* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Poster - high school teachers at CERN
Quantum electrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Quantum tunnelling wikipedia , lookup
Photoelectric effect wikipedia , lookup
Wave packet wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to gauge theory wikipedia , lookup
Compact Muon Solenoid wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Powder diffraction wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
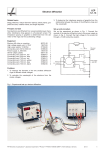
Electron Diffraction Experiment Setup Aim The aim of this experiment is to determine the interplanar spacing of graphite from the relationship between the radius of the diffraction rings and the wavelength by using de Broglie equation and Bragg’s diffraction. Introduction Electrons have both wave and particle behaviours that will show up depending on the type of the experiments, i.e., experiments measuring particle properties will not give the wave behaviour and vice versa. According to de Broglie equation, fast electrons have high momentum and hence a wavelength comparable to the spacing between layers in a crystal. These electron waves can undergo Bragg’s reflection and interfere. Making use of the wave behaviour of electrons, fast electrons are diffracted from a polycrystalline layer of graphite and interference rings appear on a fluorescent screen. The interplanar spacing in graphite is determined from the diameter of the rings and the accelerating voltage. Measurements Results Once the equipment is setup properly, an electron diffraction rings pattern appears. Ring radii vs electron wavelength 0.025 0.023 0.021 0.019 r/ 0.017 0.015 0.013 0.011 0.009 0.007 0.005 1E-11 1.2E-11 1.4E-11 1.6E-11 /m 1.8E-11 2E-11 The margin of error may be large due to the fact that the diameter measurement is difficult and not very accurate. Teacher guide The diameters of the first and second rings are measured for different accelerating potential. A graph of the radius of the rings against the wavelength of the electron wave is plotted and the gradient is used to find the interplanar spacing between graphite layers. This experiment involves two important concepts in modern physics – de Broglie relationship and Bragg’s reflection. It may be used to demonstrate wave-particle complementary and application of Bragg’s reflection As the applied voltage increases, there are additional rings to be seen. They correspond to either higher order or other lattice plane spacing. Teachers may choose to elaborate on Bragg’s conditions.