* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download From Cells to Systems
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
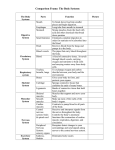
Parts of a cell 1. Nucleus - controls the activity of the cell, and responsible for the production of new cells. (A & P) 2. Chromosomes - threadlike structures that contain information about the characteristics of the organism. (A & P) 3. Cell Membrane - a covering that holds the cell together, and separates it from its surroundings. (A & P) 4. Cytoplasm - a jellylike substance that contains many chemicals to keep the cell functioning. (A & P) 5. Vacuoles - an organelle that stores food, water, and waste. (A & P) 6. Mitochondria - organelles that release energy from food. (A & P) 7. Cell wall - a rigid layer that supports and protects the plant cell. (P) 8. Chloroplasts - organelles that make food for the plant cell. (P) Tissues, Organs, and Systems Four kinds of human tissue: 1. muscle tissue - made up of cells that contract and relax when they receive signals from the brain. This allows movement of the skeleton. 2. nervous tissue - Our 5 senses are made up of nervous tissue. The brain and spinal cord are also made up of nervous tissue. 3. connective tissue - It includes the tissue in bones, cartilage, and tendons. Blood is also considered connective tissue. 4. epithelial tissue - This includes the body coverings of an animal. It also lines most internal organs. Cells make tissue, tissues make organs, and organs make systems. Systems make up organisms (humans). Ten systems make up the human body. Every system has a special job to do. From Cells to Systems (Lesson Two) There is no one system more important than the other. They are all equally important. These systems are all connected somehow. Circulatory System: Consists of the heart, blood, veins, arteries, and capillaries. This system is responsible for pumping blood throughout the body. Respiratory System: Consists of the nose, mouth, lungs, trachea, bronchi, bronchioles, and alveoli. This system supplies oxygen to all parts of the body. Digestive System: Contains the mouth, teeth, saliva, esophagus, stomach, acid, small and large intestines. Get rid of solid waste. Excretory System: Contains the kidneys, nephrons, ureters, bladder, and urethra. Gets rid of liquid waste. From Cells to Systems (Lesson Three) Bones and Joints - 206 Bones and 230 Joints in the human body. Bones contain bone marrow, which produces red and white blood cells. One key nutrient needed for healthy bones is calcium. Bones support and protect organs within the human body. They also allow us to move and give us our shape. Ligaments attach bone to bone at the joints. Muscular System - Consists of 600+ muscles. The muscles are connect to the bones by tendons. The muscles help the skeletal system move the body. Four types of muscles: 1. smooth muscle 2. skeletal muscle 3. voluntary muscle 4. cardiac muscle. Cardiac muscle can only be found within the heart.