Lec-22_Strachan
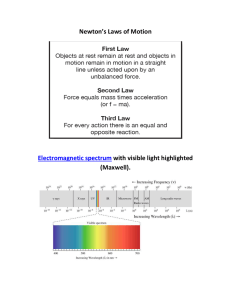
... The cutoff wavelength is related to the work function hc lc f Wavelengths greater than lC incident on a material with a work function f don’t result in the emission of photoelectrons ...
... The cutoff wavelength is related to the work function hc lc f Wavelengths greater than lC incident on a material with a work function f don’t result in the emission of photoelectrons ...
Physical Chemistry
... • (1) Atoms can exist in stable “states” without radiating. The states have discrete energies En, n= 1, 2, 3,..., where n= 1 is the lowest energy state (the most negative, relative to the dissociated atom at zero energy), n= 2 is the next lowest energy state, etc. The number “n” is an integer, a qua ...
... • (1) Atoms can exist in stable “states” without radiating. The states have discrete energies En, n= 1, 2, 3,..., where n= 1 is the lowest energy state (the most negative, relative to the dissociated atom at zero energy), n= 2 is the next lowest energy state, etc. The number “n” is an integer, a qua ...
The Relativistic Quantum World
... of an experiment and is non-deterministic, contrary to classical theory. ...
... of an experiment and is non-deterministic, contrary to classical theory. ...
Experiments in “Quantum Erasure” and “Delayed
... particle at a time, still builds a double-slit diffraction pattern over time! Particle size does not span both slits. ...
... particle at a time, still builds a double-slit diffraction pattern over time! Particle size does not span both slits. ...
poster
... Matter-Wave (MW): Each electron passes through both slits, interferes with itself, and then collapses to a point upon detection. Copenhagen/Agnostic (C/A): Electrons are modeled in terms of waves or particles accordingly; emphasis on mathematical calculation (predicting features of the interference ...
... Matter-Wave (MW): Each electron passes through both slits, interferes with itself, and then collapses to a point upon detection. Copenhagen/Agnostic (C/A): Electrons are modeled in terms of waves or particles accordingly; emphasis on mathematical calculation (predicting features of the interference ...
Ch. 5.3 study guide
... Classify each of these statements as always true, AT; sometimes true, ST; or never true, NT. 8. The speed of light is a constant that can be obtained by dividing the frequency of light by its wavelength. 9. The amplitude of a wave is the distance between the crests. 10. The energy of a body can chan ...
... Classify each of these statements as always true, AT; sometimes true, ST; or never true, NT. 8. The speed of light is a constant that can be obtained by dividing the frequency of light by its wavelength. 9. The amplitude of a wave is the distance between the crests. 10. The energy of a body can chan ...
Concepts introduced by the theories of relativity include
... measurement of the other value. This theory became known as the uncertainty principle, which prompted Albert Einstein's famous comment, "God does not play dice." ...
... measurement of the other value. This theory became known as the uncertainty principle, which prompted Albert Einstein's famous comment, "God does not play dice." ...
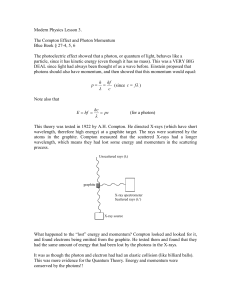
Modern Physics Lesson 3
... This can obviously only be used for objects with mass (i.e., NOT photons). It is usually used for electrons and protons, since they are the only objects that display noticeable wave-like properties. Normal sized objects (like a book or a basketball) also have a deBroglie wavelength, but it is so sma ...
... This can obviously only be used for objects with mass (i.e., NOT photons). It is usually used for electrons and protons, since they are the only objects that display noticeable wave-like properties. Normal sized objects (like a book or a basketball) also have a deBroglie wavelength, but it is so sma ...
Questions and Answers - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... 1. What happens to the interference patterns created in the electron double-slit experiment when detectors are used to determine which slit an electron is passing through? How do researchers explain this? 2. When the electrons are observed, what interpretations do researchers suggest causes the elec ...
... 1. What happens to the interference patterns created in the electron double-slit experiment when detectors are used to determine which slit an electron is passing through? How do researchers explain this? 2. When the electrons are observed, what interpretations do researchers suggest causes the elec ...
Schrödinger`s `Cat-in-the-Box Experiment
... Many students that are going into physics major as a master degree might not have the basis of Quantum theory. I recommend students pursuing physics as major to consider reading my paper to get a heads up of what they will be progressively learning from entering physics courses through to their mast ...
... Many students that are going into physics major as a master degree might not have the basis of Quantum theory. I recommend students pursuing physics as major to consider reading my paper to get a heads up of what they will be progressively learning from entering physics courses through to their mast ...
A Plausible Explanation of the double-slit Experiment in
... Abstract: A plausible non-Quantum Mechanical explanation to the double-slit experiment is considered. This is based on the view that globally energy propagates continuously as a wave while locally energy is manifested (measured or observed) in discrete units. The 1989 Tonomura 'single electron emiss ...
... Abstract: A plausible non-Quantum Mechanical explanation to the double-slit experiment is considered. This is based on the view that globally energy propagates continuously as a wave while locally energy is manifested (measured or observed) in discrete units. The 1989 Tonomura 'single electron emiss ...
Handout
... Electron spin and entanglement Electrons have spin 12 and therefore can be spinning up or down (|+i or |−i). We say a state made of more than one particle is entangled if the state is not a trivial product state: | + +i is not entangled, as each particle is spin up regardless of the other. The state ...
... Electron spin and entanglement Electrons have spin 12 and therefore can be spinning up or down (|+i or |−i). We say a state made of more than one particle is entangled if the state is not a trivial product state: | + +i is not entangled, as each particle is spin up regardless of the other. The state ...
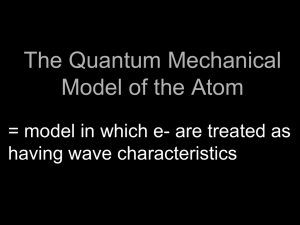
The Quantum Mechanical Model of the Atom
... An atomic orbital can be visualized as a fuzzy cloud where the electron is most likely to be at a given energy level ...
... An atomic orbital can be visualized as a fuzzy cloud where the electron is most likely to be at a given energy level ...








![introduction [Kompatibilitätsmodus]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/017596641_1-03cad833ad630350a78c42d7d7aa10e3-300x300.png)