WS 12 - Department of Chemistry | Oregon State University
... Why is dATP one of the four precursors of DNA, but dAMP is not? ...
... Why is dATP one of the four precursors of DNA, but dAMP is not? ...
DNA technology
... Recombinant DNA & Plasmids Combining genes from different sources and/or species ...
... Recombinant DNA & Plasmids Combining genes from different sources and/or species ...
Name
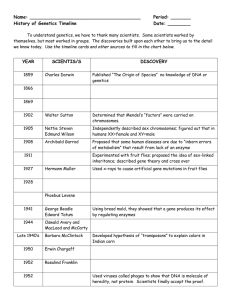
... Used viruses called phages to show that DNA is molecule of heredity, not protein. Scientists finally accept the proof. ...
... Used viruses called phages to show that DNA is molecule of heredity, not protein. Scientists finally accept the proof. ...
Jeopardy - Grayslake Central High School
... What is transformation, and why is it an important step in gene cloning? It is the absorption of foreign plasmid DNA into bacterial cells. Once the plasmid is absorbed, the bacteria can express the new genes, and they copy the whole plasmid whenever they carry out binary fission. ...
... What is transformation, and why is it an important step in gene cloning? It is the absorption of foreign plasmid DNA into bacterial cells. Once the plasmid is absorbed, the bacteria can express the new genes, and they copy the whole plasmid whenever they carry out binary fission. ...
Protein Synthesis
... The cell decides what protein is needed and the correct gene is identified The DNA strand is pulled apart Proteins and enzymes begin to copy the gene making a single strand of nucleotides called ...
... The cell decides what protein is needed and the correct gene is identified The DNA strand is pulled apart Proteins and enzymes begin to copy the gene making a single strand of nucleotides called ...
PowerPoint Slides
... •Attenuated (weakened) so they do not cause disease •Whole killed vaccines •Subunit vaccines •Part of organism (protein, inactivated toxins) •Genetic Vaccines •Part of genes from organism ...
... •Attenuated (weakened) so they do not cause disease •Whole killed vaccines •Subunit vaccines •Part of organism (protein, inactivated toxins) •Genetic Vaccines •Part of genes from organism ...
GO ON TO THE NEXT PAGE. -28- 8. In 1952 Alfred Hershey and
... label the DNA and proteins of bacteriophage T2, a virus that infects bacteria. After incubating the labeled bacteriophage particles with Escherichia coli and separating extracellular phage particles from the bacteria, Hershey and Chase measured the amounts of radioactive phosphorus and sulfur inside ...
... label the DNA and proteins of bacteriophage T2, a virus that infects bacteria. After incubating the labeled bacteriophage particles with Escherichia coli and separating extracellular phage particles from the bacteria, Hershey and Chase measured the amounts of radioactive phosphorus and sulfur inside ...
Mutations
... • If a mutation happens in the sex cell the mutation might be passed onto an offspring • If a mutation happens in a body cell, like a skin cell, it will not be passed on • A mutation is harmful if it reduces the organisms chance for survival and reproduction • A mutation is helpful if it improves an ...
... • If a mutation happens in the sex cell the mutation might be passed onto an offspring • If a mutation happens in a body cell, like a skin cell, it will not be passed on • A mutation is harmful if it reduces the organisms chance for survival and reproduction • A mutation is helpful if it improves an ...
(1) End labelling
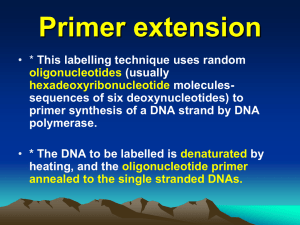
... Primer extension • * This labelling technique uses random oligonucleotides (usually hexadeoxyribonucleotide moleculessequences of six deoxynucleotides) to primer synthesis of a DNA strand by DNA polymerase. • * The DNA to be labelled is denaturated by heating, and the oligonucleotide primer annealed ...
... Primer extension • * This labelling technique uses random oligonucleotides (usually hexadeoxyribonucleotide moleculessequences of six deoxynucleotides) to primer synthesis of a DNA strand by DNA polymerase. • * The DNA to be labelled is denaturated by heating, and the oligonucleotide primer annealed ...
Chapter 18-20 review
... _____4. The ability of an E. coli bacterium to act as a donor ("male") during conjugation is usually due to a piece of DNA called a. a probe. b. a plasmid. c. recombinant DNA. d. an F factor. e. a Ti plasmid. ...
... _____4. The ability of an E. coli bacterium to act as a donor ("male") during conjugation is usually due to a piece of DNA called a. a probe. b. a plasmid. c. recombinant DNA. d. an F factor. e. a Ti plasmid. ...
Viruses
... • Use infected cell to produce more viruses • Capsid: protein coat surrounding DNA/RNA core • bacteriophage – virus that infects bacteria ...
... • Use infected cell to produce more viruses • Capsid: protein coat surrounding DNA/RNA core • bacteriophage – virus that infects bacteria ...
Human Genome Video Guide
... Free radicals can damage our genes, they can alter our genetic code and create ...
... Free radicals can damage our genes, they can alter our genetic code and create ...
genetics - Lemon Bay High School
... grew peas in the monastery gardens. He noticed patterns among the generations of plants when they were cross-pollinated by hand and then allowed to fertilize naturally. ...
... grew peas in the monastery gardens. He noticed patterns among the generations of plants when they were cross-pollinated by hand and then allowed to fertilize naturally. ...
Introduction to DNA webquest: Name http://learn.genetics.utah.
... 2. What is the protein in red blood cells called, and what does it ...
... 2. What is the protein in red blood cells called, and what does it ...
Vaksin dan sera
... DNA vaccines are at present experimental, but hold promise for future therapy since they will evoke both humoral and cellmediated immunity, without the dangers associated with live virus vaccines. The gene for an antigenic determinant of a pathogenic organism is inserted into a plasmid. This genetic ...
... DNA vaccines are at present experimental, but hold promise for future therapy since they will evoke both humoral and cellmediated immunity, without the dangers associated with live virus vaccines. The gene for an antigenic determinant of a pathogenic organism is inserted into a plasmid. This genetic ...
C13 Genetic Engineering
... with our gene in it. Animals also being used, like the cow that makes milk with a human protein. Plants are important transgenic organisms. In the year 2000, 52% of soybeans, and 25% of corn grown in the US were transgenic (or genetically modified). Most were modified for pesticide resistance. ...
... with our gene in it. Animals also being used, like the cow that makes milk with a human protein. Plants are important transgenic organisms. In the year 2000, 52% of soybeans, and 25% of corn grown in the US were transgenic (or genetically modified). Most were modified for pesticide resistance. ...
Genetics
... • Nucleotides are added to form a “messenger” RNA molecule (mRNA) • mRNA leaves nucleus through nuclear pore ...
... • Nucleotides are added to form a “messenger” RNA molecule (mRNA) • mRNA leaves nucleus through nuclear pore ...
Genetic Vaccines
... Several researchers have reported that the gene gun mediated immunization is far more efficient than needle injection, eliciting similar levels of antibody and cellular responses with 100-5000 fold less DNA. It was reported that as little as 16 ng of plasmid DNA delivered epidermally via gene gun c ...
... Several researchers have reported that the gene gun mediated immunization is far more efficient than needle injection, eliciting similar levels of antibody and cellular responses with 100-5000 fold less DNA. It was reported that as little as 16 ng of plasmid DNA delivered epidermally via gene gun c ...
Genetics - Bill Nye ANSWERS
... RNA is similar to DNA, but its different. What’s different? RNA only has one strand. There are 20 amino acids that make up proteins. Name the 2 scientists that discovered the double helix. Watson and Crick How many bases align in a sequence to code for a specific amino acid? 3 Bacteria resistant to ...
... RNA is similar to DNA, but its different. What’s different? RNA only has one strand. There are 20 amino acids that make up proteins. Name the 2 scientists that discovered the double helix. Watson and Crick How many bases align in a sequence to code for a specific amino acid? 3 Bacteria resistant to ...
Webquests_files/Genes and DNA SWQ
... The four nucleotides Difference between dominant and recessive alleles ...
... The four nucleotides Difference between dominant and recessive alleles ...
DNA vaccination

DNA vaccination is a technique for protecting an animal against disease by injecting it with genetically engineered DNA so cells directly produce an antigen, resulting in a protective immunological response. Several DNA vaccines have been released for veterinary use, and there has been promising research using the vaccines for viral, bacterial and parasitic diseases, as well as to several tumour types. Although only one DNA vaccine has been approved for human use, DNA vaccines may have a number of potential advantages over conventional vaccines, including the ability to induce a wider range of immune response types.