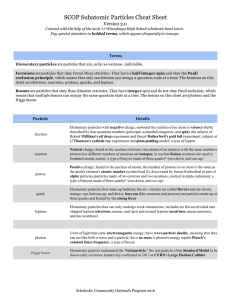
Quantum Numbers Primer The quantum numbers
... this lowest energy state the ground state. We can promote an electron in the n = 1 energy level to a higher level; such as n = 2. This excitement was demonstrated in lecture by use of the hydrogen lamp. When the electron returns to the ground state (n = 1) energy is emitted in the form of electromag ...
... this lowest energy state the ground state. We can promote an electron in the n = 1 energy level to a higher level; such as n = 2. This excitement was demonstrated in lecture by use of the hydrogen lamp. When the electron returns to the ground state (n = 1) energy is emitted in the form of electromag ...
Chapter 27
... A non-relativistic electron and a nonrelativistic proton are moving and have the same de Broglie wavelength. Which of the following are also the same for the two particles: (a) speed, (b) kinetic energy, (c) ...
... A non-relativistic electron and a nonrelativistic proton are moving and have the same de Broglie wavelength. Which of the following are also the same for the two particles: (a) speed, (b) kinetic energy, (c) ...
damped and driven oscillations, waves
... The wave has a net displacement but the medium does not Each individual particle only moves up or down or side to side with simple harmonic motion ...
... The wave has a net displacement but the medium does not Each individual particle only moves up or down or side to side with simple harmonic motion ...
Posttest for Uncertainty Principle Part 1
... Test B for Uncertainty Principle 1. Ignore normalization issues pertaining to the wave function. At time t=0, the wave packet of a quantum mechanical particle is highly peaked and can be effectively described by a delta function (x) . Is the momentum of this particle well-defined at t=0? Is the po ...
... Test B for Uncertainty Principle 1. Ignore normalization issues pertaining to the wave function. At time t=0, the wave packet of a quantum mechanical particle is highly peaked and can be effectively described by a delta function (x) . Is the momentum of this particle well-defined at t=0? Is the po ...
8.04 Final Review Schr¨ ary conditions.
... TODO: (need more here about Hermitians, conjugate adjoints and how they work backwards on dirac notation etc.) TODO: Dirac notation ...
... TODO: (need more here about Hermitians, conjugate adjoints and how they work backwards on dirac notation etc.) TODO: Dirac notation ...
PHYS6520 Quantum Mechanics II Spring 2013 HW #3
... is the same as the correction from relativistic kinetic energy between the 2s and 2p levels? How easy or difficult is it to achieve an electric field of this magnitude in the laboratory? (c) The Zeeman effect can be calculated with a “weak” or “strong” magnetic field, depending on the size of the energ ...
... is the same as the correction from relativistic kinetic energy between the 2s and 2p levels? How easy or difficult is it to achieve an electric field of this magnitude in the laboratory? (c) The Zeeman effect can be calculated with a “weak” or “strong” magnetic field, depending on the size of the energ ...














![L 35 Modern Physics [1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/001689016_1-3e506855e2f70cb00e132a79d00855e2-300x300.png)