* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download AP Biology
Pathogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Skewed X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Segmental Duplication on the Human Y Chromosome wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Y chromosome wikipedia , lookup
Neocentromere wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
DiGeorge syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Down syndrome wikipedia , lookup
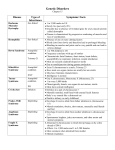
AP Biology Mrs. Morton Study Guide: Ch. 15 “The Chromosomal Basis of Inheritance” Key terms: Chromosome theory of inheritance Wild type ` Mutant phenotype Sex-linked Linked genes Parental types Recombinants Genetic map Map unit Linkage map Duchenne muscular dystrophy Hemophilia Barr body nondisjunction aneuploidy trisomic monosomic polyploidy deletion duplication translocation inversion Down syndrome Turner syndrome Klinfelter syndrome genomic imprinting Fragile X syndrome Objectives: 1. Describe the contributions that Walter Sutton, Thomas Hunt Morgan, and Theodor Boveri made to the current understanding of chromosomal inheritance. 1. Define linkage and explain why linkage interferes with independent assortment. 2. Show how cross over frequencies are used to make chromosome maps. 3. Describe the inheritance of sex-linked gene such as color-blindness. 4. Explain how sex is genetically determined in humans and the significance of the SRY gene. 5. Describe the process of X-inactivation in female mammals. 6. Distinguish among nondisjunction, aneuploidy, trisomy, and polyploidy. Explain how these major chromosomal changes occur and describe the consequences. 7. Distinguish among deletions, duplications, inversions, and translocations. 8. Describe the type of chromosomal alterations implicated in the following human disorders: Down Syndrome, Klinfelter’s syndrome, extra Y, triple X, Turner’s syndrome 9. Define genomic imprinting. 10. Give some exceptions to the chromosome theory of inheritance. Explain why extranuclear genes are not limited in a Mendelian fashion and how they can contribute to disease.