This project aims to identify differences in DNA structure of cells in
... protection by microglia, the immune cells of the central nervous system. Like replicating cells, microglia become less functional as they age. Aging of cells throughout the body can be regulated by how tightly their DNA is stored. Addition of chemical groups to the DNA-packaging proteins can either ...
... protection by microglia, the immune cells of the central nervous system. Like replicating cells, microglia become less functional as they age. Aging of cells throughout the body can be regulated by how tightly their DNA is stored. Addition of chemical groups to the DNA-packaging proteins can either ...
Preparation of Vaccines
... Routes of Administration • The majority of vaccines are administered by injection – Subcutaneous – Intramuscular – Intradermal ...
... Routes of Administration • The majority of vaccines are administered by injection – Subcutaneous – Intramuscular – Intradermal ...
IMMUNITY WORKSHEET
... a. making antibodies that float free in the body fluids b. activating the complement system c. secreting toxic substances that destroy pathogens d. phagocytizing invaders 13. Your cells have a unique MHC (major histocompatibility complex). Directions for producing MHCs come from _________________. a ...
... a. making antibodies that float free in the body fluids b. activating the complement system c. secreting toxic substances that destroy pathogens d. phagocytizing invaders 13. Your cells have a unique MHC (major histocompatibility complex). Directions for producing MHCs come from _________________. a ...
Bill Nye: Genes - stephaniemcoggins
... 2. What is inside every cell in your body? 3. What does DNA stand for? 4. How long is the DNA string model of science? 5. How many times longer is DNA than it is wide? 6. How does Bill define a Gene? 7. Why is the white blood cell dark on the computer screen? 8. What does the nucleus of the cell con ...
... 2. What is inside every cell in your body? 3. What does DNA stand for? 4. How long is the DNA string model of science? 5. How many times longer is DNA than it is wide? 6. How does Bill define a Gene? 7. Why is the white blood cell dark on the computer screen? 8. What does the nucleus of the cell con ...
DiscBio_C10 Cell division PwrPnt
... Cell splits into 2 identical cells, each with 1 DNA molecule New cells are clones to self and to the parent ...
... Cell splits into 2 identical cells, each with 1 DNA molecule New cells are clones to self and to the parent ...
DNA TECHNOLOGY
... 2. Genetic engineering is a faster & more reliable method of producing desired traits in a population. Genetic engineering is used by humans for practical purposes. ...
... 2. Genetic engineering is a faster & more reliable method of producing desired traits in a population. Genetic engineering is used by humans for practical purposes. ...
a10c Biotechnology
... 2. What is a restriction enzyme, and what does it catalyze? How do restriction enzymes differ in what they cleave? What do they "look for"? Name an example of a restriction enzyme. 3. Describe the steps of cloning (transferring a gene to bacteria for purposes of "growing" DNA or protein). What enzym ...
... 2. What is a restriction enzyme, and what does it catalyze? How do restriction enzymes differ in what they cleave? What do they "look for"? Name an example of a restriction enzyme. 3. Describe the steps of cloning (transferring a gene to bacteria for purposes of "growing" DNA or protein). What enzym ...
notes
... • First method is by “cloning”, i.e. introduce the gene into a bacterial cell then grow up large amounts and extract DNA (in vivo) • Second method is by “polymerase chain reaction” (PCR) using DNA polymerase to amplify the gene in a test-tube (in vitro) • Both methods have their uses but PCR is pref ...
... • First method is by “cloning”, i.e. introduce the gene into a bacterial cell then grow up large amounts and extract DNA (in vivo) • Second method is by “polymerase chain reaction” (PCR) using DNA polymerase to amplify the gene in a test-tube (in vitro) • Both methods have their uses but PCR is pref ...
What are the three steps in PCR?
... What are three techniques used to get recombinant DNA into cells? ...
... What are three techniques used to get recombinant DNA into cells? ...
Biology Final Review answers
... • 3. True or False: All cells in an organism have the same genetic information • DNA is same nucleotides, but sequence and ...
... • 3. True or False: All cells in an organism have the same genetic information • DNA is same nucleotides, but sequence and ...
Who am I?
... What is cloning? Clones are identical copies of living things. Humans have cloned a lot of things already. ...
... What is cloning? Clones are identical copies of living things. Humans have cloned a lot of things already. ...
chapter 19_updates
... DNA at specific nucleotide sequences • Type II restriction enzyme: most useful enzyme • By adding methyl groups to the recognition sequence to protect itself from being digested by its own enzyme in bacteria ...
... DNA at specific nucleotide sequences • Type II restriction enzyme: most useful enzyme • By adding methyl groups to the recognition sequence to protect itself from being digested by its own enzyme in bacteria ...
Genes, Chromosomes and DNA
... order in which the bases occur determines specific instructions for building proteins, much as specific letters of the alphabet combine to form words and sentences. _________ is found in the _________ of each of the body's billions of cells. Every human cell (with the exception of mature red blood c ...
... order in which the bases occur determines specific instructions for building proteins, much as specific letters of the alphabet combine to form words and sentences. _________ is found in the _________ of each of the body's billions of cells. Every human cell (with the exception of mature red blood c ...
Molecular Techniques in Cell & Molecular Biology
... cell and molecular biology in the last 20 years. These techniques are used to recombine DNA from different sources and to replicate and express these genes in other cells. They make possible new ways to study the functions of genes and their protein products and also commercial production of specifi ...
... cell and molecular biology in the last 20 years. These techniques are used to recombine DNA from different sources and to replicate and express these genes in other cells. They make possible new ways to study the functions of genes and their protein products and also commercial production of specifi ...
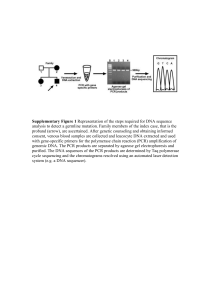
Figure 2 Representation of the steps required for DNA sequence
... Supplementary Figure 1 Representation of the steps required for DNA sequence analysis to detect a germline mutation. Family members of the index case, that is the proband (arrow), are ascertained. After genetic counseling and obtaining informed consent, venous blood samples are collected and leucocy ...
... Supplementary Figure 1 Representation of the steps required for DNA sequence analysis to detect a germline mutation. Family members of the index case, that is the proband (arrow), are ascertained. After genetic counseling and obtaining informed consent, venous blood samples are collected and leucocy ...
here - Molecular Medicine Ireland
... The work of Cornelis (Kees) Melief has contributed fundamental insights into the cellular and molecular mechanisms governing the generation of cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTL) responses, the most important adaptive immune response against viruses and tumors. This includes among the first demonstration ...
... The work of Cornelis (Kees) Melief has contributed fundamental insights into the cellular and molecular mechanisms governing the generation of cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTL) responses, the most important adaptive immune response against viruses and tumors. This includes among the first demonstration ...
TwoQuestions Darwin Could Not Answer
... – Different experiences bring new chemicals into the cell which change chemical environment ...
... – Different experiences bring new chemicals into the cell which change chemical environment ...
Assessment Questions Answer Key
... 3. Describe how bacteria can be made to produce human insulin. First, a restriction enzyme cuts both a bacterial plasmid and the human insulin gene. Then, an enzyme called ligase joins the nitrogen bases of the cut plasmid and human insulin gene together. This recreates a recombinant plasmid. Then t ...
... 3. Describe how bacteria can be made to produce human insulin. First, a restriction enzyme cuts both a bacterial plasmid and the human insulin gene. Then, an enzyme called ligase joins the nitrogen bases of the cut plasmid and human insulin gene together. This recreates a recombinant plasmid. Then t ...
Assessment Questions Answer Key
... 3. Describe how bacteria can be made to produce human insulin. First, a restriction enzyme cuts both a bacterial plasmid and the human insulin gene. Then, an enzyme called ligase joins the nitrogen bases of the cut plasmid and human insulin gene together. This recreates a recombinant plasmid. Then t ...
... 3. Describe how bacteria can be made to produce human insulin. First, a restriction enzyme cuts both a bacterial plasmid and the human insulin gene. Then, an enzyme called ligase joins the nitrogen bases of the cut plasmid and human insulin gene together. This recreates a recombinant plasmid. Then t ...
DNA vaccination

DNA vaccination is a technique for protecting an animal against disease by injecting it with genetically engineered DNA so cells directly produce an antigen, resulting in a protective immunological response. Several DNA vaccines have been released for veterinary use, and there has been promising research using the vaccines for viral, bacterial and parasitic diseases, as well as to several tumour types. Although only one DNA vaccine has been approved for human use, DNA vaccines may have a number of potential advantages over conventional vaccines, including the ability to induce a wider range of immune response types.