CHAPTER 2: Experimental
... though the soller and receiving slits and then fall on a monochromator before detection. The monochromator separates out the stray wavelength radiation as well as any fluorescent radiation emitted by the sample. The details of the X-ray production and the typical X-ray spectra are explained in sever ...
... though the soller and receiving slits and then fall on a monochromator before detection. The monochromator separates out the stray wavelength radiation as well as any fluorescent radiation emitted by the sample. The details of the X-ray production and the typical X-ray spectra are explained in sever ...
What is LIGHT? Atomic Physics and
... Light has a dual nature. At times, it behaves as a wave and at times it behaves as a particle. It can never be both simultaneously. This is the WaveParticle Duality of Light. ...
... Light has a dual nature. At times, it behaves as a wave and at times it behaves as a particle. It can never be both simultaneously. This is the WaveParticle Duality of Light. ...
Scanning transmission soft x-ray microscopy at beamline X
... assessment analysis. Iron oxides/-hydroxides are the principal corrosion products of the stainless steel canister material and commonly the dominant sorption surface in the geological host rock formation (grain coatings). During the transformation of the metastable low crystalline precursor phase hy ...
... assessment analysis. Iron oxides/-hydroxides are the principal corrosion products of the stainless steel canister material and commonly the dominant sorption surface in the geological host rock formation (grain coatings). During the transformation of the metastable low crystalline precursor phase hy ...
Lecture 23
... power fed into it, and can therefore respond with a more powerful signal. The key point is that the amplifier must be able to convert the input power into the frequency determined by the signal. This is usually done using some kind of feedback. Lasers work according to the same sort of idea. The ide ...
... power fed into it, and can therefore respond with a more powerful signal. The key point is that the amplifier must be able to convert the input power into the frequency determined by the signal. This is usually done using some kind of feedback. Lasers work according to the same sort of idea. The ide ...
The Chemical Basis of Life
... Anything that occupies space. Composed of one or more chemical elements. ...
... Anything that occupies space. Composed of one or more chemical elements. ...
Chemistry 1. The amino acid, alanine, dissolves in water. In an
... A. A zinc lamp should be used and the intensity of the light will be greater after passing through the sample in the flame. B. A zinc lamp should be used and the intensity of the light will reduce after passing through the sample in the flame. C. A copper lamp should be used and the intensity of the ...
... A. A zinc lamp should be used and the intensity of the light will be greater after passing through the sample in the flame. B. A zinc lamp should be used and the intensity of the light will reduce after passing through the sample in the flame. C. A copper lamp should be used and the intensity of the ...
ExamView - Untitled.tst
... b. solubility in water d. color 6. Which of the following is an example of a physical change? a. dissolving salt in water c. burning wood into charcoal b. cooking an egg d. rusting iron 7. The change of a substance from a solid directly to a gas is called a. condensation. c. melting. b. evaporation. ...
... b. solubility in water d. color 6. Which of the following is an example of a physical change? a. dissolving salt in water c. burning wood into charcoal b. cooking an egg d. rusting iron 7. The change of a substance from a solid directly to a gas is called a. condensation. c. melting. b. evaporation. ...
1.3.6 Electromagnetic radiation Name Symbol Definition SI
... The radiance is a normalized measure of the brightness of a source; it is the power emitted per area of source, per solid angle of the beam from each point of the source. ...
... The radiance is a normalized measure of the brightness of a source; it is the power emitted per area of source, per solid angle of the beam from each point of the source. ...
AC Circuits
... function of the wavelength of the light. Because optical absorption in the visible and near-UV portions of the spectrum is generally the result of absorption of light by electrons in atoms, ions or molecules, the absorption characteristics can yield a considerable amount of information regarding the ...
... function of the wavelength of the light. Because optical absorption in the visible and near-UV portions of the spectrum is generally the result of absorption of light by electrons in atoms, ions or molecules, the absorption characteristics can yield a considerable amount of information regarding the ...
Review Sheet Filled Out
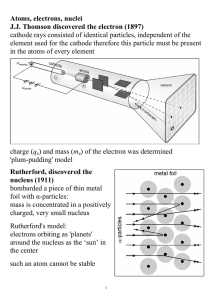
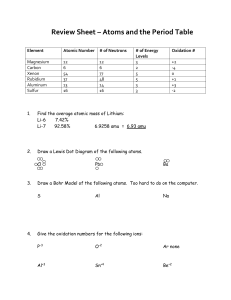
... List the number of facts you know about electrons. Electrons closest to the nucleus have the least amount of energy Electrons farthest away from the nucleus have the most energy – valence e Have a negative charge Have insignificant mass and volume Reside in the 99.996% of the atom outside t ...
... List the number of facts you know about electrons. Electrons closest to the nucleus have the least amount of energy Electrons farthest away from the nucleus have the most energy – valence e Have a negative charge Have insignificant mass and volume Reside in the 99.996% of the atom outside t ...
File - GENERAL DEPARTMENT
... other inelastic collision. The atom has now become an excited atom. A short time later, the atom will move itself to its ground state, emitting a photon of energy hf. We call this process spontaneous emission – spontaneous because the event was not triggered by any outside influence. The direction a ...
... other inelastic collision. The atom has now become an excited atom. A short time later, the atom will move itself to its ground state, emitting a photon of energy hf. We call this process spontaneous emission – spontaneous because the event was not triggered by any outside influence. The direction a ...
Lesson01
... E=119625/l kJ mol-1 or 1239.8/ l eV • To get enough energy to break up a molecule (dissociation) the wavelength must be in or below the ultraviolet. Thus dissociation typically occurs as the result of electronic transitions • Small, light chemical species generally have electronic transitions at wav ...
... E=119625/l kJ mol-1 or 1239.8/ l eV • To get enough energy to break up a molecule (dissociation) the wavelength must be in or below the ultraviolet. Thus dissociation typically occurs as the result of electronic transitions • Small, light chemical species generally have electronic transitions at wav ...
Hwk Set #14 - Publisher`s solutions
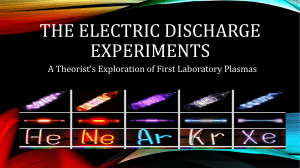
... The red-orange colors in the neon emission spectrum are due to transitions from excited 3p states to the lower energy but still excited 3s states. This occurs because the ground states are collisionally excited by the electrical discharge. The absorption spectrum of a gas consists of only those spec ...
... The red-orange colors in the neon emission spectrum are due to transitions from excited 3p states to the lower energy but still excited 3s states. This occurs because the ground states are collisionally excited by the electrical discharge. The absorption spectrum of a gas consists of only those spec ...
Lecture notes lecture 13 (quantum physics)
... Quantum physics even describes the particles which make these particles! (The model of an atom that you were taught in high-school is a approximation). The electrons don't orbit like planets; they form blurred clouds of probabilities around the nucleus. Protons and neutrons? They're each made of thr ...
... Quantum physics even describes the particles which make these particles! (The model of an atom that you were taught in high-school is a approximation). The electrons don't orbit like planets; they form blurred clouds of probabilities around the nucleus. Protons and neutrons? They're each made of thr ...
n = 2. - Cloudfront.net
... calculation of the Rydberg constant. Bohr’s theory’s major accomplishment was the agreement between the theoretical and experimental values of the Rydberg constant. ...
... calculation of the Rydberg constant. Bohr’s theory’s major accomplishment was the agreement between the theoretical and experimental values of the Rydberg constant. ...
URL - StealthSkater
... creates this oscillation going backand-forth like a laser beam, which aligns all these different particles and things together so it acts like one "Big particle". Now on the surface of our ship we know that if we have electrons at a certain distance one from another, then their energy fields will be ...
... creates this oscillation going backand-forth like a laser beam, which aligns all these different particles and things together so it acts like one "Big particle". Now on the surface of our ship we know that if we have electrons at a certain distance one from another, then their energy fields will be ...
Study Guide Answers
... 1. A change of state is a _c__ a. Process by which two states of matter co-exist b. Chemical change c. Physical change that converts a substance from one physical form to another 2. Particles in a ___solid_______ move slower than particles in a ____liquid or gas______. 3. Particles in a _a__ vibrate ...
... 1. A change of state is a _c__ a. Process by which two states of matter co-exist b. Chemical change c. Physical change that converts a substance from one physical form to another 2. Particles in a ___solid_______ move slower than particles in a ____liquid or gas______. 3. Particles in a _a__ vibrate ...
Light - UDChemistry
... • “In-between” orbitals would require a fractional number of wavelengths. “I think it is safe to say that no one understands quantum mechanics.” Physicist Richard P. Feynman ...
... • “In-between” orbitals would require a fractional number of wavelengths. “I think it is safe to say that no one understands quantum mechanics.” Physicist Richard P. Feynman ...
3-CProvencher
... [Atkins et all, 2009] → Atkins, Paula, and Friedman, Quanta, Matter, and Change, Oxford University Press, 2009. [AZoOptics, 2012] → Monitoring Argon Plasma Emission with High Resolution Spectroscopy, AZo Optics, 2012. ...
... [Atkins et all, 2009] → Atkins, Paula, and Friedman, Quanta, Matter, and Change, Oxford University Press, 2009. [AZoOptics, 2012] → Monitoring Argon Plasma Emission with High Resolution Spectroscopy, AZo Optics, 2012. ...
Franck-Hertz experiment with Ne-tube Related Topics
... Theory and evaluation Niels Bohr introduced the planetary model of the atom in 1913: An isolated atom consists of a positively charged nucleus about which electrons are distributed in successive orbits. He also postulated that only those orbits occur for which the angular momentum of the electron is ...
... Theory and evaluation Niels Bohr introduced the planetary model of the atom in 1913: An isolated atom consists of a positively charged nucleus about which electrons are distributed in successive orbits. He also postulated that only those orbits occur for which the angular momentum of the electron is ...
X-ray fluorescence

X-ray fluorescence (XRF) is the emission of characteristic ""secondary"" (or fluorescent) X-rays from a material that has been excited by bombarding with high-energy X-rays or gamma rays. The phenomenon is widely used for elemental analysis and chemical analysis, particularly in the investigation of metals, glass, ceramics and building materials, and for research in geochemistry, forensic science and archaeology.