Prof. Dr. Klaus Hornberger Universitat Duisburg
... Does the quantum superposition principle hold on mesoscopic or even macroscopic scales? The tremendous success of quantum theory notwithstanding, this question remains unsettled to date. I will discuss experimental tests of the quantum superposition principle, such as matter wave interferometry with ...
... Does the quantum superposition principle hold on mesoscopic or even macroscopic scales? The tremendous success of quantum theory notwithstanding, this question remains unsettled to date. I will discuss experimental tests of the quantum superposition principle, such as matter wave interferometry with ...
Mar 11/02 Matter Waves
... • cannot predict when a photon will be detected at any point on the screen • if we move the detector, the click rate increases near an intensity maximum • the relative probability that a single photon is detected at a particular point in a specified time ∝ Intensity at that point • intensity ∝ Em2 P ...
... • cannot predict when a photon will be detected at any point on the screen • if we move the detector, the click rate increases near an intensity maximum • the relative probability that a single photon is detected at a particular point in a specified time ∝ Intensity at that point • intensity ∝ Em2 P ...
Slides from Lecture 9-11
... In practice, no: we only need a few dozen. In theory, no: some self-adjoint ops represent things disallowed by ‘superselection’ — e.g. real particles are either bosons or fermions, not some mixture. ...
... In practice, no: we only need a few dozen. In theory, no: some self-adjoint ops represent things disallowed by ‘superselection’ — e.g. real particles are either bosons or fermions, not some mixture. ...
Chemistry Science Notebook
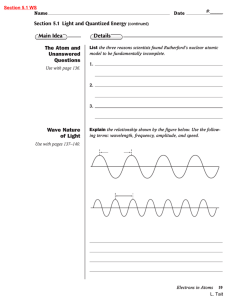
... List the three reasons scientists found Rutherford’s nuclear atomic model to be fundamentally incomplete. ...
... List the three reasons scientists found Rutherford’s nuclear atomic model to be fundamentally incomplete. ...
Objective 6: TSW explain how the quantum
... • Photoelectric effect: the ejection of electrons from a metal surface when that surface is exposed to electromagnetic radiation of sufficiently high frequency • In 1905 Einstein was able to explain the photoelectric effect by using Planck’s quantum theory (for which he won the Nobel prize in 1921) ...
... • Photoelectric effect: the ejection of electrons from a metal surface when that surface is exposed to electromagnetic radiation of sufficiently high frequency • In 1905 Einstein was able to explain the photoelectric effect by using Planck’s quantum theory (for which he won the Nobel prize in 1921) ...
Final “Intro Quantum Mechanics”
... 4 Here is a list of statements concerning quantum mechanics. Identify which are true (T) and which are false (F). (a) (T) One needs quantum mechanics to explain the spectrum of blackbody radiation, as classical physics gives the wrong answer. This was the effect that prompted Planck to introduce his ...
... 4 Here is a list of statements concerning quantum mechanics. Identify which are true (T) and which are false (F). (a) (T) One needs quantum mechanics to explain the spectrum of blackbody radiation, as classical physics gives the wrong answer. This was the effect that prompted Planck to introduce his ...
Classical: electron as particle
... Bohr implicitly assumed something like resonant electron orbital wavelengths in his successful model of the Hydrogen atom in 1913 (quantized angular momentum) ...
... Bohr implicitly assumed something like resonant electron orbital wavelengths in his successful model of the Hydrogen atom in 1913 (quantized angular momentum) ...
dual nature of light
... considered the source of secondary wavelets that spread out in all directions with a speed equal to the speed of propagation of waves. ...
... considered the source of secondary wavelets that spread out in all directions with a speed equal to the speed of propagation of waves. ...
Review PH301 -- duality, wavefunction, probability
... like nothing we’ve encountered before. Not an EM wave. does not have a direction in space. ...
... like nothing we’ve encountered before. Not an EM wave. does not have a direction in space. ...
photon may be totally absorbed by electron, but not have enough
... momentum of a particle. He proposed that only those orbits where the wave would be a circular standing wave will occur. This yields the same relation that Bohr had proposed. In addition, it makes more reasonable the fact that the electrons do not radiate, as one would otherwise expect from an accele ...
... momentum of a particle. He proposed that only those orbits where the wave would be a circular standing wave will occur. This yields the same relation that Bohr had proposed. In addition, it makes more reasonable the fact that the electrons do not radiate, as one would otherwise expect from an accele ...
powerpoint
... (d1mm) displays a pattern of alternating dark and light stripes on a screen placed in front of these two slits. ...
... (d1mm) displays a pattern of alternating dark and light stripes on a screen placed in front of these two slits. ...
Chapter 24
... principle, each portion of the slit acts as a source of waves The light from one portion of the slit can interfere with light from another portion The resultant intensity on the screen depends on the direction θ ...
... principle, each portion of the slit acts as a source of waves The light from one portion of the slit can interfere with light from another portion The resultant intensity on the screen depends on the direction θ ...
32 The Atom and the Quantum Answers and Solutions for Chapter
... 11. Yes, if there is at least one intermediate energy state that the electron can transition to along the way. 12. The relationship is given by ∆E ~ f. 13. The circumferences of orbits are discrete because they are made up of particular whole-number wavelengths of the electron. 14. In the first orbi ...
... 11. Yes, if there is at least one intermediate energy state that the electron can transition to along the way. 12. The relationship is given by ∆E ~ f. 13. The circumferences of orbits are discrete because they are made up of particular whole-number wavelengths of the electron. 14. In the first orbi ...
Brief introduction to quantum mechanics
... Solution requires: -Normalization of the wave function according ...
... Solution requires: -Normalization of the wave function according ...