“SUPERPOSITION” “interference term”
... In simplest (“BCS”) theory, Cooper pairs, once formed, must automatically ...
... In simplest (“BCS”) theory, Cooper pairs, once formed, must automatically ...
7.2.4. Normal Ordering
... photon a particle as well as anti-particle, the net number of “particles” is always conserved as long as the total number of photons present is always odd (or even). In other words, the number of photons is not conserved. Note that this is necessarily the case if photons are to be interpreted as qua ...
... photon a particle as well as anti-particle, the net number of “particles” is always conserved as long as the total number of photons present is always odd (or even). In other words, the number of photons is not conserved. Note that this is necessarily the case if photons are to be interpreted as qua ...
Document
... • Electron energy depends on frequency, not intensity. • Electrons are not ejected for frequencies below f0. • Electrons have a probability to be emitted immediately. Conclusions: • Light arrives in “packets” of energy (photons). • Ephoton = hf ← We will see that this is valid for all objects. It is ...
... • Electron energy depends on frequency, not intensity. • Electrons are not ejected for frequencies below f0. • Electrons have a probability to be emitted immediately. Conclusions: • Light arrives in “packets” of energy (photons). • Ephoton = hf ← We will see that this is valid for all objects. It is ...
Chapt25_VGO
... electrons scatter from the surface of metals. • They found that electrons incident normal to the crystal face at a speed of 4.35 106 m/s scattered at ø = 50°. • This scattering can be interpreted as a mirror-like reflection from the atomic planes that slice diagonally through the crystal. • The an ...
... electrons scatter from the surface of metals. • They found that electrons incident normal to the crystal face at a speed of 4.35 106 m/s scattered at ø = 50°. • This scattering can be interpreted as a mirror-like reflection from the atomic planes that slice diagonally through the crystal. • The an ...
PHY112-‐Spring 14, Worksheet 4
... c. have the biggest radius. d. have the greatest angular momentum. ...
... c. have the biggest radius. d. have the greatest angular momentum. ...
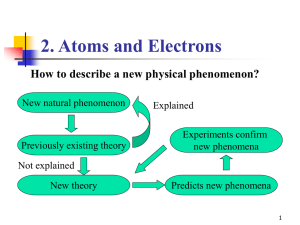
Quantum Mechanics
... ULTIMATE REALITY? Quantum fields fill all space; one field for each kind of particle. Particles are just localized bunches of energy carried by the fields. Particles can appear and disappear spontaneously from the fields. Perhaps the universe appeared in just this way. ...
... ULTIMATE REALITY? Quantum fields fill all space; one field for each kind of particle. Particles are just localized bunches of energy carried by the fields. Particles can appear and disappear spontaneously from the fields. Perhaps the universe appeared in just this way. ...
WAVE MECHANICS AND QUANTUM NUMBERS
... 1 being closest to the nucleus. Most general quantum number. b. angular momentum/orbital (l)- indicates the shape of the electron path; defined by values n – 1 for orbital within the energy level, so Set = (0, 1, 2, 3) corresponding to orbital shapes (s, p, d, f) The determines the possible shapes f ...
... 1 being closest to the nucleus. Most general quantum number. b. angular momentum/orbital (l)- indicates the shape of the electron path; defined by values n – 1 for orbital within the energy level, so Set = (0, 1, 2, 3) corresponding to orbital shapes (s, p, d, f) The determines the possible shapes f ...
CHAPTER 3: The Experimental Basis of Quantum
... Electrons have much smaller wavelengths, and electron microscopes can achieve resolutions of ~0.05nm. ...
... Electrons have much smaller wavelengths, and electron microscopes can achieve resolutions of ~0.05nm. ...
Announcements
... A series of bright and dark fringes appears on the screen. Bright for constructive interference and dark for destructive interference. The same pattern appears even if you cut down the light intensity so that only one photon goes through at a time. But the photon has to go through either the top sli ...
... A series of bright and dark fringes appears on the screen. Bright for constructive interference and dark for destructive interference. The same pattern appears even if you cut down the light intensity so that only one photon goes through at a time. But the photon has to go through either the top sli ...
1. Crystal Properties and Growth of Semiconductors
... Shortest Course in Quantum Mechanics, Cont. Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle (Nobel prize 1932 for the creation of quantum mechanics) The more precise you know the position of a particle , the less precise you know the momentum of the ...
... Shortest Course in Quantum Mechanics, Cont. Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle (Nobel prize 1932 for the creation of quantum mechanics) The more precise you know the position of a particle , the less precise you know the momentum of the ...
Quantum Theory of Atoms and Molecules
... travelling waves, transverse waves, longitudinal waves; the wave equation. ...
... travelling waves, transverse waves, longitudinal waves; the wave equation. ...
B E , 2012
... b) Derive an expression for the intensity at a point in the region of interference due to superposition of two sinusoidal waves with nearly equal amplitudes. Show graphically the intensity ...
... b) Derive an expression for the intensity at a point in the region of interference due to superposition of two sinusoidal waves with nearly equal amplitudes. Show graphically the intensity ...
correctly
... So matter contains electrons and light can be emitted in “chunks”… so what does this tell us about atoms?? Possible models of the atom ...
... So matter contains electrons and light can be emitted in “chunks”… so what does this tell us about atoms?? Possible models of the atom ...
Exam 3 review problems from the course text, Serway and Jewett
... 36.26 Images formed by refraction ...
... 36.26 Images formed by refraction ...
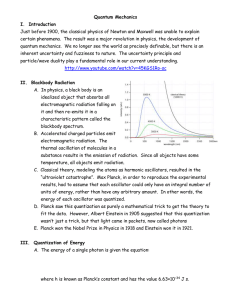
Quantum Mechanics I. Introduction Just before 1900, the classical
... C. Classical theory, modeling the atoms as harmonic oscillators, resulted in the “ultraviolet catastrophe”. Max Planck, in order to reproduce the experimental results, had to assume that each oscillator could only have an integral number of units of energy, rather than have any arbitrary amount. In ...
... C. Classical theory, modeling the atoms as harmonic oscillators, resulted in the “ultraviolet catastrophe”. Max Planck, in order to reproduce the experimental results, had to assume that each oscillator could only have an integral number of units of energy, rather than have any arbitrary amount. In ...
TPH101/201 - Btech GEU
... phenomenon like interference, diffraction, polarization and their applications. They will get knowledge how a laser light is emitted and the application of laser in technology. The students will understand the basic principle about recording and reconstruction of hologram. They also have the basic i ...
... phenomenon like interference, diffraction, polarization and their applications. They will get knowledge how a laser light is emitted and the application of laser in technology. The students will understand the basic principle about recording and reconstruction of hologram. They also have the basic i ...
The Quantum-Mechanical Model of the Atom
... • The wave characteristics of matter were clearly included and defined. • The energies were correctly determined; these were the same as the Bohr model but on a much firmer footing. • Other things such as the angular momentum of the electron orbits naturally emerged from the solution. ...
... • The wave characteristics of matter were clearly included and defined. • The energies were correctly determined; these were the same as the Bohr model but on a much firmer footing. • Other things such as the angular momentum of the electron orbits naturally emerged from the solution. ...
Problem set 5
... 5. Find the matrix elements of the spin-orbit interaction between coupled basis states h j m j l s | f (r)~L · S~ | j0 m j 0 l0 s0 i where f (r) is a function of the radial coordinate r = ...
... 5. Find the matrix elements of the spin-orbit interaction between coupled basis states h j m j l s | f (r)~L · S~ | j0 m j 0 l0 s0 i where f (r) is a function of the radial coordinate r = ...