* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Concepts introduced by the theories of relativity include
Grand Unified Theory wikipedia , lookup
Photon polarization wikipedia , lookup
Renormalization group wikipedia , lookup
Topological quantum field theory wikipedia , lookup
ALICE experiment wikipedia , lookup
Photoelectric effect wikipedia , lookup
Bell's theorem wikipedia , lookup
Scalar field theory wikipedia , lookup
History of quantum field theory wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Identical particles wikipedia , lookup
Electron scattering wikipedia , lookup
Double-slit experiment wikipedia , lookup
ATLAS experiment wikipedia , lookup
Canonical quantization wikipedia , lookup
Renormalization wikipedia , lookup
Compact Muon Solenoid wikipedia , lookup
Standard Model wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Relational approach to quantum physics wikipedia , lookup
Old quantum theory wikipedia , lookup
Eigenstate thermalization hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Theory of everything wikipedia , lookup
Uncertainty principle wikipedia , lookup
Elementary particle wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
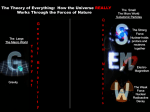
Newton’s Laws of Motion Electromagnetic spectrum with visible light highlighted (Maxwell). Concepts introduced by the theories of relativity include: • Measurements of various quantities are relative to the velocities of observers. In particular, space contracts and time dilates. • Spacetime: space and time should be considered together and in relation to each other. • The speed of light is nonetheless invariant, the same for all observers. Fundamental Forces of Nature The Development of Quantum Theory • In 1900, Planck made the assumption that energy was made of individual units, or quanta. • • In 1905, Albert Einstein theorized that not just the energy, but the radiation itself was quantized in the same manner. In 1924, Louis de Broglie proposed that there is no fundamental difference in the makeup and behavior of energy and matter -- on the atomic and subatomic level either may behave as if made of either particles or waves. • This theory became known as the principle of wave-particle duality: elementary particles of both energy and matter behave, depending on the conditions, like either particles or waves. • In 1927, Werner Heisenberg proposed that precise, simultaneous measurement of two complementary values - such as the position and momentum of a subatomic particle - is impossible. Contrary to the principles of classical physics, their simultaneous measurement is inescapably flawed; the more precisely one value is measured, the more flawed will be the measurement of the other value. This theory became known as the uncertainty principle, which prompted Albert Einstein's famous comment, "God does not play dice."