* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download chem 217 intermediate chemistry ii assignment #5 3/9/00 due: 3/23/00
Enantioselective synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Ring-closing metathesis wikipedia , lookup
George S. Hammond wikipedia , lookup
Aromaticity wikipedia , lookup
Aromatization wikipedia , lookup
Baylis–Hillman reaction wikipedia , lookup
Stille reaction wikipedia , lookup
Elias James Corey wikipedia , lookup
Discodermolide wikipedia , lookup
Organosulfur compounds wikipedia , lookup
Bottromycin wikipedia , lookup
Homoaromaticity wikipedia , lookup
Physical organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Hydroformylation wikipedia , lookup
Wolff rearrangement wikipedia , lookup
Wolff–Kishner reduction wikipedia , lookup
Asymmetric induction wikipedia , lookup
Nucleophilic acyl substitution wikipedia , lookup
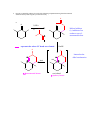
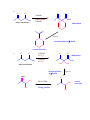
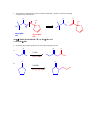
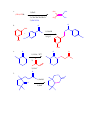
CHEM 217 INTERMEDIATE CHEMISTRY II ASSIGNMENT #5 3/9/00 DUE: 3/23/00 ANSWER KEY 1. Explain the difference in pKa's for the following dicarbonyl carbon acids: CH3COCH2CHO (5.9), CH3COCH2COCH3 (8.9), and CH3COCH2CO2Et (10.7). The differences are due to the fact that carbonyl groups of ketones and esters are less electronwithdrawing that those of aldehydes because alkyl (ketone) and alkoxy (ester) groups are electron donating thus counteracting the electron-withdrawing effect of the carbonyl group. Thus, ketones and esters don't stabilize the conjugate bases (enolates) as well as aldehydes do. Resonance structure III below is the key resonance structure. O -O O - O O R O R R I II III R = H (aldehyde), CH3 (ketone) and OEt (ester) The decreasing order of electron-withdrawing ability is CHO > COR > CO2R hence the order of pKa values given. Resonance structures best illustrate this: O O - O O - O - H + H + CH 3 H aldehyde H H H H H - not an EDG H + ketone alkyl groups EDG by resonance (hyperconjugation) and induction O O - O R R R + O O O + ester alkoxy groups EDG by resonance Remember that the more resonance structures of approximately equal energy you can draw the more stable the resonance hybrid. 2. Provide a reasonable synthesis for each of the following compounds starting from the indicated substrate and any other reagents you deem necessary. O a. O 1) LDA 2) O Michael addition (1,4 addition of an enolate to an unsaturated ketone. O represents the where CC bonds were formed NaOH O O Intramolecular Aldol condensation -H 2O -unsaturated ketone HO not isolated -hydroxy ketone b. O O O O 1) NaOEt 2) Br(CH2)5Br 3) NaOEt OEt ethyl acetoacetate OEt dialkylation O H3O+/ decarboxylation of -diacid acetone derivative c. O 1) NaOEt 2) CH3I O OEt O O dialkylation 3) NaOEt 4) CH3I OEt CH 3 ethyl acetoacetate decarboxylation of -diacid CH 3 H3O+/ CHPh O CH 3 CH 3 Ph3P=CHPh Wittig reaction CH 3 CH 3 acetone derivative 3. The following compound is the result of an aldol condensation. What two carbonyl-containing compounds was it made from? * O O H Ph O nucleophile side electrophile side cut double bond and add 2 H's to the -side and a =O to the -side 4. Predict the major organic product(s) for each of the following reactions: O a. Ph + O O 1) LDA Ph 2) PhCOOEt O O b. 1) NaNH2 2) CH3CH2CH2Br c. 1) Ph3P CH 3 CH 3 2) CH3CH2CH2CH2-Li+ CH 3 Ph (CH3)2CHBr 3) PhCOCH3 O O d. CHO 1) NaOH + 2) H3O+ Cl Cl OMe OMe e. O O O 1) LDA, -78oC 2) O 3) H3O+ O f. O 1) NaOH O 2) H3O+ g. CO 2Et H3O+/ CO 2H CO 2Et O O h. OEt 1) NaOEt OEt OEt 2) H3O+ O O i. O O OH O 3) NaOEt 1) SOCl2 2 O 2 OEt 2) EtOH O OEt 4) H3O+ O O 5) NaOEt + 7) H3O / CH 2Ph OEt 6) PhCH2Br CH 2Ph j. O O 1) NaOEt O O 2) NaNH2 CH 3CH 2 3) CH3CH2Cl 4) H3O+ k. O O O 1) xs. I2/NaOH 2) H3O+ 3) SOCl2 OH 4) EtOH OEt