* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download II. Purpose of Meiosis #1
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis wikipedia , lookup
Saethre–Chotzen syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Copy-number variation wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Gene nomenclature wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Gene desert wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy of the human retina wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Y chromosome wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Hybrid (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Neocentromere wikipedia , lookup
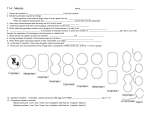
Meiosis and Sexual Reproduction Why you are unique Outline This outline is the same as is found in your Lecture Guide. In order to obtain an overview of the material in the Lecture Guide and to be able to see the ‘big’ picture while you study, fill in the missing components of the following outline from the Lecture Guide. I. Introduction A. Karyotype 1. Replicated Chromosomes= Sister Chromatids 2. Sister Chromatids vs. B. Gametes vs. C. Diploid vs. 1. 2. Diploid a) Homozygous vs. b) Human somatic cells remain diploid after Haploid 1 D. Functions of Meiosis 1. 2. II. Purpose of Meiosis #1: A. B. C. Initial cell in the ovaries or testes: 1. 1. Diploid or Haploid? 2. Are the Chromosomes Replicated or Unreplicated? What does REPLICATED and UNREPLICATED that mean? 3. Total Number of Chromosomes? 4. Number of copies each gene on all of the chromosomes? The Two Cells after Meiosis I: 1. 1. Diploid or Haploid? 2. Are the Chromosomes Replicated or Unreplicated? 3. Total Number of Chromosomes? 4. Number of copies each gene on all of the chromosomes? The Four Cells after Meiosis II: 1. 1. Diploid or Haploid? 2. Are the Chromosomes Replicated or Unreplicated? 3. Total Number of Chromosomes? 4. Number of copies each gene on all of the chromosomes? 2 III. Purpose of Meiosis #2: A. Meiosis I 1. Prophase I a. b. c. d. 2. Metaphase a. b. c. d. 3. 4. B. Meiosis II 1. Prophase II 2. Metaphase II 3. 4. 3 IV. V. Summary: Genetic Variability Due To Meiosis and Sexual Reproduction A. Crossing Over B. Independent Assortment (What does this mean?) C. D. 4 II. Overview of meiosis A. Before Meiosis 1. Total number of chromosomes? 2. Homologous Pairs? (Diploid? Haploid?) 3. Number of copies of each gene? B. After Meiosis I 1. Total number of chromosomes? 2. Homologous Pairs? (Diploid? Haploid?) 3. Number of copies of each gene? C. After Meiosis II 1. Total number of chromosomes? 2. Homologous Pairs? (Diploid? Haploid?) 3. Number of copies of each gene? D. After Fertilization 1. Total number of chromosomes? 2. Homologous Pairs? (Diploid? Haploid?) 3. Number of copies of each gene? III. Stages of meiosis A. Meiosis I 5 1. 2. 3. 4. B. Meiosis II 1. 2. 3. 4. IV. Fertilization V. Genetic variability due to meiosis and sexual reproduction A. 6 B. C. D. 7 8