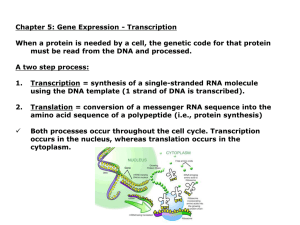
DNA, RNA and Protein Synthesis 1. Define: Nucleotide
... Nucleotide – Nucleotides are small, organic molecules made up of a pentose sugar (ribose or deoxyribose), a phosphate group and one nitrogenous base (adenine, guanine, cytosine, thymine or uracil). Nucleotides are used as the "building blocks" of nucleic acids (DNA and RNA). They are also used to fo ...
... Nucleotide – Nucleotides are small, organic molecules made up of a pentose sugar (ribose or deoxyribose), a phosphate group and one nitrogenous base (adenine, guanine, cytosine, thymine or uracil). Nucleotides are used as the "building blocks" of nucleic acids (DNA and RNA). They are also used to fo ...
Proein Synthesis Note Fill-in
... 39. How many nucleotides make up the mature mRNA molecule? 40. What is the start codon? 41. What are the 3 stop codons? 42. What is the function of tRNA? 43. How many nucleotides make up a tRNA molecule? 44. What are anticodons and where do we find them? 45. Sketch and label a tRNA molecule. 46. Ho ...
... 39. How many nucleotides make up the mature mRNA molecule? 40. What is the start codon? 41. What are the 3 stop codons? 42. What is the function of tRNA? 43. How many nucleotides make up a tRNA molecule? 44. What are anticodons and where do we find them? 45. Sketch and label a tRNA molecule. 46. Ho ...
Gene regulation - Department of Plant Sciences
... • Transcriptional activator-like (TAL) effectors bind with plant promoters to express genes beneficial for the bacteria ...
... • Transcriptional activator-like (TAL) effectors bind with plant promoters to express genes beneficial for the bacteria ...
3rd Quarter Biology Assessment
... FYI for the teacher: The white moth was highly visible and eaten more often than the less white w/ many black spots. The more black-spotted moth survived to reproduce. Eventually the population of peppered moths was all dark with only a few spots of white. That is evolution due to a mutation that be ...
... FYI for the teacher: The white moth was highly visible and eaten more often than the less white w/ many black spots. The more black-spotted moth survived to reproduce. Eventually the population of peppered moths was all dark with only a few spots of white. That is evolution due to a mutation that be ...
Test your nucleic acid knowledge!
... 11. Process where RNA is synthesized from DNA. 14. Nucleic acid research took a great leap forward when Watson and Crick proposed the __________ structure of DNA in 1953. ...
... 11. Process where RNA is synthesized from DNA. 14. Nucleic acid research took a great leap forward when Watson and Crick proposed the __________ structure of DNA in 1953. ...
Searching for the “Secret of Life”
... structure of DNA How DNA replicates Differences b/w DNA & RNA Steps of Transcription & Translation Parts of tRNA 3 types of RNA ...
... structure of DNA How DNA replicates Differences b/w DNA & RNA Steps of Transcription & Translation Parts of tRNA 3 types of RNA ...
STAAR Review 4
... a. All of their daughters will be color blind. b. The mother is a carrier of the color blindness gene. c. All of their sons will have normal color vision. d. All of their sons will be color blind. ...
... a. All of their daughters will be color blind. b. The mother is a carrier of the color blindness gene. c. All of their sons will have normal color vision. d. All of their sons will be color blind. ...
BACTERIAL VIRUSES ("Bacteriophage") “Mein Gott!” They`ve got
... times shortened to “phage”. Synonomous wit “bacterial virus”. The term “coliphage” is sometimes used to designate bacteriophage that infect and replicate in E. coli host cells. ...
... times shortened to “phage”. Synonomous wit “bacterial virus”. The term “coliphage” is sometimes used to designate bacteriophage that infect and replicate in E. coli host cells. ...
DNA Functions
... back together. The RNA migrates out of the nucleus of the cell and into the cytoplasm. ...
... back together. The RNA migrates out of the nucleus of the cell and into the cytoplasm. ...
AP Protein synthesis
... RNA Polymerase II, and Transcription factors all combined and ready to start transcription. ...
... RNA Polymerase II, and Transcription factors all combined and ready to start transcription. ...
Gene expression - El Camino College
... Review of Nucleic Acid (DNA and RNA) • They are long chain of ____________________ • A nucleotide is different from another by the type of _______ • Information in a nucleic acid is used for making ________ ...
... Review of Nucleic Acid (DNA and RNA) • They are long chain of ____________________ • A nucleotide is different from another by the type of _______ • Information in a nucleic acid is used for making ________ ...
Genetics and Protein Synthesis
... The complex then shifts along the mRNA to the next triplet, opening the A site. The new tRNA enters at the A site. When the codon in the A site is a termination codon, a releasing factor binds to the site, stopping translation and releasing the ribosomal complex and mRNA. ...
... The complex then shifts along the mRNA to the next triplet, opening the A site. The new tRNA enters at the A site. When the codon in the A site is a termination codon, a releasing factor binds to the site, stopping translation and releasing the ribosomal complex and mRNA. ...
Method of localizing, either mRNA within the cytoplasm or DNA
... Method of localizing, either mRNA within the ...
... Method of localizing, either mRNA within the ...
coding region of DNA. o Introns – non
... Addition of up to 200 adenine bases in the form of a Poly(A) tail. Enhances mRNA stability and regulates transport to cytoplasm. o RNA splicing. Removal of introns. Primary transcript is spliced. Exons are joined up to make the final transcript. Small nuclear RNAs (snRNA) joined with pro ...
... Addition of up to 200 adenine bases in the form of a Poly(A) tail. Enhances mRNA stability and regulates transport to cytoplasm. o RNA splicing. Removal of introns. Primary transcript is spliced. Exons are joined up to make the final transcript. Small nuclear RNAs (snRNA) joined with pro ...