Elucidating Principles of Gene Regulation from Stochastic Models
... The complexity of multicellular organisms arises largely from reusing many of the same genes in numerous combinations, rather than by the introduction of novel genes for each new celltype. Put another way, what makes you human is not so much which genes you have but how you use them. The instruction ...
... The complexity of multicellular organisms arises largely from reusing many of the same genes in numerous combinations, rather than by the introduction of novel genes for each new celltype. Put another way, what makes you human is not so much which genes you have but how you use them. The instruction ...
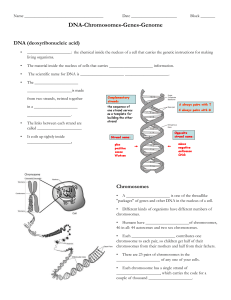
DNA-Chromosomes-Genes-Genome student notesheet
... chromosome to each pair, so children get half of their chromosomes from their mothers and half from their fathers. • There are 23 pairs of chromosomes in the _____________________ of any one of your cells. • Each chromosome has a single strand of _____________________, which carries the code for a c ...
... chromosome to each pair, so children get half of their chromosomes from their mothers and half from their fathers. • There are 23 pairs of chromosomes in the _____________________ of any one of your cells. • Each chromosome has a single strand of _____________________, which carries the code for a c ...
Recombinant DNA - Richmond School District
... inserted into the plasmid will only work if it DOESN’T have any introns. One way to do this is to synthesize the gene in a machine. Another method is to isolate the mRNA for the gene and use “REVERSE TRANSCRIPTASE” to make a DNA copy of it. (= complementary DNA ...
... inserted into the plasmid will only work if it DOESN’T have any introns. One way to do this is to synthesize the gene in a machine. Another method is to isolate the mRNA for the gene and use “REVERSE TRANSCRIPTASE” to make a DNA copy of it. (= complementary DNA ...
Lesson 1 DNA and proteins
... • Polypeptides are chains of amino acid residues joined by peptide bonds. • There are 20 different aa and their sequence determines the structure and function of the protein. • The sequence of bases in a DNA molecule determines the sequence of aa. • A gene is a length of DNA that codes for one (or m ...
... • Polypeptides are chains of amino acid residues joined by peptide bonds. • There are 20 different aa and their sequence determines the structure and function of the protein. • The sequence of bases in a DNA molecule determines the sequence of aa. • A gene is a length of DNA that codes for one (or m ...
Honors Biology Final Outline
... DNA structure and function is essential to understanding genetics Chargaff’s Rules & the relationship to Watson & Crick’s proposed base-pairs The central dogma for biological information: DNA, RNA, & Protein The DNA of a gene serves as a template for transcribing this information into RNA (b ...
... DNA structure and function is essential to understanding genetics Chargaff’s Rules & the relationship to Watson & Crick’s proposed base-pairs The central dogma for biological information: DNA, RNA, & Protein The DNA of a gene serves as a template for transcribing this information into RNA (b ...
poster SIBBM 2016
... Accurate processing of genetic information by transcription is vital for development and survival of the organism. Execution of gene expression programs requires the coordinated assembly of the transcription apparatus at selected gene promoter and a highly choreographed cascade of events. These even ...
... Accurate processing of genetic information by transcription is vital for development and survival of the organism. Execution of gene expression programs requires the coordinated assembly of the transcription apparatus at selected gene promoter and a highly choreographed cascade of events. These even ...
Gene Section SATB1 (SATB homeobox 1) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics
... SATB1 was identified by virtue of its high affinity and specificity to a DNA probe containing a nucleation site for base-unpairing, a phenomena whereby these sites become continuously unpaired under negative helical strain. Evidence suggests these base unpairing regions (BURs) mark the genome as ess ...
... SATB1 was identified by virtue of its high affinity and specificity to a DNA probe containing a nucleation site for base-unpairing, a phenomena whereby these sites become continuously unpaired under negative helical strain. Evidence suggests these base unpairing regions (BURs) mark the genome as ess ...
Document
... TFIID is a complex of proteins within the basal/general transcriptional machinery that turns on genes. It includes the TATA-binding factor, which binds to the TATA box, located at -35 of many eukaryotic promoters. Riboswitches are small molecules which stabilize one of two alternate stemloop conform ...
... TFIID is a complex of proteins within the basal/general transcriptional machinery that turns on genes. It includes the TATA-binding factor, which binds to the TATA box, located at -35 of many eukaryotic promoters. Riboswitches are small molecules which stabilize one of two alternate stemloop conform ...
Review Questions: Gene Regulation and Expression
... The code on the DNA is a series of nitrogen bases (A,T,C,G). The order of the nitrogen bases is a code “read” by a ribosome during translation. The ribosome puts together amino acids to make a protein based on the code from the gene. An RNA polymerase transcribes the DNA gene to make an mRNA to be t ...
... The code on the DNA is a series of nitrogen bases (A,T,C,G). The order of the nitrogen bases is a code “read” by a ribosome during translation. The ribosome puts together amino acids to make a protein based on the code from the gene. An RNA polymerase transcribes the DNA gene to make an mRNA to be t ...
DNA Assessment - WordPress.com
... 6) Individual genes store bits of information that make cells function. Identify which of the following describes a gene. A) a segment of DNA B) a segment of RNA C) a segment of protein D) a segment of carbohydrate 7) Genetic information is stored in________________. A) DNA molecules B) RNA molecule ...
... 6) Individual genes store bits of information that make cells function. Identify which of the following describes a gene. A) a segment of DNA B) a segment of RNA C) a segment of protein D) a segment of carbohydrate 7) Genetic information is stored in________________. A) DNA molecules B) RNA molecule ...
glossary of technical terms
... chromosomes of almost all organisms, made up of four different kinds of bases, which are abbreviated A, C, T and G. A DNA fragment that is ten bases long might have a base sequence of, for example, ATCGTTCCTG. The particular sequence of bases encodes important information in an individual’s genetic ...
... chromosomes of almost all organisms, made up of four different kinds of bases, which are abbreviated A, C, T and G. A DNA fragment that is ten bases long might have a base sequence of, for example, ATCGTTCCTG. The particular sequence of bases encodes important information in an individual’s genetic ...
Transcription and Translation Eukaryotic Cell
... Amino Acid- Organic molecule possessing both carboxyl and amino groups. Serve as monomers of proteins. mRNA- is a single-stranded polymer of nucleotides, each of which contains a nitrogenous base, a sugar and a phosphate group. Messenger RNA contains genetic information. It carries genetic informati ...
... Amino Acid- Organic molecule possessing both carboxyl and amino groups. Serve as monomers of proteins. mRNA- is a single-stranded polymer of nucleotides, each of which contains a nitrogenous base, a sugar and a phosphate group. Messenger RNA contains genetic information. It carries genetic informati ...
DNA
... All cells have the same set of genes Different kinds of cells use different combinations of genes ...
... All cells have the same set of genes Different kinds of cells use different combinations of genes ...
DNA Vocabulary Study Option
... 1. Cut the chart apart completely by cutting on all lines. 2. Have your child mix up the cards and try to match the correct definition with the correct vocabulary term. (A second chart can be printed to act as a key) ...
... 1. Cut the chart apart completely by cutting on all lines. 2. Have your child mix up the cards and try to match the correct definition with the correct vocabulary term. (A second chart can be printed to act as a key) ...
Gene Section SEPT5 (septin 5) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics
... just 5'of GPIb beta (platelet membrane glycoprotein Ib beta precursor), and GPIb beta is co-expressed with hCDCRel-1; this is due to a non-consensus polyadenylation signal in 3' of hCDCRel-1. ...
... just 5'of GPIb beta (platelet membrane glycoprotein Ib beta precursor), and GPIb beta is co-expressed with hCDCRel-1; this is due to a non-consensus polyadenylation signal in 3' of hCDCRel-1. ...
Microbial Genetics
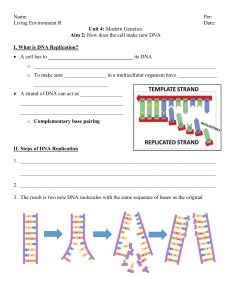
... DNA strands are antiparallel Bidirectional replication animation Rolling circle animation Replication always starts at new 5’ end ...
... DNA strands are antiparallel Bidirectional replication animation Rolling circle animation Replication always starts at new 5’ end ...
Sensing the antisense: study of gene expression in differentiating
... has undergone many genetic changes. Such changes can be rearrangements of DNA sequences throughout the genome, deletions or duplications of several parts of the chromosomes and alteration in expression of several genes. Studies of these changes can reveal the way the physiology of the cell changes w ...
... has undergone many genetic changes. Such changes can be rearrangements of DNA sequences throughout the genome, deletions or duplications of several parts of the chromosomes and alteration in expression of several genes. Studies of these changes can reveal the way the physiology of the cell changes w ...
GENETICS PROBLEMS - Review Questions
... cell). Also unique was the fact that the adult sheep was no longer living. 3. recombinant DNA has the DNA of more than one species in it (DNA from another organism has been spliced into the existing DNA) 4. a restriction enzyme (cuts DNA at specific sites) 5. in artificial insemination, the fertiliz ...
... cell). Also unique was the fact that the adult sheep was no longer living. 3. recombinant DNA has the DNA of more than one species in it (DNA from another organism has been spliced into the existing DNA) 4. a restriction enzyme (cuts DNA at specific sites) 5. in artificial insemination, the fertiliz ...