No Slide Title
... • Acetylation leads to recruitment of co-activators, chromatin remodeling complex, and RNA pol II. ...
... • Acetylation leads to recruitment of co-activators, chromatin remodeling complex, and RNA pol II. ...
BINF 730 Biological Sequence Analysis Lecture 1 Biological
... cyanobacteria (blue-green algae) and common bacteria (Escherichia coli) Eukaryotes – unicellular organisms such as yeast and multicellular organisms Archaebacteria – no nuclear membrane but similar to eukaryotes in transcription and translation mechanisms, discovered in deep sea thermal vents in 198 ...
... cyanobacteria (blue-green algae) and common bacteria (Escherichia coli) Eukaryotes – unicellular organisms such as yeast and multicellular organisms Archaebacteria – no nuclear membrane but similar to eukaryotes in transcription and translation mechanisms, discovered in deep sea thermal vents in 198 ...
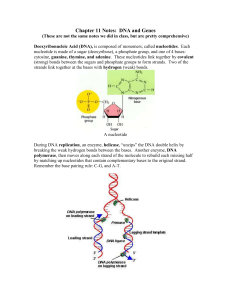
Chapter 11 Notes: DNA and Genes
... During DNA replication, an enzyme, helicase, “unzips” the DNA double helix by breaking the weak hydrogen bonds between the bases. Another enzyme, DNA polymerase, then moves along each strand of the molecule to rebuild each missing half by matching up nucleotides that contain complementary bases to t ...
... During DNA replication, an enzyme, helicase, “unzips” the DNA double helix by breaking the weak hydrogen bonds between the bases. Another enzyme, DNA polymerase, then moves along each strand of the molecule to rebuild each missing half by matching up nucleotides that contain complementary bases to t ...
TARBP2 mediated post-transcriptional regulation of gene
... Double stranded RNA binding protein TARBP2 TARBP2 ...
... Double stranded RNA binding protein TARBP2 TARBP2 ...
FREE Sample Here - We can offer most test bank and
... 1.12 Hemophilia is an inherited disorder in which the blood clotting mechanism is defective. Because of this defect, people with hemophilia may die from cuts or bruises, especially if internal organs such as the liver, lungs, or kidneys have been damaged. One method of treatment involves injecting a ...
... 1.12 Hemophilia is an inherited disorder in which the blood clotting mechanism is defective. Because of this defect, people with hemophilia may die from cuts or bruises, especially if internal organs such as the liver, lungs, or kidneys have been damaged. One method of treatment involves injecting a ...
Analysis of Differential Gene Expression in a Myotonic Dystrophy
... atrophy), eyes (cataracts), heart, and endocrine system. ...
... atrophy), eyes (cataracts), heart, and endocrine system. ...
Chapter 4 Genetics: The Science of Heredity
... 1. The set of information that controls a trait; a segment of DNA on a chromosome that codes for a specific trait. 2. An organism’s genetic makeup, or allele combinations. 3. A condition in which neither of two alleles of a gene is dominant or recessive. 4. Having two different alleles for a trait. ...
... 1. The set of information that controls a trait; a segment of DNA on a chromosome that codes for a specific trait. 2. An organism’s genetic makeup, or allele combinations. 3. A condition in which neither of two alleles of a gene is dominant or recessive. 4. Having two different alleles for a trait. ...
From Gene to Protein
... Transcription unit: stretch of DNA that codes for a polypeptide or RNA (eg. tRNA, rRNA) RNA polymerase: Separates DNA strands and transcribes mRNA mRNA elongates in 5’ 3’ direction Uracil (U) replaces thymine (T) when pairing to adenine (A) Attaches to promoter (start of gene) and stops at ...
... Transcription unit: stretch of DNA that codes for a polypeptide or RNA (eg. tRNA, rRNA) RNA polymerase: Separates DNA strands and transcribes mRNA mRNA elongates in 5’ 3’ direction Uracil (U) replaces thymine (T) when pairing to adenine (A) Attaches to promoter (start of gene) and stops at ...
Document
... A. In the promoter for gene a. B. In the promoter for gene b. C. At the end of gene a. D. The RNA polymerase subunit gene. ...
... A. In the promoter for gene a. B. In the promoter for gene b. C. At the end of gene a. D. The RNA polymerase subunit gene. ...
translational - Bioinformatics Institute
... Transcription is initiated at a specific base pair and is controlled by the binding of trans-acting proteins (transcription factors) to cis-acting regulatory DNA sequences. However, eukaryotic cis-acting elements are often much further from the promoter they regulate, and transcription from a single ...
... Transcription is initiated at a specific base pair and is controlled by the binding of trans-acting proteins (transcription factors) to cis-acting regulatory DNA sequences. However, eukaryotic cis-acting elements are often much further from the promoter they regulate, and transcription from a single ...
Bioinformatics III: Genomics
... HAR1F and HAR1R (black, with a chevroned line indicating introns), and the predicted RNA structure (green) based on the May 2004 human assembly in the UCSC Genome Browser41. The level of conservation in the orthologous region in other vertebrate species (blue) is plotted for this region using the Ph ...
... HAR1F and HAR1R (black, with a chevroned line indicating introns), and the predicted RNA structure (green) based on the May 2004 human assembly in the UCSC Genome Browser41. The level of conservation in the orthologous region in other vertebrate species (blue) is plotted for this region using the Ph ...
DNA Transcription and Translation
... nucleus so that the cell can make a protein out of the information obtained from the DNA in the gene Every 3 nitrogen bases in the DNA that makes up a gene is called a codon, and codes for a specific amino acid DNA does not leave the nucleus so a carrier molecule called messanger RNA (mRNA) i ...
... nucleus so that the cell can make a protein out of the information obtained from the DNA in the gene Every 3 nitrogen bases in the DNA that makes up a gene is called a codon, and codes for a specific amino acid DNA does not leave the nucleus so a carrier molecule called messanger RNA (mRNA) i ...
gene
... Instead, a protein called a release factor binds to the stop codon, the polypeptide is cut from the last tRNA, and the polypeptide (protein) is released into the ctyoplasm, where other proteins will help fold it. ...
... Instead, a protein called a release factor binds to the stop codon, the polypeptide is cut from the last tRNA, and the polypeptide (protein) is released into the ctyoplasm, where other proteins will help fold it. ...
MS Word file
... Transcription and Nucleosome Structure – Chromatin modification before transcription Enhancers: distant regions of DNA that increase transcription levels Bound by initiation complex proteins and loop around to interact with promoter region Polymerase I and polymerase III promoters Distinct from thos ...
... Transcription and Nucleosome Structure – Chromatin modification before transcription Enhancers: distant regions of DNA that increase transcription levels Bound by initiation complex proteins and loop around to interact with promoter region Polymerase I and polymerase III promoters Distinct from thos ...
USMLE Step 1 Web Prep — Transcription and RNA Processing: Part
... The primary transcript must undergo extensive posttranscriptional processing inside the nucleus to form the mature mRNA molecule A 7-methylguanosine cap is added to the 5' end while the RNA molecule is still being synthesized. The cap structure serves as a ribosome-binding site and also helps to pro ...
... The primary transcript must undergo extensive posttranscriptional processing inside the nucleus to form the mature mRNA molecule A 7-methylguanosine cap is added to the 5' end while the RNA molecule is still being synthesized. The cap structure serves as a ribosome-binding site and also helps to pro ...
Stem Cells, Cancer, and Human Health
... Cells use three main types of RNA molecules to construct proteins: – Messenger RNA (mRNA) = recipe must “edit” first (remove introns) – Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) = part of ribosome (chef) ribosome also contains protein – Transfer RNA (tRNA) = helper chef brings amino acids (ingredients) to the ribosome ...
... Cells use three main types of RNA molecules to construct proteins: – Messenger RNA (mRNA) = recipe must “edit” first (remove introns) – Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) = part of ribosome (chef) ribosome also contains protein – Transfer RNA (tRNA) = helper chef brings amino acids (ingredients) to the ribosome ...