PHYS6520 Quantum Mechanics II Spring 2013 HW #5
... matching right and left going waves on the left with a right going wave on the right at x = 0. You’ll need to integrate the Schrödinger equation across x = 0 to match the derivatives. (e) We showed last semester that this potential has one, and only one, bound state. Show that your results for T (k ...
... matching right and left going waves on the left with a right going wave on the right at x = 0. You’ll need to integrate the Schrödinger equation across x = 0 to match the derivatives. (e) We showed last semester that this potential has one, and only one, bound state. Show that your results for T (k ...
Teaching Modern Physics - IMSA Digital Commons
... two rows on the screen Here is a video of a real experiment. ...
... two rows on the screen Here is a video of a real experiment. ...
Rutherford Model of the Atom Objective
... A study of the paths of the alpha particles revealed that they were curved rather than sharp. ...
... A study of the paths of the alpha particles revealed that they were curved rather than sharp. ...
Part A One reason that Fraunhofer diffraction is relatively easy to
... Express your answer in millimeters to two significant figures. ...
... Express your answer in millimeters to two significant figures. ...
Historical Introduction to the Elementary Particles
... • 2. Einstein, in 1905, put forward a far more radical view. He argued that quantization was a feature of the electromagnetic field itself, having nothing to do with the emission mechanism. ...
... • 2. Einstein, in 1905, put forward a far more radical view. He argued that quantization was a feature of the electromagnetic field itself, having nothing to do with the emission mechanism. ...
double-slit teacher
... interference pattern of two slits. c) Superposition If we don’t know what state an object is in, then it is in a combination or superposition of those states and these possibilities can interfere with each other. If we don’t try to detect which slit the electron goes through then electron can be in ...
... interference pattern of two slits. c) Superposition If we don’t know what state an object is in, then it is in a combination or superposition of those states and these possibilities can interfere with each other. If we don’t try to detect which slit the electron goes through then electron can be in ...
Quantum Trinity Lecture, Wroclaw, October 2016 All phrases are to
... By measuring the position of the electrons, one ignores their wavelength. By measuring their wavelength, one ignores their position. We have now arrived at the heart of quantum mechanics, the duality of particles and waves. By 1925 it became clear that the question whether something is a particle or ...
... By measuring the position of the electrons, one ignores their wavelength. By measuring their wavelength, one ignores their position. We have now arrived at the heart of quantum mechanics, the duality of particles and waves. By 1925 it became clear that the question whether something is a particle or ...
Particle-like Properties of Electromagnetic Radiation
... 3) Light energy can behave both as a wave and as small particles 4) atoms emit light quanta (photons) only of a few specific energies; this gives rise to the line spectrum (discussed in the previous lecture) ...
... 3) Light energy can behave both as a wave and as small particles 4) atoms emit light quanta (photons) only of a few specific energies; this gives rise to the line spectrum (discussed in the previous lecture) ...
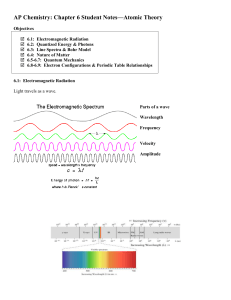
Ch. 6 notes
... Calculate the energy required to excite the hydrogen electron from level n=1 to level n=2. Also calculate the wavelength of light that must be absorbed by a hydrogen atom in its ground state to reach this excited state. ...
... Calculate the energy required to excite the hydrogen electron from level n=1 to level n=2. Also calculate the wavelength of light that must be absorbed by a hydrogen atom in its ground state to reach this excited state. ...
qp2
... of wave-particle duality and was studied extensively. The most interesting part of the theory was when it was tested using a double-slit experiment similar to the original one carried out for light by Thomas Young. In Young's experiment light was shot through a ‘double slit’ apparatus (see figure) a ...
... of wave-particle duality and was studied extensively. The most interesting part of the theory was when it was tested using a double-slit experiment similar to the original one carried out for light by Thomas Young. In Young's experiment light was shot through a ‘double slit’ apparatus (see figure) a ...
1 pt
... What is the name of the term given to the minimum quantity of energy that can be lost or gained by an atom? ...
... What is the name of the term given to the minimum quantity of energy that can be lost or gained by an atom? ...
What is Light?
... • Compton Scattering – Arthur H. Compton (1922) – X-rays fired at electron target – Scattered X-rays have lower frequency (lower E) • Greater scatter angle – greater the change in frequency ...
... • Compton Scattering – Arthur H. Compton (1922) – X-rays fired at electron target – Scattered X-rays have lower frequency (lower E) • Greater scatter angle – greater the change in frequency ...
DOC - 嘉義大學
... 1. The total energy of a neutron is five times its rest energy. Answer the following questions: (20%) (a) Find the neutron’s rest energy in electron volts. (Hint: mn = 1.681027 kg) (b) Determine the kinetic energy of the neutron in electron volts. (c) What speed (in units of c) is the neutron movi ...
... 1. The total energy of a neutron is five times its rest energy. Answer the following questions: (20%) (a) Find the neutron’s rest energy in electron volts. (Hint: mn = 1.681027 kg) (b) Determine the kinetic energy of the neutron in electron volts. (c) What speed (in units of c) is the neutron movi ...
Chapter 27
... depends on the wave characteristics of electrons Microscopes can only resolve details that are slightly smaller than the wavelength of the radiation used to illuminate the object The electrons can be accelerated to high energies and have small wavelengths ...
... depends on the wave characteristics of electrons Microscopes can only resolve details that are slightly smaller than the wavelength of the radiation used to illuminate the object The electrons can be accelerated to high energies and have small wavelengths ...
AS_Unit1_Quantum_06_Wave_Particle_Duality
... Beam of electrons directed at a thin metal foil. Rows of atoms cause the electron beam to be diffracted in certain directions only. We observe rings due to electrons being diffracted by the same amount from grains of different orientations, at the same angle to the incident beam. ...
... Beam of electrons directed at a thin metal foil. Rows of atoms cause the electron beam to be diffracted in certain directions only. We observe rings due to electrons being diffracted by the same amount from grains of different orientations, at the same angle to the incident beam. ...
Simple alternative model of the dual nature of light
... Although a model based upon hypotheses n° 1-5 in section 2 may look simplistic and naïve, it might be possible to define a thought, or Gedanken experiment in order to verify or refute it. For that purpose the latter should incorporate one source of single-photons, using for instance the technique of ...
... Although a model based upon hypotheses n° 1-5 in section 2 may look simplistic and naïve, it might be possible to define a thought, or Gedanken experiment in order to verify or refute it. For that purpose the latter should incorporate one source of single-photons, using for instance the technique of ...