RNA to Protein
... 7.1 Impacts/Issues Ricin and Your Ribosomes The ability to make proteins is critical to all life processes – ricin kills because it inactivates ribosomes that assemble proteins ...
... 7.1 Impacts/Issues Ricin and Your Ribosomes The ability to make proteins is critical to all life processes – ricin kills because it inactivates ribosomes that assemble proteins ...
Unit VII Study Guide KEY
... And a third important difference is the organization of genes in the prokaryotic chromosome. Multiple genes required for a single metabolic pathway are organized together in groups known as _operons______. In addition to the genes coding for necessary _enzymes_____ for a particular metabolic pathway ...
... And a third important difference is the organization of genes in the prokaryotic chromosome. Multiple genes required for a single metabolic pathway are organized together in groups known as _operons______. In addition to the genes coding for necessary _enzymes_____ for a particular metabolic pathway ...
CHAPTER 17 - HCC Learning Web
... • Enzymes in the eukaryotic nucleus modify premRNA (RNA processing) before the genetic messages are dispatched to the cytoplasm • During RNA processing, both ends of the primary transcript are usually altered • Also, usually some interior parts of the molecule are cut out, and the other parts splice ...
... • Enzymes in the eukaryotic nucleus modify premRNA (RNA processing) before the genetic messages are dispatched to the cytoplasm • During RNA processing, both ends of the primary transcript are usually altered • Also, usually some interior parts of the molecule are cut out, and the other parts splice ...
Gene Expression
... amino acids into long polypeptides (which are proteins) – There are only 20 naturally occurring amino acids ...
... amino acids into long polypeptides (which are proteins) – There are only 20 naturally occurring amino acids ...
A. Introduction
... b) The coding strand sequence is given when talking about double stranded DNA (1) Same polarity as RNA (2) Easier when referring to the genetic code (3) Always given in the 5' to 3' direction 2. Template strand a) This is the strand of DNA that RNA polymerase binds to during transcription b) It is c ...
... b) The coding strand sequence is given when talking about double stranded DNA (1) Same polarity as RNA (2) Easier when referring to the genetic code (3) Always given in the 5' to 3' direction 2. Template strand a) This is the strand of DNA that RNA polymerase binds to during transcription b) It is c ...
Organic Molecules Notes
... the principal structural components of living cells, and that include fats and waxes and related and derived compounds. The main type of fat found in the body. ...
... the principal structural components of living cells, and that include fats and waxes and related and derived compounds. The main type of fat found in the body. ...
Eukaryotes - Daniel Guetta
... They're HUGE, because they contain "introns" that need to be removed before translation ...
... They're HUGE, because they contain "introns" that need to be removed before translation ...
(RBPs) have been demonstrated to perform central roles in these
... mulated significantly lower levels of mature miRNAs and concurrently higher levels o f pri-miRNAs than wild type. The dramatic reductions of mature miRNAs were associ ated with the accumulation of their target gene transcripts and the corresponding devel opmental defects. The reduction of miRNA accu ...
... mulated significantly lower levels of mature miRNAs and concurrently higher levels o f pri-miRNAs than wild type. The dramatic reductions of mature miRNAs were associ ated with the accumulation of their target gene transcripts and the corresponding devel opmental defects. The reduction of miRNA accu ...
Nature Rev.Genet
... local unwinding and interrogates flanking DNA for the target PAM binding activates the Cas9-RNA nuclease activity and generates a ds break Specificity is determined by the crRNA sequence ...
... local unwinding and interrogates flanking DNA for the target PAM binding activates the Cas9-RNA nuclease activity and generates a ds break Specificity is determined by the crRNA sequence ...
Name
... 3. Proteins are made from smaller units called amino acids. Genes 4. What is created from the instructions found within genes? Proteins 5. Where are genes located? Inside the nucleus of cells 6. Which organelle creates proteins? Ribosomes Meet Melissa 7. What is Melissa’s task? To design a new high- ...
... 3. Proteins are made from smaller units called amino acids. Genes 4. What is created from the instructions found within genes? Proteins 5. Where are genes located? Inside the nucleus of cells 6. Which organelle creates proteins? Ribosomes Meet Melissa 7. What is Melissa’s task? To design a new high- ...
Transcription and Translation
... ribosomal RNA and 40% protein. • Messenger RNAs – (mRNA) "record" information from DNA in the cell nucleus and carry it to the ribosomes. • Transfer RNAs- (tRNA) delivers amino acids one by one to protein chains growing at ribosomes ...
... ribosomal RNA and 40% protein. • Messenger RNAs – (mRNA) "record" information from DNA in the cell nucleus and carry it to the ribosomes. • Transfer RNAs- (tRNA) delivers amino acids one by one to protein chains growing at ribosomes ...
Biology 6 Study Guide – Exam #2
... Your actual studying should involve the textbook, Powerpoint slides, your notes and other supplemental material such as Mastering Biology. Keep in mind that you will not be tested on material in the book that was not covered in class, and should know all of the key terms at the end of the Powerpoint ...
... Your actual studying should involve the textbook, Powerpoint slides, your notes and other supplemental material such as Mastering Biology. Keep in mind that you will not be tested on material in the book that was not covered in class, and should know all of the key terms at the end of the Powerpoint ...
PRE-AP Stage 3 – Learning Plan
... SCAFFOLD: Students will identify the components of DNA and describe how genetic information is carried in DNA. After identifying the components of the structure of DNA, students will explain how DNA is transcribed and translated into amino acids to make proteins. ACCELERATE: PREAP – purines, pyrimid ...
... SCAFFOLD: Students will identify the components of DNA and describe how genetic information is carried in DNA. After identifying the components of the structure of DNA, students will explain how DNA is transcribed and translated into amino acids to make proteins. ACCELERATE: PREAP – purines, pyrimid ...
Eukaryotic Transcription
... Where is the TATAA box located? In which step does the initiation complex form? Transcription factors are associated with which structures in the diagram? Where would the codon AUG be located? Where are the genes to make a polypeptide located? Where is the termination signal located? What unwinds or ...
... Where is the TATAA box located? In which step does the initiation complex form? Transcription factors are associated with which structures in the diagram? Where would the codon AUG be located? Where are the genes to make a polypeptide located? Where is the termination signal located? What unwinds or ...
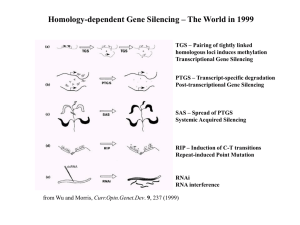
RNA interference: the new somatic cell genetics?
... the half-life of the silencing complex itself, and cell division, which serves to dilute the effect over time. Design and expression of dsRNA triggers Tuschl and colleagues have elaborated several guidelines for designing siRNA oligos for chemical synthesis (Elbashir et al., 2002). The selection of ...
... the half-life of the silencing complex itself, and cell division, which serves to dilute the effect over time. Design and expression of dsRNA triggers Tuschl and colleagues have elaborated several guidelines for designing siRNA oligos for chemical synthesis (Elbashir et al., 2002). The selection of ...
Lecture 7
... • How many amino acids would one protein contain if it was translated from an mRNA that is 690 nucleotides long? ...
... • How many amino acids would one protein contain if it was translated from an mRNA that is 690 nucleotides long? ...
Slide 1
... many freshwaters, yet substantial numbers of microorganisms exist there. Many of these use light to drive ATP synthesis. In terms of prokaryotes, species of the domain Bacteria tend to predominate in oceanic surface waters whereas Archaea are more prevalent in ...
... many freshwaters, yet substantial numbers of microorganisms exist there. Many of these use light to drive ATP synthesis. In terms of prokaryotes, species of the domain Bacteria tend to predominate in oceanic surface waters whereas Archaea are more prevalent in ...
Hypothesis: Variations in the rate of DNA replication determine the
... hence, if two identical copies of a gene compete for a limited number of RNA polymerases, one copy is expressed and the other silent. Related ideas about the primordial role of the cell cycle in generating not just diversity but coherent diversity have also been developed [6, 4]. ...
... hence, if two identical copies of a gene compete for a limited number of RNA polymerases, one copy is expressed and the other silent. Related ideas about the primordial role of the cell cycle in generating not just diversity but coherent diversity have also been developed [6, 4]. ...