RNA
... an anticodon whose bases are complementary to a codon on the mRNA strand. The ribosome positions the start codon to attract its anticodon, which is part of the tRNA that binds methionine. The ribosome also binds the next codon and its anticodon. ...
... an anticodon whose bases are complementary to a codon on the mRNA strand. The ribosome positions the start codon to attract its anticodon, which is part of the tRNA that binds methionine. The ribosome also binds the next codon and its anticodon. ...
gene expression
... Noncoding RNAs and gene expression • Discovering more about RNA’S that do not make protein • MicroRNAs (miRNA) – small, single stranded RNA generated from a hairpin on precursor RNA; associates with proteins that can degrade or prevent translation of mRNA with complementary sequence • Small interfe ...
... Noncoding RNAs and gene expression • Discovering more about RNA’S that do not make protein • MicroRNAs (miRNA) – small, single stranded RNA generated from a hairpin on precursor RNA; associates with proteins that can degrade or prevent translation of mRNA with complementary sequence • Small interfe ...
DNA and RNA are nucleic acids that carry out cellular
... The entire genetic content of a cell is known as its genome and the study of genomes is genomics. In eukaryotic cells, but not in prokaryotes, DNA forms a complex with histone proteins to form chromatin, the substance of eukaryotic chromosomes. A chromosome may contain tens of thousands of genes. Ma ...
... The entire genetic content of a cell is known as its genome and the study of genomes is genomics. In eukaryotic cells, but not in prokaryotes, DNA forms a complex with histone proteins to form chromatin, the substance of eukaryotic chromosomes. A chromosome may contain tens of thousands of genes. Ma ...
Chap 12 VOCAB - local.brookings.k12.sd.us
... Nitrogen base with 2 rings like adenine and guanine Purine Subunit composed of a sugar, nitrogen base, and a phosphate group used to make DNA and RNA nucleotide ...
... Nitrogen base with 2 rings like adenine and guanine Purine Subunit composed of a sugar, nitrogen base, and a phosphate group used to make DNA and RNA nucleotide ...
DNA and RNA are nucleic acids that carry out cellular
... The entire genetic content of a cell is known as its genome and the study of genomes is genomics. In eukaryotic cells, but not in prokaryotes, DNA forms a complex with histone proteins to form chromatin, the substance of eukaryotic chromosomes. A chromosome may contain tens of thousands of genes. Ma ...
... The entire genetic content of a cell is known as its genome and the study of genomes is genomics. In eukaryotic cells, but not in prokaryotes, DNA forms a complex with histone proteins to form chromatin, the substance of eukaryotic chromosomes. A chromosome may contain tens of thousands of genes. Ma ...
Genes chapt15
... • Elongation of translation involves the addition of amino acids: – a charged tRNA binds to the A site if its anticodon is complementary to the codon at the A site – peptidyl transferase forms a peptide ...
... • Elongation of translation involves the addition of amino acids: – a charged tRNA binds to the A site if its anticodon is complementary to the codon at the A site – peptidyl transferase forms a peptide ...
chapter 3 outline
... consensus target sequences in the promoter that are critical for these interactions. The strength of the promoters is to some extent a function of how close the target sequences are to the consensus. Mutations in these target sites can have UP or DOWN effects depending on whether the resulting seque ...
... consensus target sequences in the promoter that are critical for these interactions. The strength of the promoters is to some extent a function of how close the target sequences are to the consensus. Mutations in these target sites can have UP or DOWN effects depending on whether the resulting seque ...
VII. Some methods for studying gene expression
... • Effective as initiation of new RNA chains in isolated nuclei does not generally occur, one can be fairly confident that any transcription observed in the isolated nuclei is simply a continuation of transcription that was already occurring in vivo • Therefore, the transcripts should reveal not only ...
... • Effective as initiation of new RNA chains in isolated nuclei does not generally occur, one can be fairly confident that any transcription observed in the isolated nuclei is simply a continuation of transcription that was already occurring in vivo • Therefore, the transcripts should reveal not only ...
Ch. 13 Section Assessment Answers
... 30. DNA-binding proteins regulate genes by helping switch genes on or off before transcription. 31. The term cell specialization means the adaptation of eukaryotic cells for specialized functions by the regulation of gene expression. 32. A TATA box is usually found just before a gene. It binds trans ...
... 30. DNA-binding proteins regulate genes by helping switch genes on or off before transcription. 31. The term cell specialization means the adaptation of eukaryotic cells for specialized functions by the regulation of gene expression. 32. A TATA box is usually found just before a gene. It binds trans ...
bio_ch08-5_transcript redo
... puncture.” Punctuation, in a general sense, signifies an interruption. The word punctuate can also be used to describe the act of placing stress or emphasis on a point. Although most DNA is found in the nucleus, a small amount is located in the mitochondria and chloroplasts. Scientists were shocked ...
... puncture.” Punctuation, in a general sense, signifies an interruption. The word punctuate can also be used to describe the act of placing stress or emphasis on a point. Although most DNA is found in the nucleus, a small amount is located in the mitochondria and chloroplasts. Scientists were shocked ...
Translation - Net Start Class
... transcribed from DNA in the nucleus and released in the cytoplasm ...
... transcribed from DNA in the nucleus and released in the cytoplasm ...
From Gene to Protein
... How many nucleotides are in an mRNA molecule to code for a protein with 200 amino acids? ...
... How many nucleotides are in an mRNA molecule to code for a protein with 200 amino acids? ...
Lecture 5
... RNA and protein construction • The nucleotide base sequence of mRNA is encoded from DNA and transmits sequences of bases used to determine the amino acid sequence of the protein. • mRNA (“Messenger RNA”) associates with the ribosome (mRNA and protein portion). • RNA (“Transfer RNA”) also required • ...
... RNA and protein construction • The nucleotide base sequence of mRNA is encoded from DNA and transmits sequences of bases used to determine the amino acid sequence of the protein. • mRNA (“Messenger RNA”) associates with the ribosome (mRNA and protein portion). • RNA (“Transfer RNA”) also required • ...
DNA RNA Lecture Website
... 2. There are ___ different nucleotides (since there are four different nitrogenous bases). three nucleotides in 3. It was discovered that ______________ amino acid sequence must specify each __________. This would provide for ___ 64 possible combinations of amino acids. triplet of nucleotides is cal ...
... 2. There are ___ different nucleotides (since there are four different nitrogenous bases). three nucleotides in 3. It was discovered that ______________ amino acid sequence must specify each __________. This would provide for ___ 64 possible combinations of amino acids. triplet of nucleotides is cal ...
Slide ()
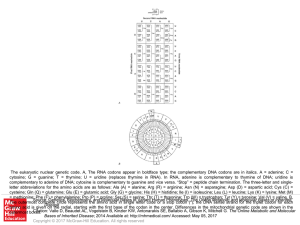
... The eukaryotic nuclear genetic code. A, The RNA codons appear in boldface type; the complementary DNA codons are in italics. A = adenine; C = cytosine; G = guanine; T = thymine; U = uridine (replaces thymine in RNA). In RNA, adenine is complementary to thymine of DNA; uridine is complementary to ade ...
... The eukaryotic nuclear genetic code. A, The RNA codons appear in boldface type; the complementary DNA codons are in italics. A = adenine; C = cytosine; G = guanine; T = thymine; U = uridine (replaces thymine in RNA). In RNA, adenine is complementary to thymine of DNA; uridine is complementary to ade ...
BIO 101: Transcription and Translation
... In eukaryotes, pre-mRNA must be further processed to mRNA before it leaves the nucleus ...
... In eukaryotes, pre-mRNA must be further processed to mRNA before it leaves the nucleus ...
Nucleic Acids - cpprashanths Chemistry
... • Polymers of nucleic acids are chains of nucleotides joined by condensation reactions • They are held together by covalent bonds between the sugar of one nucleotide and the phosphate of another - called phosphodiester bonds ...
... • Polymers of nucleic acids are chains of nucleotides joined by condensation reactions • They are held together by covalent bonds between the sugar of one nucleotide and the phosphate of another - called phosphodiester bonds ...
Molecular Testing and Clinical Diagnosis
... • Click on link for information sheet National Institutes of Health – Information Sheet ...
... • Click on link for information sheet National Institutes of Health – Information Sheet ...
Nucleic Acids and Protein Synthesis
... • Chromosomes hold genes. Genes are made of DNA. A gene holds information that decides our colour of hair, colour of eyes etc. It also holds information for making proteins that may become enzymes or hormone for use within the body. ...
... • Chromosomes hold genes. Genes are made of DNA. A gene holds information that decides our colour of hair, colour of eyes etc. It also holds information for making proteins that may become enzymes or hormone for use within the body. ...
Unit 4 - University of Colorado Boulder
... The central dogma is a cellular “chain of command.” 7. Define the “central dogma” in one sentence 8. List the major steps in the process of transcription in the order in which they happen; describe the roles played by the main molecules or DNA regions that are involved (RNA polymerase, transcription ...
... The central dogma is a cellular “chain of command.” 7. Define the “central dogma” in one sentence 8. List the major steps in the process of transcription in the order in which they happen; describe the roles played by the main molecules or DNA regions that are involved (RNA polymerase, transcription ...
CHAPTER 4, PART 2
... Jacob and Monod predicted properties of mRNA: 1. A polynucleotide (RNA) 2. Base composition complementary to a DNA template 3. Size variation reflects variety of protein sizes (3 bases/a.a.) 4. Transient association with ribosomes 5. Rapid turnover (~2 minute half life in E. coli) ...
... Jacob and Monod predicted properties of mRNA: 1. A polynucleotide (RNA) 2. Base composition complementary to a DNA template 3. Size variation reflects variety of protein sizes (3 bases/a.a.) 4. Transient association with ribosomes 5. Rapid turnover (~2 minute half life in E. coli) ...