzerland in the Roman era wikipedia , lookup
Roman historiography wikipedia , lookup
Roman technology wikipedia , lookup
Culture of ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Early Roman army wikipedia , lookup
Roman agriculture wikipedia , lookup
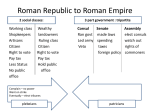
Unit 5: Ancient Rome 700 B.C. to 500 A.D. Standard(s) WHI.6a-6k The student will demonstrate knowledge of ancient Rome from about 700 B.C. (B.C.E.) to 500 A.D. (C.E.) in terms of its impact on Western civilization by a) assessing the influence of geography on Roman economic, social, and political development; b) describing Roman mythology and religion; c) explaining the social structure and role of slavery, significance of citizenship, and the development of democratic features in the government of d) sequencing events leading to Roman military domination of the Mediterranean basin and Western Europe and the spread of Roman culture in these areas; e) assessing the impact of military conquests on the army, economy, and social structure of Rome; f) assessing the roles of Julius and Augustus Caesar in the collapse of the Republic and the rise of imperial monarchs; g) explaining the economic, social, and political impact of the Pax Romana; h) describing the origin, beliefs, traditions, customs, and spread of Christianity; i) explaining the development and significance of the Church in the late Roman Empire; j) listing contributions in art and architecture, technology and science, medicine, literature and history, language, religious institutions, and law; k) citing the reasons for the decline and fall of the Western Roman Empire. Locations and places Rome: Centrally located in the Mediterranean Basin and distant from eastern Mediterranean powers Italian Peninsula Alps: Protection Mediterranean Sea: Protection, sea-borne commerce Roman mythology Based on the Greek polytheistic religion Explanations of natural phenomena, human qualities, and life events Roman gods and goddesses Jupiter, Juno, Apollo, Diana, Minerva, and Venus Symbols and images in literature, art, and architecture Social structure in the Roman Republic Patricians: Powerful nobility (few in number) Plebeians: Majority of population Slaves: Not based on race Citizenship Patrician and plebeian men Selected foreigners Rights and responsibilities of citizenship (e.g., taxes, military service) Features of democracy Representative democracy Assemblies The Senate Consuls Laws of Rome codified as Twelve Tables Punic Wars: Rome vs. Carthage (264–146 B.C. [B.C.E.]) Rome and Carthage were in competition for trade. Hannibal invaded the Italian Peninsula. Three wars resulted in Roman victory, the destruction of Carthage, and expanded trade and wealth for Rome. Evolution of the Roman Empire and spread of Roman culture Mediterranean basin (Africa, Asia, Europe, including the Hellenistic world of the Eastern Mediterranean) Western Europe (Gaul, British Isles) Causes for the decline of the Roman Republic Spread of slavery in the agricultural system Migration of small farmers into cities and unemployment Civil war over the power of Julius Caesar Devaluation of Roman currency; inflation The origin and evolution of Imperial Rome First triumvirate Julius Caesar: Seizure of power, assassination Augustus Caesar: Civil war, defeat of Marc Anthony, Rome’s first emperor Empire: Unified and enlarged, using imperial authority and the military Failure to provide for peaceful succession of Emperors The Pax Romana Two centuries of peace and prosperity under imperial rule Expansion and solidification of the Roman Empire, particularly in the Near East Economic impact of the Pax Romana Established uniform system of money, which helped to expand trade Guaranteed safe travel and trade on Roman roads Promoted prosperity and stability Social impact of the Pax Romana Returned stability to social classes Increased emphasis on the family Political impact of the Pax Romana Created a civil service Developed a uniform rule of law Origins of Christianity Had its roots in Judaism Was led by Jesus of Nazareth, who was proclaimed the Messiah Conflicted with polytheistic beliefs of Roman Empire Beliefs, traditions, and customs of Christianity Monotheism Jesus as both Son and incarnation of God Life after death New Testament, containing accounts of the life and teachings of Jesus, as well as writings of early Christians Christian doctrines established by early church councils Spread of Christianity Popularity of the message Early martyrs inspired others Carried by the Apostles, including Paul, throughout the Roman Empire Analyze why the story of Romulus and Remus was a perfect myth to describe the founding of Rome. In the box below defend the position that Rome was the perfect location to dominate trade in the Mediterranean. republic-or a government which elects representatives to run things patricians-founders of Rome, certain families, only ones allowed to hold public office at first plebeians-all other citizens, made up of all levels of wealth, but not from the right families Forum-center of the city and government Fill in the chart below. Why would the Plebeians strike against the Patricians? What are some important items that our own legal system adopted from the 12 Tables? Twelve Tables-Law code of Rome written on bronze tablets and placed in the Forum Dictator-one supreme leader makes all decisions, Romans appointed one in times of crisis Consul-two elected representatives that had veto power over one another Veto-the power to refuse a law checks and balances-the process of using one branch of government to keep another branch from becoming too powerful censors-registered citizens according to wealth and supervised public morality Using the chart to the right, explain how the Roman government used checks and balances to keep one branch from dominating others. Create a theory as to why the Romans adapted so many gods from other cultures. Explain why the Punic Wars were so important to Rome becoming the dominant force in the Mediterranean region. Carthage-major seaport city in Northern Africa, major rival to Romans Punic Wars-series of wars between Rome and Carthage Hannibal-Carthaginian general that leads second war against Rome Scipio-Roman general that defeats Hannibal at Zama Fill in the chart to the right. Analyze how Julius Caesar’s life changed Rome’s governments. Julius Caesar-rising senator who would go on to become dictator of Rome Pompey-initial ally of Caesar, became enemy lost civil war with Caesar for control of Rome Marc Antony-top ally and general of Caesar and later ruler with Octavian Cleopatra-Egyptian queen, lost civil war to Augustus, lover of both Caesar and Antony Augustus (Octavian)-Caesar adopted son (grandnephew) greatest and first Emperor of Rome. Pax Romana-200 year period of peace brought on by Roman dominance Impact of Pax Romana Create a theory as to why Pax Romana was so successful in the Roman Empire. Julian Emperors-a series of inept emperors that hurt Roman government Five Good Emperors-a series of good rulers that helped continue Pax Romana Hadrian’s Wall-wall built by emperor represents northern border of Empire Describe the characteristics of the Julian Emperors and the Good Emperors. gladiators-trained fighters, usually slaves, that fought to death for entertainment aqueducts-covered channels to carry water to Roman cities Ptolemy-developed formula for ellipse, and everything revolved around Earth Latin-Language of the Roman Empire Virgil-poet wrote Aeneid Evaluate why you think the entertainment of the Romans was so violent and how does it compare to our entertainment? Evaluate the Roman accomplishments in engineering and pick which you think is most important. Why was Christianity able to survive in the Roman Empire and what made it different from Judaism? Factors that led to Downfall of Roman Empire 1. Size: Empire too big 2. Economy: Inflation and cost of military 3. Military: Discipline lost-army not all Romans 4. Moral: People lose faith in Rome and family 5. Political: Civil conflict and weak leaders inflation-when prices rise and the value of money decreases martyrs-someone who dies for a cause Jesus-religious leader that is considered the Messiah by Christians Constantine-moved capital from Rome to Constantinople, adopted Christianity Council of Nicea-Council of religious leaders gathered by Constantine to create the rules of Christianity Attila-Hun that threatened Roman Empire In the box below pick the two biggest ways the Romans influenced us in your opinion then defend your choices.