* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Descent with Modification: Darwinism
Precambrian body plans wikipedia , lookup
Sexual selection wikipedia , lookup
Sociobiology wikipedia , lookup
Punctuated equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
Inclusive fitness wikipedia , lookup
Natural selection wikipedia , lookup
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
Evidence of common descent wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary mismatch wikipedia , lookup
Evolving digital ecological networks wikipedia , lookup
Saltation (biology) wikipedia , lookup
The Descent of Man, and Selection in Relation to Sex wikipedia , lookup
Theistic evolution wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
Transitional fossil wikipedia , lookup
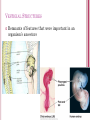
DESCENT WITH MODIFICATION Chapter 22 PRE-DARWINIAN THOUGHT Earth only about 6000 years old Each species is specially created Adaptation to environment is the work of a creator Variations = imperfection ARISTOTLE Species were fixed Perfect & permanent Scala naturae or Ladder of Life Rank for everything CAROLUS LINNAEUS Binomial naming system Nesting fashion Related Group & specific name Similar organisms into general categories Creation pattern not resemblance of species GEORGES CUVIER Father of Paleontology Studied strata and fossil record Catastrophism Sudden events different than current mechanisms Creator’s role in re-creation THE CHANGING EARTH James Hutton Gradualism Charles Lyell Change from slow, continuous processes Valleys from river flow Uniformitarianism Change constant over time What’s been has always been JEAN-BAPTISTE DE LAMARK Proposed 1st mechanism for evolution Organisms innately driven to complexity Remembered for being wrong Match to environment Principles Use and disuse Inheritance of acquired characteristics Phenotypes don’t affect genotype ≠ inherited INHERITANCE OF ACQUIRED TRAITS CHARLES DARWIN Father of evolution Descent with modification Organisms change to better fit habitats Decades of backlash and denial Distorted to justify societal causes (Nazi ideologies) Cartoon of Darwin as half ape, half human 200 years old this year 150 years since theory DARWINIAN INFLUENCE TIMELINE DARWIN’S RESEARCH Observed adaptations Realized adaptations centered on natural selection Similarities stronger between regions than climates Individuals with certain inherited traits left more offspring Charles Lyell and Thomas Malthus influence THEORIST OF EVOLUTION Darwin reluctant to publish his ideas Lyell didn’t unconvinced, but pushed publishing Alfred Russel Wallace developed a similar hypothesis Important before someone else did Published 1st Wallace’s work with excerpts from Darwin Wallace conceded because Darwin’s better supported ON THE ORIGIN OF SPECIES BY MEANS OF NATURAL SELECTION Main ideas Descent with modification Natural selection Avoided reference to humans Evolution not mentioned, descent with modification History of life like a branched tree Match organisms to environment Exclusions Life’s unity & diversity Matched with Linnaeus Relied on familiar examples ARTIFICIAL SELECTION All species Canis familiaris, but different breeds Bred from artificial selection Common vegetables from wild mustard NATURAL SELECTION Observations Diversity in populations Traits from parents to offspring Over production of offspring common Many offspring don’t survive Inferences Certain traits enhance probability of survival Favorable traits will accumulate in populations SUMMARIZING NATURAL SELECTION Individuals with heritable characteristics survive and reproduce at a higher rate Over time, it can increase the match between organisms and their environment If an environment changes or individuals move, adaptations to these can give rise to new species KEY POINTS OF NATURAL SELECTION Individuals do not evolve Only heritable traits are diminished or amplified Change between generations Not encoded by genes = acquired characteristics can’t be passed to offspring Not goal directed Is not a perfect process Often trade-off of needs Editing, not a creative, mechanism EVOLUTIONARY EVIDENCE FOSSILS Record is relatively incomplete Soft tissues are rarely preserved Movement of the Earth’s crust covered or destroyed many fossils Fossils only formed in certain environments and habitats All the fossils haven’t been discovered yet Show differences in past and present organisms Document evolutionary changes Can test evolutionary hypotheses Radioactive dating HOMOLOGOUS STRUCTURES Similarity in structure due to common descent, but different functions Mammalian forelimbs = variations on a common theme ANALOGOUS STRUCTURES Similarity in structure based on adaptation for same function, but not common descent Convergent evolution, independent evolution of similar features VESTIGIAL STRUCTURES Remnants of features that were important in an organism’s ancestors EVOLUTIONARY TREE Reflects evolutionary relationships among groups of organisms Homologous structure pattern All tetrapods have 4 limbs, but ancestors don’t Branch points represent common ancestors that descended from it BIOGEOGRAPHY Geographic distribution of species Organisms evolved in one location and then spread Many species are endemic Oldest fossils at origin Galapagos finches Influenced by continental drift Pangea & today’s continents CONTINENTAL DRIFT & PLATE TECTONICS BIOCHEMICAL Protein comparison DNA comparison Universality of the genetic code