* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download GO ON TO THE NEXT PAGE. -28- 8. In 1952 Alfred Hershey and
Community fingerprinting wikipedia , lookup
Gel electrophoresis of nucleic acids wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
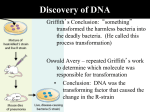
8. In 1952 Alfred Hershey and Martha Chase used radioactive phosphorus and radioactive sulfur to selectively label the DNA and proteins of bacteriophage T2, a virus that infects bacteria. After incubating the labeled bacteriophage particles with Escherichia coli and separating extracellular phage particles from the bacteria, Hershey and Chase measured the amounts of radioactive phosphorus and sulfur inside infected E. coli cells and in the liquid growth medium outside the E. coli cells. (a) Predict the experimental result that would best support the claim that DNA is the source of heritable information, and provide reasoning to explain how the result supports the claim. (b) Bacteriophages, like other viruses, consist primarily of a protein coat and packaged DNA. Describe the function of ONE critical enzyme in bacterial cells that is necessary for replicating bacteriophage DNA. PAGE FOR ANSWERING QUESTION 8 Unauthorized copying or reuse of any part of this page is illegal. GO ON TO THE NEXT PAGE. -28-