* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Sex Chromosomes
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Copy-number variation wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Hybrid (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Ridge (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Segmental Duplication on the Human Y Chromosome wikipedia , lookup
Saethre–Chotzen syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Skewed X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Y chromosome wikipedia , lookup
Neocentromere wikipedia , lookup
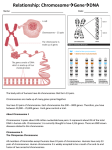
Notes - The Chromosomal Basis of Inheritance _________________________ was the first to associate a specific _____________ with a specific ____________________ in the early 20th century Like Mendel, Morgan made an insightful choice as an experimental animal, ______________________________________, a fruit fly species that eats fungi on fruit Fruit flies have three pairs of _________________ and a pair of ________chromosomes (________ in females, ________ in males) He discovered a single __________ fly with ____________eyes instead of the usual red The normal character phenotype is the ____________ type Alternative traits are ______________ phenotypes When Morgan crossed his white-eyed male with a red-eyed female, all the _______ offspring had __________ eyes The red allele appeared _________________ to the white allele Crosses between the _______offspring produced the classic ___________ phenotypic ratio in the _________ offspring Surprisingly, the _________________ trait appeared only in ____________ All the ______________ and half the ____________ had _________ eyes Morgan concluded that a fly’s eye color was _____________ to its sex Morgan deduced that the gene with the _________________ mutation is on the _______ chromosome alone, a ______________________ gene Females (XX) may have two _________________ alleles and have red eyes or may be ___________________ and have red eyes Males (XY) have only a single allele and will be _________________ if they have a red-eyed allele or ____________________ if they have a white-eyed allele Each chromosome has __________________ or _____________________ of genes Genes located on the same chromosome, ______________________, tend to be inherited _______________ because the chromosome is passed along as a unit Results of crosses with linked genes _______________ from those expected according to _____________________________________ Morgan observed this linkage and its deviations when he followed the inheritance of characters for __________________________ and _________________________ Morgan reasoned that body color and wing shape are usually inherited ________________ because their genes are on the same _____________________ Independent assortment of chromosomes and crossing over produce genetic recombinants The production of offspring with new ____________________ of traits inherited from two parents is _______________________________________ Genetic recombination can result from independent assortment of genes located on __________________ chromosomes or from ________________________ of genes located on homologous chromosomes A _________ frequency of recombination is observed for any two genes located on different (____________________) chromosomes The _________________________ of recombination between unlinked genes is the random orientation of homologous chromosomes at __________________________ In contrast, linked genes tend to move together through _____________ and ______________________ Under normal Mendelian genetic rules, we would not expect ____________________ to recombine into assortments of alleles not found in the ______________ The results of Morgan’s testcross for body color and wing shape _____________________________ to either ______________________________ or ___________________ linkage Under independent assortment the testcross should produce a ________________ ____________________ ratio If completely linked, we should expect to see a _________________ ratio with only parental phenotypes among offspring Morgan proposed that some mechanism occasionally exchanged ______________ between _____________________ chromosomes This _________________ alleles between ___________________ chromosomes The actual mechanism, ________________________ during prophase I, results in the production of more _____________ of gametes than one would predict by Mendelian rules alone Sex Chromosomes Although the _________________and ___________________ differences between women and men are _________________, the chromosomal basis of sex is rather _____________ In ______________ and other __________________, there are two varieties of sex chromosomes, ______ and _____ This ___________ system of mammals is not the only chromosomal mechanism of determining ___________ Other options include the __________ system, the __________ system, and the ______________________system In the X-Y system, Y and X chromosomes behave as _________________ chromosomes during _______________ In reality, they are only _______________ homologous and ______________ undergo _________________________ In both ______________ (XY) and ______________ (XX), the two sex chromosomes ____________________ during meiosis and each gamete receives ___________ In humans, the ___________________ signs of sex first appear when the embryo is about ________ months old In individuals with the __________gene (_______-determining ___________ of the _____ chromosome), the generic embryonic gonads are modified into _____________ Activity of the SRY gene triggers a cascade of __________________, ____________________, and ___________________ features because it regulates many other genes In addition, other ___________ on the Y chromosome are necessary for the production of functional ____________ In individuals lacking the ____________ gene, the generic embryonic gonads develop into _________________ In addition to their role in ______________________________, the sex chromosomes, especially the ________ chromosome, have genes for many _________________ unrelated to __________ If a _______________________ trait is due to a _________________ allele, a female will have this phenotype only if _____________________ Heterozygous females will be __________________ Because males have only __________ _____ chromosome (__________________), any male receiving the _________________allele from his mother will express the trait The chance of a female inheriting a _________________________ of the mutant allele is much ____________ than the chance of a male inheriting a ____________________ Therefore, _____________ are far more likely to inherit _____________________ recessive disorders than are __________________ Several serious human disorders are sex-linked 1. ____________________________________ affects one in ____________ males born in the United States Affected individuals rarely live past their early ___________ This disorder is due to the _______________ of an X-linked gene for a key muscle protein, called __________________ The disease is characterized by a progressive ______________________ of the muscles and a loss of _____________________ 2. ________________________ is a sex-linked recessive trait defined by the absence of one or more ___________________________ These proteins normally ____________ and then _____________ bleeding Individuals with hemophilia have _________________ bleeding because a firm clot forms _______________ Bleeding in ______________ and _______________ can be painful and lead to serious ____________________ Individuals can be treated with _____________________________ of the missing ________________ Although female mammals inherit __________ X chromosomes, only ___________ X chromosome is ________________ Therefore, males and females have the same _______________________ (one copy) of genes on the ______ chromosome During female development, one X chromosome per cell _______________ into a compact object, a ____________body This _________________ most of its _______________ The condensed Barr body chromosome is _________________ in _______________ cells that produce _________ As a consequence, females consist of a mosaic of cells, some with an active _____________________, others with an active ________________________ After Barr body formation, all ____________________ cells have the same ____________________ If a female is ____________________ for a sex-linked trait, approximately _________ her cells will express one allele and the other half will express the other allele _______________________ occurs when problems with the _____________spindle cause errors in ____________________________ This may occur if ____________ chromosomes do not separate properly during _____________________ Alternatively, ______________________________ may fail to separate during _______________________ As a consequence of nondisjunction, some gametes receive _________ of the same type of chromosome and another gamete receives _________ copy Offspring results from fertilization of a ______________ gamete with one after ____________________will have an abnormal chromosome number or ____________________ ________________ cells have three copies of a particular chromosome type and have ____________________ total chromosomes ________________ cells have only one copy of a particular chromosome type and have ____________________ chromosomes If the organism survives, __________________ typically leads to a distinct __________ If aneuploidy happens ___________ in development, this condition will be passed along by ________________ to a large number of ____________ This is likely to have a __________________ effect on the organism Organisms with ______________ than two complete sets of chromosomes, have undergone _______________________ This may occur when a ________________ gamete fertilizes another gamete in which there has been _____________________ of all its chromosomes The resulting zygote would be _____________________ If a _________ zygote failed to divide after replicating its chromosomes, a ____________________ embryo would result from subsequent successful cycles of mitosis ___________________ is relatively common among ______________ and much less common among __________________ ____________________ are more nearly normal in phenotype than __________________ One ______________ or _______________ chromosome apparently upsets the genetic balance during development more than does an _________________________ set of chromosomes ____________________ of a chromosome can lead to four types of changes in chromosome structure 1. _____________________ - occurs when a chromosome fragment lacking a centromere is lost during cell division This chromosome will be missing certain _____________ 2. ____________________ - occurs when a fragment becomes attached as an extra segment to a _______________________________ 3. ____________________ - occurs when a chromosomal fragment reattaches to the ________________ chromosome but in the ____________ orientation 4. ____________________ - a chromosomal fragment joins a ____________________ chromosome Some ____________________ are ____________________, others are not _________________ and _____________________ are common in _______________ Homologous chromatids may break and rejoin at _________________________, such that one chromatid will ____________ more genes than it receives A diploid embryo that is _________________ for a large _______________ or __________ with a large deletion to its ____________________ chromosome is usually missing many __________________ genes and this leads to a _____________ outcome __________________ and _____________________ are typically harmful _______________________________ or __________________ can alter __________________ because a gene’s expression is influenced by its location Several serious human disorders are due to alterations of chromosome number and structure Although the frequency of _________________ zygotes may be quite high in humans, most of these alterations are so _________________ that the embryos are spontaneously ______________ long before birth These developmental problems result from an _________________ among gene products Certain aneuploid conditions upset the balance ____________, leading to ____________________ to birth and beyond These individuals have a set of _____________________ — a ____________________ — characteristic of the type of aneuploidy One aneuploid condition, _____________________________, is due to three copies of chromosome ________ It affects one in __________ children born in the United States. Although chromosome 21 is the _______________ human chromosome, it _______________ alters an individual’s __________________ in specific ways Most cases of Down syndrome result from ____________________ during ____________ production in one parent The frequency of Down syndrome correlates with the __________ of the ____________ This may be linked to some ________________________ abnormality in the ______________checkpoint during ____________________, leading to nondisjunction _____________________ of other chromosomes also increase in incidence with ___________________ age, but it is rare for infants with these autosomal trisomies to ________________ for long _________________________ of sex chromosomes produces a variety of ______________ conditions in humans Unlike autosomes, this aneuploidy upsets the genetic balance ____________________ This may be because the ________ chromosome contains relatively few ___________ Also, extra copies of the ______ chromosome become inactivated as ___________ bodies in _______________ cells 1. ______________________ syndrome - an _________________, occurs once in every _____________ live births These individuals have male _______________________, but are ______________ There may be ___________________ characteristics Their intelligence is _______________ 2. Males with an extra ______ chromosome (____________) tend to somewhat ___________ than average Associated with ___________________________ 3. ___________________ - (_________), which occurs once in every _________ live births, produces _______________ females 4. ___________________ or ______________________ (_________) - , which occurs once in every 5000 births, produces _________________, but _______________ females ___________________________________ of chromosomes can also cause human ________________ __________________, even in a heterozygous state, cause severe ______________ and _________________ problems One syndrome, _______________________, results from a specific deletion in chromosome _______ These individuals are ___________________________, have a small __________ with unusual facial features, and a cry like the ___________ of a distressed _________ This syndrome is ____________ in infancy or early childhood The phenotypic effects of some mammalian genes depend on whether they were inherited from the mother or the father (imprinting) For most ______________ it is a reasonable assumption that a specific allele will have the same effect regardless of whether it was ________________ from the ______________ or _______________ However, for some _____________ in ____________________, it does depend on which _________________ passed along the alleles for those traits The genes involved are not _____________________ and may or may not lie on the ________ chromosome Two disorders with different phenotypic effects, __________________________ syndrome and _____________________ syndrome, are due to the same cause, a __________________ of a specific segment of chromosome _________ __________________________ syndrome is characterized by ______________________, _______________, _____________ stature, and unusually small _________ and _______________ These individuals inherit the abnormal chromosome from their _______________ Individuals with ____________________ syndrome exhibit spontaneous ______________, _______________ movements, and other _____________ and _______________ symptoms This is inherited from the __________________ The difference between the disorders is due to _______________________________ In this process, a gene on one homologous chromosome is _________________, while its allele on the homologous chromosome is ______________________ The ___________________ status of a given gene depends on whether the gene resides in a ______________ or a _____________ The same alleles may have different effects on offspring, depending on whether they arrive in the _______________ via the ____________ or via the _____________ In the new generation, both maternal and paternal imprints are apparently “_________________” in ______________-producing cells Then, all chromosomes are __________________ according to the ____________ of the ______________________ in which they reside Several hundred mammalian genes, many critical for ________________________, may be subject to ________________________ ______________________ is critical for _____________________ development