* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ms - cloudfront.net
Bent's rule wikipedia , lookup
Metastable inner-shell molecular state wikipedia , lookup
Electrochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Atomic orbital wikipedia , lookup
Atomic nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Molecular Hamiltonian wikipedia , lookup
Computational chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Fluorochemical industry wikipedia , lookup
Gas chromatography–mass spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Chemical element wikipedia , lookup
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Bond valence method wikipedia , lookup
Molecular orbital diagram wikipedia , lookup
Resonance (chemistry) wikipedia , lookup
Hydrogen atom wikipedia , lookup
Rutherford backscattering spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Periodic table wikipedia , lookup
X-ray fluorescence wikipedia , lookup
History of chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Electronegativity wikipedia , lookup
Electron configuration wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
History of molecular theory wikipedia , lookup
Stoichiometry wikipedia , lookup
Chemistry: A Volatile History wikipedia , lookup
Extended periodic table wikipedia , lookup
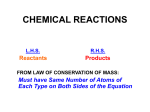
Metallic bonding wikipedia , lookup
Hypervalent molecule wikipedia , lookup
Alkaline earth metal wikipedia , lookup
Chemical bond wikipedia , lookup
IUPAC nomenclature of inorganic chemistry 2005 wikipedia , lookup
Ms. Mai Chemistry Name: Period: 1st Semester Final Exam Review Sheet YOU MUST COMPLETE THIS ENTIRE REVIEW SHEET BEFORE TAKING THE FINAL EXAM. THERE WILL BE NO CALCULATORS ALLOWED DURING THE FINAL EXAM. SHOW ALL WORK ON A SEPARATE SHEET OF PAPER. Atomic Structure 1. What is the difference between mass number and atomic number? 2. Which elements have similar chemical properties? 3. What is an isotope? 4. What do all atoms of a given element have the same number? 5. Which particle plays the greatest role in determining the properties of an element? 6. Differentiate between period and group. 7. Where are metals, semi-metals, and nonmetals located on the periodic table? 8. Where are alkali metals, alkaline earth metals, halogens, noble gases, and transitions metals located? 9. Use your periodic table to complete the table below ATOM SYMBOL ATOMIC MASS # OF # OF # OF NUMBER NUMBER PROTONS ELECTRONS NEUTRONS Fe 56 CHLORINE ARGON 26 17 40 Al HYDROGEN TITANIUM NITROGEN KRYPTON SULFUR 10. Fill in the following chart Element Chromium Iodine Potassium Vanadium Lithium Neon Californium Barium Strontium Platinum 1 27 1 48 26 18 13 18 22 13 1 22 7 36 32 Group Name (ex. Noble Gas) 7 36 7 16 Metal/Nonmetal/Metalloid Trends in the Periodic Table 11. Describe the following trend on the periodic table. a. Atomic Number b. Atomic Size c. Ionization Energy d. Electronegativy 12. Which atom is more electronegative, fluorine or lithium? 13. Which atom has a greater ionization energy, nitrogen or bismuth? 14. Which atom has a larger atomic radius, fluorine or barium? 15. Which element is more like lithium in terms of properties, sodium or beryllium? 16. Which element has more electrons in its valence shell, sodium or magnesium? 17. Which element is closer to achieving noble gas configuration, magnesium or lithium? Bonding 18. Describe how a cation and an anion is formed. 19. What do metals typically do when they become ions? What about nonmetals? 20. What type of elements bond together in ionic bonds? covalent bonds? metallic bonds? 21. How do electrons in ionic bonding interact? Covalent bonding? 22. How does the relative size of an anion and cation compare to its neutral atom? 23. Which element would calcium more likely bond with, oxygen or fluorine? 24. Which element would nitrogen more likely bond with, magnesium or chlorine? 25. Which element will react more readily with chlorine, sodium or magnesium? 26. Draw Lewis Dot Structures for the following compounds a. Cl2 d. CH2Cl2 a. H2 e. NH3 b. CH4 f. CH3OH c. CH3I g. H2O h. i. j. k. 27. Label each of the following compounds as ionic or covalent. a. C6H12O6 c. NH2CH2 b. NaCl d. SiO2 e. H2O f. MgBr2 28. How many valence electrons do the following atoms have? a. Magnesium d. Helium b. Carbon e. Silicon c. Argon f. Potassium g. Sulfur h. Calcium i. Hydrogen Balancing Equations 29. In balancing equations, what must be the same on both sides of the equation? 30. What is the only thing you can change when you balance an equation? O2 N2 HCN C2H2 31. Balance the following equations a. NaOH + H2SO4 Na2SO4 + H2O b. Pb(C2H3O2)2 + H2S PbS + HC2H3O2 c. KOH + Al2(SO4)3 K2SO4 + Al(OH)3 d. Ca(NO3)2 + K3PO4 Ca3(PO4)2 + KNO3 e. Na2CO3 + Al2(SO4)3 + H2O Na2SO4 + Al(OH)3 + CO2 f. C2H5OH + O2 CO2 + H2O 32. Complete the following equations and identify which type of reaction it is. a. Fe + Cl2 b. Cu + Br2 c. PCl5 d. H2SO4 e. Mg + PbSO4 f. K + HgCl2 g. Na3PO4 + MgSO4 h. Pb(NO3)2 + H2SO4 Mole Conversions 33. What does Avogadro’s number represent? 34. Calculate the molar mass of each of these substances. a. AlCl3 d. TeF4 b. KF e. ZnO c. KMnO4 f. CaSO4 g. PbS h. Ba(SCN)2 i. H2CO3 35. Calculate the mass of 1.000 mole of CaCl2 36. How many moles are in 4 grams of H2O? 37. Calculate number of moles in 32.0 g of CH4 38. Determine mass in grams of 40.0 moles of Na2CO3 39. Calculate moles in 168.0 g of HgS 40. How many moles are in 27.00 g of H2O 41. Calculate the number of molecules in the following: a. 67.2 grams NaCl b. 1 mole H2O c. 33 grams of CH4 d. 3.00 mole AlCl3 42. Determine the number of atoms from moles. (In other words, convert from moles into atoms.) a. 2.00 mole HC2H3O2 b. 5.00 mole Ag2O c. 0.000300 mole AuCl3 d. 0.00550 mole CH4 43. Use the following equation to answer the questions below: N2 + 3H2 2NH3 a. How many moles of NH3 are in 1.75 moles of N2? b. How many moles of N2 are in 5.23 moles of H2? c. How many moles of H2 are in 3.02 moles of NH3? 44. Determine the mass of carbon dioxide produced when 0.85 grams of butane (C4H10) reacts with oxygen according to the following unbalanced chemical equation: C4H10(l) + O2(g) CO2(g) + H2O(g) 45. Determine the mass of sodium nitrate produced when 0.73 grams of nickel (II) nitrate reacts with sodium hydroxide according to the following unbalanced chemical equation: Ni(NO3)2(aq) + NaOH(aq) Ni(OH)2(aq) + NaNO3(aq) 46. When iron (II) hydroxide is mixed with phosphoric acid, iron (II) phosphate precipitate results. a. Balance the following equation: Fe(OH)2(aq) + H3PO4(aq) 3(PO4)2(s) + H2O(l) b. If 3.20g of Fe(OH)2 is treated with 2.50 g of H3PO4, what is the limiting reagent and what is the excess reagent? c. Using the previous information, how many grams of Fe3(PO4)2 precipitate can be formed? 47. Quicklime (CaO) can be prepared by roasting limestone (CaCO3). When 2.00 x 103g of CaCO3 are heated, the actual yield of CaO is 1.50 x 103g. What is the percent yield? CaCO3 CaO + CO2 48. If 1.85g of Aluminum reacts with an excess of Copper (II) Sulfate (CuSO4), the percentage yield of Cu is 56.6%. What mass of Cu is produced? 2Al + 3CuSO4 3Cu + Al2(SO4)3 49. Assume that 2.0mol of methane (CH4) is burned in the presence of excess oxygen. What is the percentage yield if the reaction produces 87.0g of CO2? CH4 + 2O2 CO2 + 2H2O 50. Calculate the volume of 45.9 grams of C6H12O11 gas at STP. Thermodynamics Study the chart below. You will have 2-3 questions on your final exam. Exothermic Endothermic Releases energy/heat Absorbs energy/heat Condensation and Freezing Evaporation and Melting Energy is on the right side of the equation Energy is on the left side of the equation Example: CH4 + 2O2 CO2 + 2H2O + energy Example: N2 + O2 + energy 2NO Graph goes from higher to lower Graph goes from lower to higher