* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Build a Paper Model of Transfer RNA (tRNA)
Cell-penetrating peptide wikipedia , lookup
Multi-state modeling of biomolecules wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Protein (nutrient) wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Protein adsorption wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Protein folding wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Circular dichroism wikipedia , lookup
Bottromycin wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
Homology modeling wikipedia , lookup
Expanded genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Build a Paper Model of Transfer RNA (tRNA)
pdb101.rcsb.org
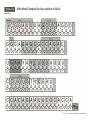
I. The primary structure
bases
phosphates
1
Cut out each
piece, leaving
the grey tabs
intact.
sugars
nucleotide
numbering
phosphodiester
backbone
2
Following the nucleotide
numbering, tape the pieces into
a long strip. The blank grey tabs
should be hidden.
3
Make slits in-between each
double line (16 total).
Be careful not to cut through
the entire strip.
4
Fold back ("mountain fold")
on the horizontal dashed lines
II. The secondary structure
Acceptor
arm
TΨC arm
Anticodon
arm
Anticodon
Acceptor
Fold in ("valley fold") on the
small vertical dotted lines.
6
Bring colored/patterned sections
together, and tape so the grey
tab is hidden. It is important
that you match the bases in the
following order:
1. 10-13 with 25-22
2. 27-31 with 43-39
3. 49-53 with 65-61
4. 1-7 with 72-66
or
or
or
or
Notice the almost-perfect base pairing
(G:C and A:U bases pair up). At this
point the model is a cloverleaf shape–
the secondary structure of tRNA. Each
colored region represents the double
helical regions of the structure.
What is tRNA?
III. The tertiary structure
7
Bring together
bases G19 and C56
(colored yellow) to
form a base pair –
hide the grey tab
by taping it under.
This forms the
beginnings of
the tRNA tertiary
structure– the
inverted L-shape.
Transfer RNA (tRNA) "translates" the genetic code into the language
of proteins. Each tRNA molecule binds to a specific amino acid on
the acceptor arm, recognizes its corresponding code on the mRNA
through the anticodon loop region and delivers the amino acid to a
growing peptide chain in the ribosome for protein synthesis.
Go to pdb101.rcsb.org to:
n
6
y
Anticodon
5
t
D-arm
&
Acceptor
Arm
Anticodon
Loop
• READ the Molecule of the Month articles
on tRNA and Ribosomes
3D • DOWNLOAD additional copies of this model, WATCH a video demonstration
of how to build it, and to access the DIGITAL ACTIVITY PAGE allowing for
futher exploaration of the 3D model (Learn > Paper Models)
PDB-101 is the educational portal of RCSB Protein Data Bank (rcsb.org)
tRNA Model Template for Reproduction in Black
pdb101.rcsb.org
pdb101.rcsb.org
PDB-101 is the educational portal of RCSB Protein Data Bank (rcsb.org)
tRNA Model Template for Reproduction in Color
pdb101.rcsb.org
pdb101.rcsb.org
PDB-101 is the educational portal of RCSB Protein Data Bank (rcsb.org)