* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Questions and Answers - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
Bremsstrahlung wikipedia , lookup
Particle in a box wikipedia , lookup
Atomic orbital wikipedia , lookup
Molecular Hamiltonian wikipedia , lookup
Quantum electrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Bohr–Einstein debates wikipedia , lookup
Matter wave wikipedia , lookup
Wheeler's delayed choice experiment wikipedia , lookup
Auger electron spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Ultrafast laser spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Rutherford backscattering spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Atomic theory wikipedia , lookup
Electron configuration wikipedia , lookup
Delayed choice quantum eraser wikipedia , lookup
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
X-ray fluorescence wikipedia , lookup
Wave–particle duality wikipedia , lookup
Double-slit experiment wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
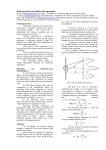
Quantum Physics – The Double-Slit Experiment 1. What happens to the interference patterns created in the electron double-slit experiment when detectors are used to determine which slit an electron is passing through? How do researchers explain this? 2. When the electrons are observed, what interpretations do researchers suggest causes the electrons to travel the way they do? Which interpretation do you think is true and why? Quantum Physics – The Photoelectric Effect 1. Which of the coloured lights (red, orange, blue) on a Christmas tree emits photons with the most and least energy? Explain. 2. Does your stove emit energy when the burner is not turned on? Explain. 3. A single photon is ejected from a light source with a frequency of 2.0 x 1014 Hz. How much energy does it possess? 4. What is the maximum kinetic energy of a photoelectron that has been liberated from a platinum metal surface by a photon that has a frequency of 3.13 x 1015 Hz? 5. The maximum kinetic energy of electrons emitted form a metal surface is 3.65 x 10-19 J when photons with a frequency of 1.25 x 10 15 Hz strike the surface. What is the most likely type of metal surface that the photons are striking? Quantum Physics – The Double-Slit Experiment 1. What happens to the interference patterns created in the electron double-slit experiment when detectors are used to determine which slit an electron is passing through? How do researchers explain this? 2. When the electrons are observed, what interpretations do researchers suggest causes the electrons to travel the way they do? Which interpretation do you think is true and why? Quantum Physics – The Photoelectric Effect 1. Which of the coloured lights (red, orange, blue) on a Christmas tree emits photons with the most and least energy? Explain. 2. Does your stove emit energy when the burner is not turned on? Explain. 3. A single photon is ejected from a light source with a frequency of 2.0 x 1014 Hz. How much energy does it possess? 4. What is the maximum kinetic energy of a photoelectron that has been liberated from a platinum metal surface by a photon that has a frequency of 3.13 x 1015 Hz? 5. The maximum kinetic energy of electrons emitted form a metal surface is 3.65 x 10-19 J when photons with a frequency of 1.25 x 10 15 Hz strike the surface. What is the most likely type of metal surface that the photons are striking? Answers: Double Slit 1. The interference pattern goes away once it is observed. The electrons act like particles instead of waves, as previously seen. Researchers suggest that the observation disturbs the electrons and changes the “reality”. 2. Interpretations: Collapse (electron wave collapses to a particle), Many Worlds (electrons choose one slit to go through but there is another world where the electron chooses another slit to go through), Copenhagen (smoke and mirrorsdon’t worry about what happens between the slits and the screen just worry about the math!), Pilot Wave (the electron particle follows an invisible wave “path”). Photoelectric Effect 1. The red light has less energy and a smaller frequency according to the visible light spectrum. The green light has more energy than red but less than blue. Blue would be the “hottest” or have the most energy. 2. The stove emits energy but not enough for the radiation to be visible to us. Not on the visible spectrum. When it is turned on it turns red, the lowest energy light that we can see. 3. E = hf E = (6.626*10-34)(2.0 x 1014) E = 1.3 x 10-19 J 4. What is the maximum kinetic energy of a photoelectron that has been liberated from a silver metal surface by a photon that has a frequency of 3.13 x 1015 Hz? Change eV to J: 1.60 x 10 -19 5.65eV 1eV J 9.04 x10 19 E k (max) hf W E k (max) 6.625 x10 34 (3.13x1015 ) 9.04 x10 19 E k (max) 2.0736 x10 18 9.04 x10 19 E k (max) 1.17 x10 18 J 5. 2.90 eV so Lithium