Optical Measurements
... A beam of monocromatic light is directed through a sample and the fluctuation of the intensity of scattered light by the molecules is analyzed by an Avalanche Photo Diode. The Avalanche Photo Diode then sends electrical pulses to the Digital Signal Processor which counts the number of photons detect ...
... A beam of monocromatic light is directed through a sample and the fluctuation of the intensity of scattered light by the molecules is analyzed by an Avalanche Photo Diode. The Avalanche Photo Diode then sends electrical pulses to the Digital Signal Processor which counts the number of photons detect ...
Creation of Colloidal Periodic Structure
... polarization along the x-direction. The incident light is assumed to be linearly polarized at an angle q with respect to the x-direction. ...
... polarization along the x-direction. The incident light is assumed to be linearly polarized at an angle q with respect to the x-direction. ...
Flanged Sample Compartment Flanged Beam Splitter Holder
... The 78150 Beam Splitter Mount holds a 2 inch (51 mm) square beam splitter, up to 0.25 inch (6 mm) thick, at a 45° angle. Since it can be coupled directly to Oriel light sources, monochromators, and detectors via the 1.5 Inch Series flanges, it is a convenient device for splitting a beam in an enclos ...
... The 78150 Beam Splitter Mount holds a 2 inch (51 mm) square beam splitter, up to 0.25 inch (6 mm) thick, at a 45° angle. Since it can be coupled directly to Oriel light sources, monochromators, and detectors via the 1.5 Inch Series flanges, it is a convenient device for splitting a beam in an enclos ...
Chapter 6:Electronic Structure of Atoms
... changed the quantum theory to explain how electrons are arranged in an atom. ...
... changed the quantum theory to explain how electrons are arranged in an atom. ...
Slide
... •Energy fluctuations make the geometry of space-time fluctuate. At a small enough size scale, the assumption of a smooth, continuous space and time breaks down. ...
... •Energy fluctuations make the geometry of space-time fluctuate. At a small enough size scale, the assumption of a smooth, continuous space and time breaks down. ...
Frank-Hertz experiment with Neon
... frequency as the orbit got smaller and faster. This would produce electromagnetic radiation with continuous spectrum. However, late 19th century experiments with electric discharges through various low-pressure gasses in evacuated glass tubes had shown that atoms will only emit light (that is, elect ...
... frequency as the orbit got smaller and faster. This would produce electromagnetic radiation with continuous spectrum. However, late 19th century experiments with electric discharges through various low-pressure gasses in evacuated glass tubes had shown that atoms will only emit light (that is, elect ...
SWIR (Short Wave Infrared) to Visible Image Up
... An up-conversion imaging layer, which converts infrared images into visible images. It is composed of a quantum dots or quantum columns detection layer that absorbs the infrared light, and the absorption is enhanced by surface plasmons. Holes and electrons generated by the incidental SWIR light are ...
... An up-conversion imaging layer, which converts infrared images into visible images. It is composed of a quantum dots or quantum columns detection layer that absorbs the infrared light, and the absorption is enhanced by surface plasmons. Holes and electrons generated by the incidental SWIR light are ...
Physics 30 - Structured Independent Learning
... The curves of light intensity Vs wavelength for different temperatures are called blackbody radiation curves. The term blackbody, introduced by the German physicist Gustav Kirchhoff in 1862, refers to an object that completely and perfectly absorbs any light energy that falls on it and then perfectl ...
... The curves of light intensity Vs wavelength for different temperatures are called blackbody radiation curves. The term blackbody, introduced by the German physicist Gustav Kirchhoff in 1862, refers to an object that completely and perfectly absorbs any light energy that falls on it and then perfectl ...
Group 2 - Index of
... micrometers), where most molecular absorption bands are. QCLs are the only semiconductor laser able to produce mid-IR wavelength beams at or above room temperature. Excellent for sensing trace gases: sensors based on QCL can have sensitivities in the range of parts per trillion Because QCLs can oper ...
... micrometers), where most molecular absorption bands are. QCLs are the only semiconductor laser able to produce mid-IR wavelength beams at or above room temperature. Excellent for sensing trace gases: sensors based on QCL can have sensitivities in the range of parts per trillion Because QCLs can oper ...
Total Reflection X-Ray Fluorescence Spectrometer
... available x-ray tubes only provide the necessary minimal intensity for this technique. The only really powerful x-ray sources which exist, synchrotron facilities, appear to be unsuitable for the majority of analytical application owing to their high cost and lack of availability. Another approach fo ...
... available x-ray tubes only provide the necessary minimal intensity for this technique. The only really powerful x-ray sources which exist, synchrotron facilities, appear to be unsuitable for the majority of analytical application owing to their high cost and lack of availability. Another approach fo ...
PHYSICS 113 Assignment #3 SOLUTIONS Chapter 4 19. How many
... 5. Compare the eye, photographic film, and CCD's as detectors of light. What are the advantages and disadvantages of each? EYE: While the eye was the first detector of starlight, it has been replaced by various detectors. Although the eye also us to “see” objects in the universe, it is very limited: ...
... 5. Compare the eye, photographic film, and CCD's as detectors of light. What are the advantages and disadvantages of each? EYE: While the eye was the first detector of starlight, it has been replaced by various detectors. Although the eye also us to “see” objects in the universe, it is very limited: ...
11 Applications III
... introduced in the last chapter to quantum models of solids and radiation. These applications are singularly important. Application: Simple Models of Solids A solid material was profitably viewed as an assembly of classical harmonic oscillators with a common frequency . Applying the equipartition th ...
... introduced in the last chapter to quantum models of solids and radiation. These applications are singularly important. Application: Simple Models of Solids A solid material was profitably viewed as an assembly of classical harmonic oscillators with a common frequency . Applying the equipartition th ...
Frank-Herze experiment with Neon
... with electric discharges through various low-pressure gasses in evacuated glass tubes had shown that atoms will only emit light (that is, electromagnetic radiation) at certain discrete frequencies. To overcome this difficulty, Niels Bohr proposed, in 1913, what is now called the Bohr model of the at ...
... with electric discharges through various low-pressure gasses in evacuated glass tubes had shown that atoms will only emit light (that is, electromagnetic radiation) at certain discrete frequencies. To overcome this difficulty, Niels Bohr proposed, in 1913, what is now called the Bohr model of the at ...
File
... the wave theory of light, but after the turn of the century more detailed study of this effect by Philipp Lenard showed that the speed of the ejected electro ns did not depend on the intensity of the light but its frequency. This could not be explained using Maxwell’s laws and a wave view of light. ...
... the wave theory of light, but after the turn of the century more detailed study of this effect by Philipp Lenard showed that the speed of the ejected electro ns did not depend on the intensity of the light but its frequency. This could not be explained using Maxwell’s laws and a wave view of light. ...
Ch 11 WS Orbitals and Electron Arrangement
... Three rules determine the electron arrangement in an atom: the aufbau principle, the Pauli exclusion principle, and Hund’s rule. ...
... Three rules determine the electron arrangement in an atom: the aufbau principle, the Pauli exclusion principle, and Hund’s rule. ...
Quantum-Mechanical Model of the Atom
... • He found an equaDon that fit the data. • This equaDon forced vibraDonal frequencies to be mulDples of a fundamental frequency instead of conDnuous. Energy is quan-zed! • He put in an adjustable p ...
... • He found an equaDon that fit the data. • This equaDon forced vibraDonal frequencies to be mulDples of a fundamental frequency instead of conDnuous. Energy is quan-zed! • He put in an adjustable p ...
Chemistry Notes
... I. The Chemistry of matter A. All matter in the universe is composed of atoms. B. Parts of an atom 1. Electron Shell – The outer part of an atom. This is where the electrons are found. a) Electrons – Negatively charged particles found in the electron shell. Electrons orbit the nucleus. 2. Nucleus – ...
... I. The Chemistry of matter A. All matter in the universe is composed of atoms. B. Parts of an atom 1. Electron Shell – The outer part of an atom. This is where the electrons are found. a) Electrons – Negatively charged particles found in the electron shell. Electrons orbit the nucleus. 2. Nucleus – ...
Chapter 7
... cloverleaves, and if most of the volume of an atom is empty space diffusely occupied by electrons in these orbitals, then why do we often depict atoms as spheres? • The shape of the atom (as spherical) is obtained by superimposing all of the orbitals it contains. Meaning laying each over top of the ...
... cloverleaves, and if most of the volume of an atom is empty space diffusely occupied by electrons in these orbitals, then why do we often depict atoms as spheres? • The shape of the atom (as spherical) is obtained by superimposing all of the orbitals it contains. Meaning laying each over top of the ...
The Nature of Molecules
... ***Inner energy shells (those closest to the nucleus) contain electrons with lower energy than the outer energy shells ***important concept as it will be discussed in the Light Dependent reaction of Photosynthesis ...
... ***Inner energy shells (those closest to the nucleus) contain electrons with lower energy than the outer energy shells ***important concept as it will be discussed in the Light Dependent reaction of Photosynthesis ...
Electrons and Photons
... bonding occurs, the constituent atoms are “free” to wander around. They are in an antibonding state. We could take silicon as an example. When two such free silicon atoms meet, they may bond together. They will do so because the bonding state is at a lower energy than what existed previously. The va ...
... bonding occurs, the constituent atoms are “free” to wander around. They are in an antibonding state. We could take silicon as an example. When two such free silicon atoms meet, they may bond together. They will do so because the bonding state is at a lower energy than what existed previously. The va ...
High Harmonic Generation
... 1. When the intensity high enough, electrons can tunnel through the barrier into the continuum. This is called first step. 2. The laser field accelerates the electron away from the parent ion and drives it back when the electric field sign is changed. During this process the electron gains kinetic e ...
... 1. When the intensity high enough, electrons can tunnel through the barrier into the continuum. This is called first step. 2. The laser field accelerates the electron away from the parent ion and drives it back when the electric field sign is changed. During this process the electron gains kinetic e ...
De Broglie waves
... were observed with their positions depending on the electron energy. • The Bragg equation for maxima in the diffraction pattern is: n 2d sin • In a particular case, a beam of 54eV electrons were directed perpendicularly at the nickel target and a sharp maximum in the electron distribution occur ...
... were observed with their positions depending on the electron energy. • The Bragg equation for maxima in the diffraction pattern is: n 2d sin • In a particular case, a beam of 54eV electrons were directed perpendicularly at the nickel target and a sharp maximum in the electron distribution occur ...
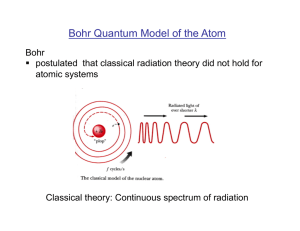
Bohr Quantum Model of the Atom
... § postulated that the electron orbital momentum is quantized Justification of Bohr’s postulates: comparison with experimental observations! ...
... § postulated that the electron orbital momentum is quantized Justification of Bohr’s postulates: comparison with experimental observations! ...
X-ray fluorescence

X-ray fluorescence (XRF) is the emission of characteristic ""secondary"" (or fluorescent) X-rays from a material that has been excited by bombarding with high-energy X-rays or gamma rays. The phenomenon is widely used for elemental analysis and chemical analysis, particularly in the investigation of metals, glass, ceramics and building materials, and for research in geochemistry, forensic science and archaeology.