Models of Light Student Worksheet
... glucose which moves to wherever glucose is being used. The tracer emits a positron (the antimatter equivalent of an electron) which annihilates when it meets an electron. The mass of the particles is turned into the energy of two photons. These move off in opposite directions to conserve momentum. T ...
... glucose which moves to wherever glucose is being used. The tracer emits a positron (the antimatter equivalent of an electron) which annihilates when it meets an electron. The mass of the particles is turned into the energy of two photons. These move off in opposite directions to conserve momentum. T ...
Learning Goals
... 2) You will: see quantum mechanics as the most fascinating physics you have encountered, and see it as a way to understand the world at a level you never imagined possible; recognize and be able to describe how quantum mechanics is visible in the world all around you; recognize that physics required ...
... 2) You will: see quantum mechanics as the most fascinating physics you have encountered, and see it as a way to understand the world at a level you never imagined possible; recognize and be able to describe how quantum mechanics is visible in the world all around you; recognize that physics required ...
Chapter 13 – Electrons in Atoms
... Atoms/elements emit light when the electrons are excited (first absorb then emit energy in the form of light) at specific frequencies. ...
... Atoms/elements emit light when the electrons are excited (first absorb then emit energy in the form of light) at specific frequencies. ...
Liad Elmelech 7.1-7.3 The Nature of Light, Atomic Spectroscopy
... • Low frequency light does not eject electrons because no single photon has enough energy to dislodge • Energy of a photon that is beyond what is needed to dislodge an electron is transferred to the electron in the form of kinetic energy • KE = hv – φ ...
... • Low frequency light does not eject electrons because no single photon has enough energy to dislodge • Energy of a photon that is beyond what is needed to dislodge an electron is transferred to the electron in the form of kinetic energy • KE = hv – φ ...
<< Previous
... different this time because electrons are fermions - and therefore obey the Pauli exclusion principle - whereas photons are bosons and do not. Credit where it's due So why are Jönsson, Tonomura and the other pioneers of the double-slit experiment not well known? One obvious reason is that Jönsson's ...
... different this time because electrons are fermions - and therefore obey the Pauli exclusion principle - whereas photons are bosons and do not. Credit where it's due So why are Jönsson, Tonomura and the other pioneers of the double-slit experiment not well known? One obvious reason is that Jönsson's ...
teacher`s notes
... squeeze the pencils closer and closer. Give the students time to explore by looking through their slits at a laser spot on the wall. Afterwards, point the beam through two pencils so that everyone is looking at exactly the same pattern. Use clamps to hold everything steady and to apply pressure to t ...
... squeeze the pencils closer and closer. Give the students time to explore by looking through their slits at a laser spot on the wall. Afterwards, point the beam through two pencils so that everyone is looking at exactly the same pattern. Use clamps to hold everything steady and to apply pressure to t ...
quantum1
... Newtonian Mechanics, however, we know that a large number of events will behave in a statistically predictable way. probability for an electron to be found between x and x+dx ...
... Newtonian Mechanics, however, we know that a large number of events will behave in a statistically predictable way. probability for an electron to be found between x and x+dx ...
Physics 120 Homework Set #1 (due Sunday
... in the experimental techniques. Rather, it signifies that an electron which is located at a precise position in space, does not posses any particular value of momentum; conversely an electron with a precise value of momentum is not located in any specific position, but can be found anywhere with equ ...
... in the experimental techniques. Rather, it signifies that an electron which is located at a precise position in space, does not posses any particular value of momentum; conversely an electron with a precise value of momentum is not located in any specific position, but can be found anywhere with equ ...
The Particulate Nature of Light
... nh/2 demonstrates that the angular momentum is a multiple of h/2 as Bohr had previously postulated. ...
... nh/2 demonstrates that the angular momentum is a multiple of h/2 as Bohr had previously postulated. ...
quantum theory. Schrödinger equation
... 1. Louis de Broglie hypothesized that electrons have wavelike properties. Other investigators verified his theory by proving that electrons can be bent or diffracted. In his 1924 PhD thesis he postulated the wave nature of electrons and suggested that all matter has wave properties. This concept is ...
... 1. Louis de Broglie hypothesized that electrons have wavelike properties. Other investigators verified his theory by proving that electrons can be bent or diffracted. In his 1924 PhD thesis he postulated the wave nature of electrons and suggested that all matter has wave properties. This concept is ...
Commentary - Absurd Being
... even if the particles are fired so slowly that they are passing through the slits just one at a time. This ...
... even if the particles are fired so slowly that they are passing through the slits just one at a time. This ...
Chp.23 Outline - Redlands High School
... value? Give some examples of other quantum values besides the photon. Write the equation relating the frequency of a photon to its energy. Does a photon fit better in the particle or wave nature of light? What does an electron volt measure? How many Joules are in an electron volt? 2) What is a black ...
... value? Give some examples of other quantum values besides the photon. Write the equation relating the frequency of a photon to its energy. Does a photon fit better in the particle or wave nature of light? What does an electron volt measure? How many Joules are in an electron volt? 2) What is a black ...
Learning station IV: Wave Particle Duality
... The wave-particle duality and the probability is treated in Quantum Field Theory as a foundation of new physics where matter and light have symmetric properties. In the modern view of quantum field theory even forces (with remote action, remember) are seen as the result of the exchange of quanta bet ...
... The wave-particle duality and the probability is treated in Quantum Field Theory as a foundation of new physics where matter and light have symmetric properties. In the modern view of quantum field theory even forces (with remote action, remember) are seen as the result of the exchange of quanta bet ...
Heisenberg microscope and which-way experiments
... experiment. It is one of the most important experiments of wave theory and a clear example of the diffraction of light conducted with essentially basic scientific equipment. The double-slit experiment consists of letting light diffract through two slits producing fringes on a screen. These fringes o ...
... experiment. It is one of the most important experiments of wave theory and a clear example of the diffraction of light conducted with essentially basic scientific equipment. The double-slit experiment consists of letting light diffract through two slits producing fringes on a screen. These fringes o ...
The Dual Nature of the Electron
... Contrary to Feynman’s conjecture, the experimental results of the double-slit interferometer experiment can be explained in a classical way. The electron is a classical electromagnetic object, not a quantum object. Gauss’s classical law of electric fields recognizes that the distribution of charge i ...
... Contrary to Feynman’s conjecture, the experimental results of the double-slit interferometer experiment can be explained in a classical way. The electron is a classical electromagnetic object, not a quantum object. Gauss’s classical law of electric fields recognizes that the distribution of charge i ...
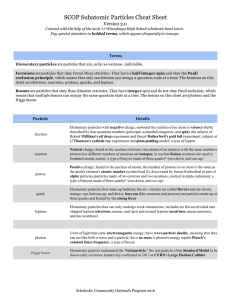
SCOP Subatomic Particles Cheat Sheet
... Fermions are particles that obey FermiDirac statistics. They have a halfinteger spin and obey the Pauli exclusion principle , which means that only one fermion can occupy a quantum state at a time. The fermions on this sheet are ...
... Fermions are particles that obey FermiDirac statistics. They have a halfinteger spin and obey the Pauli exclusion principle , which means that only one fermion can occupy a quantum state at a time. The fermions on this sheet are ...
Quantum Mechanics
... If we try to find out which slit the particle goes through the interference pattern vanishes! We cannot see the wave/particle nature at the same time. time. If we know which path the particle takes, we lose the fringes . ...
... If we try to find out which slit the particle goes through the interference pattern vanishes! We cannot see the wave/particle nature at the same time. time. If we know which path the particle takes, we lose the fringes . ...