* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ch 11 WS Orbitals and Electron Arrangement
Matter wave wikipedia , lookup
Bremsstrahlung wikipedia , lookup
Density functional theory wikipedia , lookup
History of quantum field theory wikipedia , lookup
EPR paradox wikipedia , lookup
Renormalization wikipedia , lookup
Molecular Hamiltonian wikipedia , lookup
Ferromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
X-ray fluorescence wikipedia , lookup
Particle in a box wikipedia , lookup
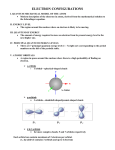
Wave–particle duality wikipedia , lookup
Chemical bond wikipedia , lookup
Rutherford backscattering spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Molecular orbital wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
Auger electron spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Quantum electrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Tight binding wikipedia , lookup
Electron scattering wikipedia , lookup
Hydrogen atom wikipedia , lookup
Electron-beam lithography wikipedia , lookup
Atomic theory wikipedia , lookup
Name Class Date Chemistry Chapter 11 Electron Arrangement Electrons in Atoms 1. Is the following sentence true or false? The electrons in an atom can exist between energy levels. 2. What are the fixed energies of electrons called? 3. Circle the letter of the term that completes the sentence correctly. A quantum of energy is the amount of energy required to a. move an electron from its present energy level to the next lower level b. maintain an electron in its present energy level. c. move an electron from its present energy level to a higher one. 4. In general, the higher the electron is on the energy ladder, the it is from the nucleus. The Quantum Mechanical Model 5. What is the difference between the previous models of the atom and the modern quantum mechanical model? 6. Is the following sentence true or false? The quantum mechanical model of the atom estimates the probability of finding an electron in a certain position. Atomic Orbitals 7. A(n) is often thought of as a region of space in which there is a high probability of finding an electron. 8. Circle the letter of the term that is used to label the energy levels of electrons. a. atomic orbitals c. quantum b. quantum mechanical numbers d. principal quantum numbers (n) 9. Principal energy levels are assigned values in order of ______________________ energy: n = 1, 2, 3, 4, and so forth. 10. In the quantum mechanical model the regions where electrons are likely to be found are called ______________________ and are denoted by______________________ . 11. The letter is used to denote a spherical orbital. 12. Label each diagram below px, py, or pz. ___________ ___________ ___________ 13. Use the diagram above. Describe how the px, py, and pz orbitals are similar. 14. Circle the letter of the formula for the maximum number of electrons that can occupy a principal energy level. Use n for the principal quantum number. a. 2n2 b. n2 c. 2n d. n 11.7 Electron Arrangement in Atoms Essential Understanding Three rules determine the electron arrangement in an atom: the aufbau principle, the Pauli exclusion principle, and Hund’s rule. Electron Configurations 1. The ways in which electrons are arranged into orbitals around the nuclei of atoms are called . Match the name of the rule used to find the electron configurations of atoms with the rule itself. 2. aufbau principle 3. Pauli exclusion principle 4. Hund’s rule a. When electrons occupy orbitals of equal energy, one electron enters each orbital until all the orbitals contain one electron with the same spin direction. b. Electrons occupy orbitals of lowest energy first. c. An atomic orbital may describe at most two electrons.