* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Immune System Basics - Wayzata Public Schools
Complement system wikipedia , lookup
Vaccination wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Lymphopoiesis wikipedia , lookup
Autoimmune encephalitis wikipedia , lookup
Sociality and disease transmission wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Immune system wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Immunocontraception wikipedia , lookup
Common cold wikipedia , lookup
Anti-nuclear antibody wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Hygiene hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Innate immune system wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
X-linked severe combined immunodeficiency wikipedia , lookup
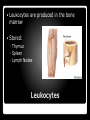
Immune System Basics It is when the immune system attacks organisms and substances that invade our body. Immune Response Two Basic types of leukocytes: Phagocytes – Consume foreign invaders ◦ Neutrophil – Kills bacteria Lymphocytes – Allow the body to remember and recognize previous invaders and help the body to destroy them. Leukocytes (White Blood Cells) Leukocytes are produced in the bone marrow Stored: ◦ Thymus ◦ Spleen ◦ Lymph Nodes Leukocytes B Lymphocytes – create antibodies to protect against invasion in the future. T Lymphocytes – Come in behind B-Cells and kills the foreign invaders. Known as “killer cells”. 2 types of Lymphocytes A pathogen is a foreign substance that invades the body. Two examples: ◦ Bacteria – Live on their own and are in soil, animals, and in the human body. ◦ Virus – Smaller than bacteria, can only live inside the host cell. Pathogen The Lymphatic System We come in contact with about 60,000 types of germs a day. ◦ One to two percent of them are potentially dangerous to people with normal immunity ◦ A cold virus can live up to SIX hours outside the human body Colds usually get into your body through your NOSE or EYES – seldom through your mouth You can’t catch the same cold virus twice, but there are hundreds of strains of viruses Average adult has 2-3 colds a year / Average child 6-12 colds a year Money/loss spent on colds a year in the US: 1. $75-100 million on physician visits 2. $7.7 billion on physician costs 3. $2.9 billion on over-the-counter drugs 4. $400 million on prescription drugs 5. 189 million school days lost a year to colds 6. 126 million work days missed by parents caring for their children 7. 150 million employees missed days a year 8. Total cold-related work loss exceeds $20 billion a year Make a List of the most Germ Riddled Items You come in Contact with Daily? 1. Kitchen faucet – biofilm on the screen 2. Garbage disposal – 1000 x’s more bacteria then a toilet 3. Welcome mat 4. Vacuum cleaner 5. Dish towel (7% are contaminated with MRSA) 6. Car dashboard 7. Soap dispenser 8. Restaurant ketchup bottle 9. Refrigerator seal (83% have molds) 10. Cell phones Top 10 germ-riddled spots in a restaurant 1. Seats 2. Menus 3. Lemon wedges (50% tested positive for fecal matter) 4. Salt & pepper shakers 5. Tables (especially edges) 6. Rims of glasses 7. Bathroom door knobs 8. Bathroom faucets 9. Ketchup bottles 10. Salad bar thongs Money is full of germs–paper money the most. The metals in coins often kill the bacteria, especially the nickel. Most effective mechanism to avoid picking up a cold or other bacteria is washing hands – cuts your risk to almost “Nil”–wash your hands before you eat, drink or touch your face. Sanitize items-Don’t share things-Stay home if you are sick-Keep tissues handy-Avoid infested areas Build immune system–good sleep, naps, nutrition Vit C&D and exercise Hands off – especially your nose and eyes immunization Pick Your Team gle s 25% Ea ts 25% Ho rn e s pe r Sk ip D. 25% s C. 25% oj an B. Trojans Skippers Hornets Eagles Tr A. T – Lymphocytes are responsible 1. 2. 3. 4. For producing antibodies For producing phagocytes For killing foreign invaders For providing vaccines 0% 1 0% 2 0% 3 0% 4 Leukocytes are produced in the 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Spleen Bone marrow Thymus Lymph Nodes Digestive System 0% 1 0% 0% 2 3 0% 0% 4 5 What is B – Lymphocytes not responsible for 1. 2. 3. 4. Creating Antibodies Continue to circulate in your body for years Killing foreign invaders Send messages to T-Cells 0% 1 0% 2 0% 3 0% 4 Tiny hair like structures that stop pathogens 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Mucus Membrane Skin Fungi Digestive System Cilia 0% 1 0% 0% 2 3 0% 0% 4 5 Which is not a storage area for Leukocytes? 1. 2. 3. 4. Bone marrow Spleen Thymus Lymph Nodes 0% 1 0% 2 0% 3 0% 4 Infectious Diseases are caused by 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Phagocytes Cilia Pathogens Vaccines Neutrophils 0% 1 0% 0% 2 3 0% 0% 4 5 White Blood cells that carry out most of the immune system’s functions are called? 1. Neutrophils 2. Lymphocytes 3. Phagocytes 4. Antibodies 5. Leukocytes 0% 1 0% 0% 2 3 0% 0% 4 5 Points Team Team Scores Points Team The first exposure to the pathogen generated… 1. 2. 3. 4. More antibodies than the 2nd exposure Fewer antibodies than the 2nd exposure No antibodies The same number of antibodies than the 2nd exposure 0% 1 0% 2 0% 3 0% 4 The 2nd exposure occurred how many days after the first? 1. 2. 3. 4. 14 21 28 30 days days days days 0% 1 0% 2 0% 3 0% 4 The amount of time for the antibody concentration to reach its peak after the 1st exposure was 1. 2. 3. 4. 4 days 6 days 8 days 12 days 0% 1 0% 2 0% 3 0% 4 The amount of time for the antibody concentration to reach its peak after the 2nd exposure was 1. 2. 3. 4. 4 days 8 days 12 days 14 days 0% 1 0% 2 0% 3 0% 4 Points Team Team Scores Points Team Points Participant Points Participant Leaders Participant