Midterm Exam No. 02 (Fall 2014) PHYS 520A: Electromagnetic Theory I
... where ωp , ω0 , and γ are material dependent parameters, and ω is the frequency of oscillation of the electric field. (a) [Reχ(ω)] is a measure of the square of the refractive index. Plot [Reχ(ω)] as a function of ω. (b) [Imχ(ω)] is a measure of absorption of light. Plot [Imχ(ω)] as a function of ω. ...
... where ωp , ω0 , and γ are material dependent parameters, and ω is the frequency of oscillation of the electric field. (a) [Reχ(ω)] is a measure of the square of the refractive index. Plot [Reχ(ω)] as a function of ω. (b) [Imχ(ω)] is a measure of absorption of light. Plot [Imχ(ω)] as a function of ω. ...
Nov 2009 - Vicphysics
... 12. Standing waves mean the wavelength is quantised (1). Electron energy (E = hc/) depends on wavelength, so it is quantised as well. (1) [ /2, %] Electrons in atoms are in confined space. Electrons also have a wavelength that depends on their energy. In this confined space, this wavelength propert ...
... 12. Standing waves mean the wavelength is quantised (1). Electron energy (E = hc/) depends on wavelength, so it is quantised as well. (1) [ /2, %] Electrons in atoms are in confined space. Electrons also have a wavelength that depends on their energy. In this confined space, this wavelength propert ...
lecture25
... If light is particles, theory predicts: • Increasing intensity increases number of electrons but not energy • Above a minimum energy required to break atomic bond, kinetic energy will increase linearly with frequency • There is a cutoff frequency below which no electrons will be emitted, regardless ...
... If light is particles, theory predicts: • Increasing intensity increases number of electrons but not energy • Above a minimum energy required to break atomic bond, kinetic energy will increase linearly with frequency • There is a cutoff frequency below which no electrons will be emitted, regardless ...
Electromagnetic radiation – the nature of light
... molecules and atoms that move from one energy level to another. The light we see with our eyes is really a very small portion of the electromagnetic spectrum. A rainbow shows the optical (visible) part of the electromagnetic spectrum; infrared (if you could see it) would be located just beyond the r ...
... molecules and atoms that move from one energy level to another. The light we see with our eyes is really a very small portion of the electromagnetic spectrum. A rainbow shows the optical (visible) part of the electromagnetic spectrum; infrared (if you could see it) would be located just beyond the r ...
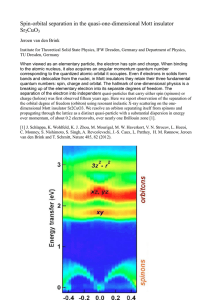
Spin-orbital separation in the quasi-one
... Institute for Theoretical Solid State Physics, IFW Dresden, Germany and Department of Physics, TU Dresden, Germany When viewed as an elementary particle, the electron has spin and charge. When binding to the atomic nucleus, it also acquires an angular momentum quantum number corresponding to the qua ...
... Institute for Theoretical Solid State Physics, IFW Dresden, Germany and Department of Physics, TU Dresden, Germany When viewed as an elementary particle, the electron has spin and charge. When binding to the atomic nucleus, it also acquires an angular momentum quantum number corresponding to the qua ...
1_Quantum theory_ introduction and principles
... The sun has a number of holes in its corona from which high energy particles (e-, p+, n0) stream out with enormous velocity. These particles are thrown out through our solar system, and the phenomenon is called solar wind. A part of this solar wind meets the earth’s magneto sphere, the solar wind pa ...
... The sun has a number of holes in its corona from which high energy particles (e-, p+, n0) stream out with enormous velocity. These particles are thrown out through our solar system, and the phenomenon is called solar wind. A part of this solar wind meets the earth’s magneto sphere, the solar wind pa ...
... 2.1 You are designing an accelerator to hurl relativistic particles of mass ma at a stationary target of particles of mass mb . The beam particles have energy Ea = K + ma c2 , where K is the kinetic energy of the beam. The design should be such that collisions can create a resonance of mass M > ma + ...
collapses - Marc Madou
... Where H is the one-dimensional Hamiltonian operator and in which the energy E of the particles is called the eigenvalue, and the eigenfunction. Expressed yet another way, kinetic and potential energies are transformed into the Hamiltonian which acts upon the wavefunction to generate the evolut ...
... Where H is the one-dimensional Hamiltonian operator and in which the energy E of the particles is called the eigenvalue, and the eigenfunction. Expressed yet another way, kinetic and potential energies are transformed into the Hamiltonian which acts upon the wavefunction to generate the evolut ...
Constructive Interference
... Electron at a definite location Single electron at a superposition of two locations ...
... Electron at a definite location Single electron at a superposition of two locations ...